|
Livermore Valley
The Livermore Valley, historically known as the Valle de San José (Valley of San José), is a valley in Alameda County, California, located in the East Bay region. The city of Livermore is located in the valley. The valley became known as "Livermore's Valley", and today as the "Livermore Valley" after Robert Livermore, an early settler and rancher in the region who received together with José Noriega a land grant composing most of modern Livermore.* Livermore Heritage GuildLivermore-Amador Genealogical Society/ref> The groundwater basin underlying the valley is the Livermore Basin, the largest sub-unit of which is the Mocho Subbasin. The Livermore Basin is one of five aquifers in the San Francisco Bay Area that supply most of the metropolitan Bay Area population. The entire Livermore Basin aquifer faces a concern over elevated total dissolved solids by the year 2020 due to an expanding human population leading to higher rates of return water flows to the aquifer containin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livermore, California
Livermore is a city in Alameda County, California. With a 2020 population of 87,955, Livermore is the most populous city in the Tri-Valley, giving its name to the Livermore Valley. It is located on the eastern edge of California's San Francisco Bay Area, making it the easternmost city in the area. Livermore was a railroad town named for Robert Livermore, a local rancher who settled in the area in the 1840s. It is the home of the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, for which the chemical element livermorium is named (and thus, placing the city's name in the periodic table). It is also the California site of Sandia National Laboratories, which is headquartered in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Its south side is home to local vineyards, and its downtown district is being redeveloped . The United States Census Bureau defines an urban area of Tri-Valley-area cities, with Livermore as the principal city: the Livermore–Pleasanton, California, Pleasanton–Dublin, California, Dublin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south. With almost 40million residents across an area of , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, largest state by population and List of U.S. states and territories by area, third-largest by area. Prior to European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. European exploration in the 16th and 17th centuries led to the colonization by the Spanish Empire. The area became a part of Mexico in 1821, following Mexican War of Independence, its successful war for independence, but Mexican Cession, was ceded to the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amador Valley
Amador Valley is a valley in eastern Alameda County, California and is the location of the cities of Dublin and Pleasanton. Part of Tri-Valley, the valley is bounded by the foothills of the Diablo Range on the north and south, Pleasanton Ridge to the west, and Livermore Valley to the east. Watercourses draining into the Amador Valley include South San Ramon Creek, Tassajara Creek, Arroyo Mocho, Arroyo Valle, and Arroyo Las Positas, as well as runoff from Pleasanton Ridge. These waters drain south through Arroyo de la Laguna to Alameda Creek, ultimately ending up in San Francisco Bay. History Amador Valley was once marshland characterized by tules and willow trees, with Tulare Lake Tulare Lake () or Tache Lake ( Yokuts: ''Pah-áh-su'', ''Pah-áh-sē'') is a freshwater lake in the southern San Joaquin Valley, California, United States. Historically, Tulare Lake was once the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi R ... at its center. Euro-American developmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Gold Rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the United States and abroad. The sudden influx of gold into the money supply reinvigorated the American economy; the sudden population increase allowed California to grow rapidly into statehood in the Compromise of 1850. The gold rush had severe effects on Native Californians and accelerated the Native American population's decline from disease, starvation, and the California genocide. The effects of the gold rush were substantial. Whole indigenous societies were attacked and pushed off their lands by the gold-seekers, nicknamed "forty-niners" (referring to 1849, the peak year for gold rush immigration). Outside of California, the first to arrive were from Oregon, the Sandwich Islands (Hawaii), and Latin America in late 1848. Of the approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Canada De Los Vaqueros
