|
Languages Of Montenegro
Languages of Montenegro are languages that are spoken in Montenegro. According to the Constitution of Montenegro that was adopted in 2007, Montenegro has only one official language, specified as Montenegrin, even though Serbian is used by 43% of the population and Montenegrin by 35% of population. There is an ongoing debate about the distinct nature of Montenegrin language in relation to the Serbo-Croatian dialectal continuum. Montenegrin can be written in both the Latin and Cyrillic alphabets, but there is a growing political movement to use only the Latin alphabet. Legally recognized minority languages are Albanian, Bosnian, and Croatian. As of 2017, Albanian is an official language of the municipalities of Podgorica, Ulcinj, Bar, Pljevlja, Rozaje and Tuzi. Additionally, there are a few hundred Italians in Montenegro, concentrated in the Bay of Kotor (''Cattaro''). Romani is a protected language. Minority languages of Montenegro The European Charter for Regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Language
Serbian (, ) is the standard language, standardized Variety (linguistics)#Standard varieties, variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and Kosovo. It is a recognized minority language in Croatia, North Macedonia, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic. Standard Serbian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian (more specifically on the dialects of Šumadija–Vojvodina dialect, Šumadija-Vojvodina and Eastern Herzegovinian dialect, Eastern Herzegovina), which is also the basis of Croatian language, standard Croatian, Bosnian language, Bosnian, and Montenegrin language, Montenegrin varieties and therefore the Declaration on the Common Language of Croats, Bosniaks, Serbs, and Montenegrins was issued in 2017. The other dialect spoken by Serbs is Torlakian dialect, Torlakian in south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pljevlja
Pljevlja (, ) is a town located in the Northern Montenegro, Northern Region of Montenegro, situated along Ćehotina, Ćehotina river. The town lies at an altitude of . In the Middle Ages, Pljevlja had been a crossroad of the important commercial roads and cultural streams, with important roads connecting the littoral with the Balkan interior. In 2023, the municipality of Pljevlja had a population of 24,542, while the city itself had a population of 16,419. The municipality borders those of Žabljak, Bijelo Polje and Mojkovac in Montenegro, as well as Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west and Serbia to the northeast. With a total area of , it is the second largest municipality in Montenegro. History Prehistory and antiquity The first traces of human life in the region date between 50,000 and 40,000 Before Christ, BC, while reliable findings show that the Ćehotina, Ćehotina River valley was inhabited no later than 30,000 BC. The oldest traces of human presence in the town area, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Yugoslavia
Languages of Yugoslavia are all languages spoken in former Yugoslavia. They are mainly Indo-European languages and dialects, namely dominant South Slavic varieties (Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, and Slovene) as well as Albanian, Aromanian, Bulgarian, Czech, German, Italian, Venetian, Balkan Romani, Romanian, Pannonian Rusyn, Slovak and Ukrainian languages. There are also pockets where varieties of non-Indo-European languages, such as those of Hungarian and Turkish, are spoken. Language policies in Yugoslavia From 1966, linguistic and ethnic divisions were part of the public discussion in Yugoslavia. Language policies were delegated to the communal level. Language situation was reflected in each republic's constitution, and more detailed in communal constitutions. Yugoslavia established its language policies at the federal, republic, and communal levels. Federal language policy was drafted by the following four principles: # Domestic measures were the basis of langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
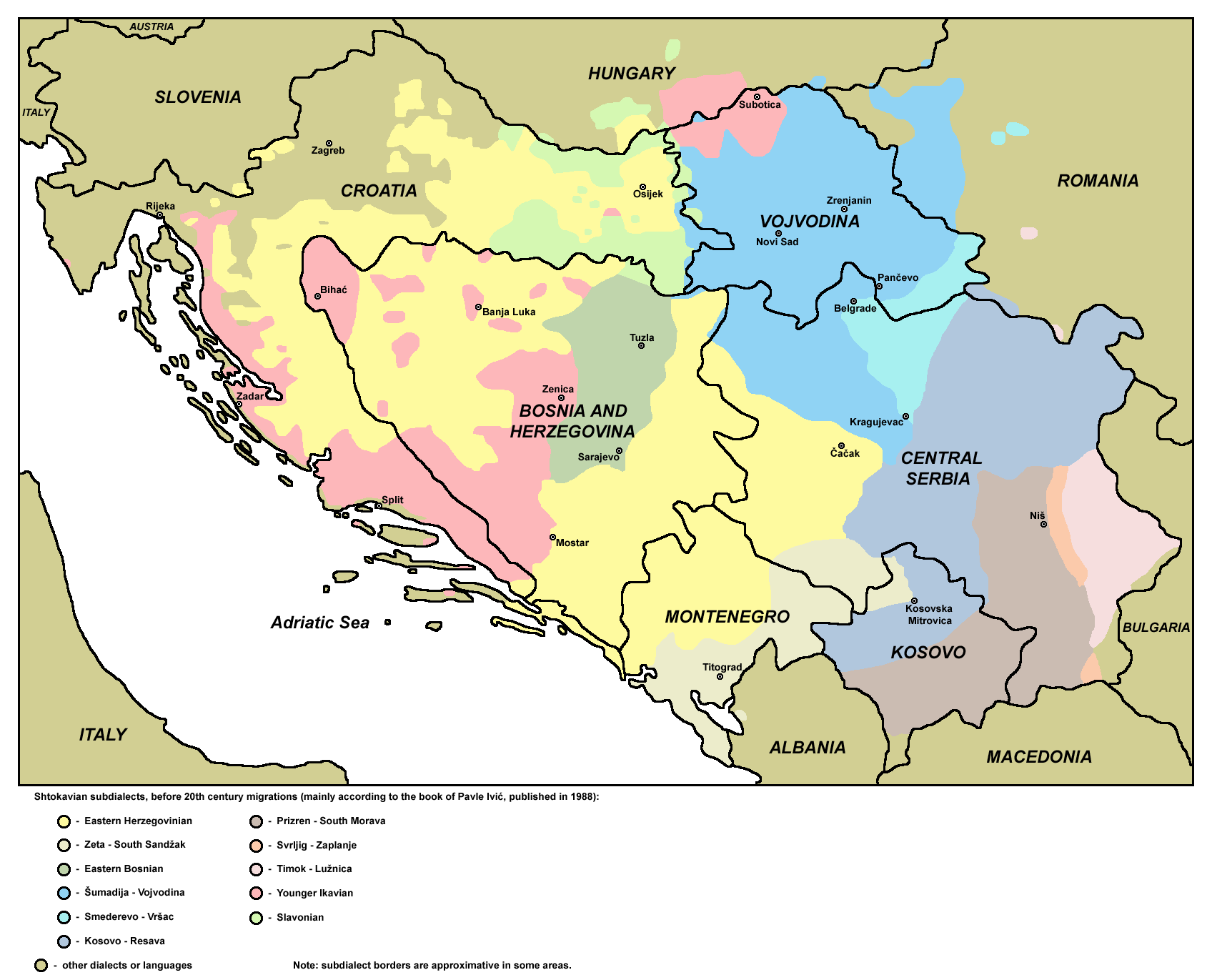
Shtokavian
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige supradialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It is a part of the South Slavic dialect continuum. Its name comes from the form for the interrogative pronoun for "what" . This is in contrast to Kajkavian and Chakavian ( and also meaning "what"). Shtokavian is spoken in Serbia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Herzegovina, much of Croatia, and the southern part of Austria's Burgenland. The primary subdivisions of Shtokavian are based on three principles: one is different accents whether the subdialect is Old-Shtokavian or Neo-Shtokavian, second is the way the old Slavic phoneme ''yat'' has changed (Ikavian, Ijekavian or Ekavian), and third is presence of Young Proto-Slavic isogloss (Schakavian or Shtakavian). Modern dialectology generally recognises seven Shtokavian subdialects. Early h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Herzegovinian Dialect
The Eastern Herzegovinian dialect (, sh-Latn-Cyrl, istočnohercegovački dijalekt, источнохерцеговачки дијалект, separator=" / ") is the most widespread subdialect of the Shtokavian supradialect or language, both by territory and the number of speakers. It is the dialectal basis for all modern literary Serbo-Croatian standards: Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian, and Montenegrin (in this last only partially codified). Distribution It covers large areas of Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro. It is also spoken in four villages in White Carniola, Slovenia ( Miliči, Bojanci, Marindol and Paunoviči), the inhabitants of which are descendants of Uskoks. It is composed of two larger zones that are territorially separated: * Southeastern zone, where it originated from (eastern Herzegovina, western Montenegro, western Serbia, eastern Bosnia, Posavinan Podrinje) * Northwestern zone (western and northwestern Bosnia, northern Dalmatia with Gor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Dialects
The dialects of Serbo-Croatian include the nonstandard dialect, vernacular forms and Standard language, standardized sub-dialect forms of Serbo-Croatian as a whole or as part of its standard language, standard varieties: Bosnian language, Bosnian, Croatian language, Croatian, Montenegrin language, Montenegrin, and Serbian language, Serbian. They are part of the dialect continuum of South Slavic languages that joins through the transitional Torlakian dialects the Dialects of Macedonian, Macedonian dialects to the south, Bulgarian dialects to the southeast and Slovene dialects to the northwest. The division of South Slavic dialects to "Slovene", "Serbo-Croatian", "Macedonian" and "Bulgarian" is mostly based on political grounds: for example all dialects within modern Slovenia are classified as "Slovene", despite some of them historically originating from other regions, while all dialects in modern Croatia are classified as "Croatian" (or "Croato-Serbian" before 1990) despite n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youth Initiative For Human Rights
Youth is the time of life when one is young. The word, youth, can also mean the time between childhood and adulthood ( maturity), but it can also refer to one's peak, in terms of health or the period of life known as being a young adult. Youth is also defined as "the appearance, freshness, vigor, spirit, etc., characteristic of one, who is young". Its definitions of a specific age range varies, as youth is not defined chronologically as a stage that can be tied to specific age ranges; nor can its end point be linked to specific activities, such as taking unpaid work, or having sexual relations. Youth is an experience that may shape an individual's level of dependency, which can be marked in various ways according to different cultural perspectives. Personal experience is marked by an individual's cultural norms or traditions, while a youth's level of dependency means the extent to which they still rely on their family emotionally and economically. Terminology and definitions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, representing 46 member states from Europe, with a population of approximately 675 million ; it operates with an annual ordinary budget of approximately 500 million euros. The organisation is distinct from the European Union (EU), although people sometimes confuse the two organisations – partly because the EU has adopted the original Flag of Europe, European flag, designed for the Council of Europe in 1955, as well as the Anthem of Europe, European anthem. No country has ever joined the EU without first belonging to the Council of Europe. The