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California ** List of California Ranchos * Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California * Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada * Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California * Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Bautista Alvarado
Juan Bautista Valentín Alvarado y Vallejo (February 14, 1809 – July 13, 1882) usually known as Juan Bautista Alvarado, was a Californio politician that served as governor of Alta California from 1837 to 1842. Prior to his term as governor, Alvarado briefly led a movement for independence of Alta California from 1836 to 1837, in which he successfully deposed interim governor Nicolás Gutiérrez, declared independence, and created a new flag and constitution, before negotiating an agreement with the Mexican government resulting in his recognition as governor and the end of the independence movement. Early years Alvarado was born in Monterey, Alta California, to Jose Francisco Alvarado and María Josefa Vallejo. His grandfather Juan Bautista Alvarado accompanied Gaspar de Portolá as an enlisted man in the Spanish Army in 1769. His father died a few months after his birth and his mother remarried three years later, leaving Juan Bautista in the care of his grandparents on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Las Positas
Rancho Las Positas was a Mexican land grant in present-day Alameda County, California given in 1839 by governor Juan Alvarado to Robert Livermore and José Noriega. Las Positas means "little watering holes" in Spanish. The rancho included the present-day city of Livermore. History In 1834 Livermore and his business partner José Noriega were keeping livestock at Rancho Las Positas, where they also built an adobe. Livermore and his wife Josefa Higuera Molina, first settled in the Sunol Valley, but later moved to Rancho Las Positas, as Livermore was making regular trips there to manage his rancho. Initially an adobe structure built by Livermore and Amador served as their house on the rancho. *Livermore Heritage Guild With the |
Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of First Mexican Empire, Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the present-day U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, and Colorado. The territory was with Baja California Territory, Baja California (as a single ) in Mexico's 1836 ''Siete Leyes'' (Seven Laws) constitutional reform, granting it more autonomy. That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the outcome of the Mexican–American War in 1848, when most of the areas formerly comprising Alta California Mexican Cession, were ceded to the U.S. in Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, the treaty which ended the war. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
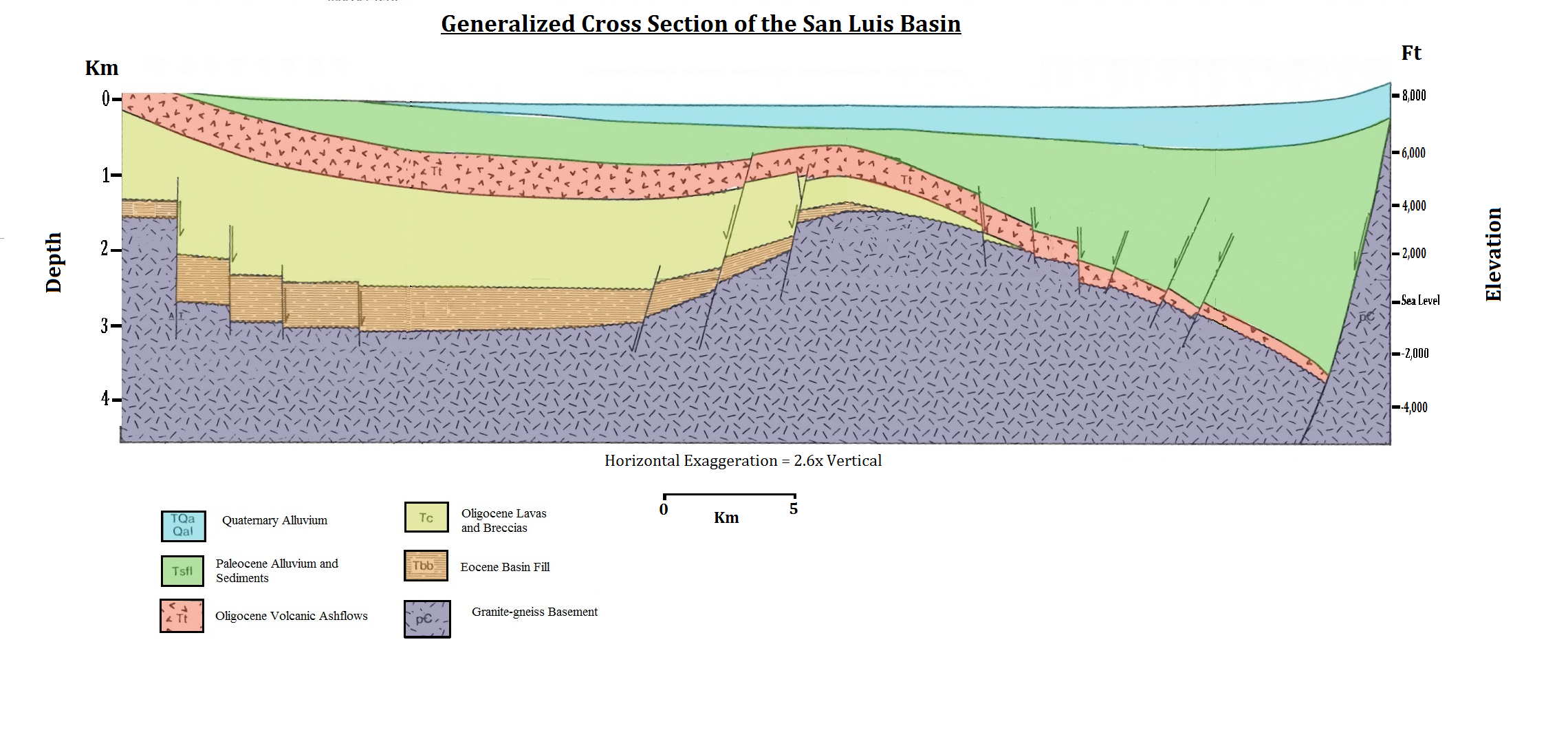
Alluvium
Alluvium (, ) is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluvium is also sometimes called alluvial deposit. Alluvium is typically geologically young and is not Consolidation (geology), consolidated into solid rock. Sediments deposited underwater, in seas, estuaries, lakes, or ponds, are not described as alluvium. Floodplain alluvium can be highly fertile, and supported some of the earliest human civilizations. Definitions The present Scientific consensus, consensus is that "alluvium" refers to loose sediments of all types deposited by running water in floodplains or in alluvial fans or related landforms. However, the meaning of the term has varied considerably since it was first defined in the French dictionary of Antoine Furetière, posthumously published in 1690. Drawing upon concepts from Roman law, Furetière defined ''alluvion'' (the French term for al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the Phanerozoic eon. It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today); a proposed third epoch, the Anthropocene, was rejected in 2024 by IUGS, the governing body of the ICS. The Quaternary is typically defined by the Quaternary glaciation, the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Tertiary
The Neogene ( ,) is a Geologic time scale#Terminology, geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period million years ago. It is the second period of the Cenozoic and the eleventh period of the Phanerozoic. The Neogene is sub-divided into two Epoch (geology), epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hoernes, Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary (period), Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphy, stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use. During this period, mammals an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |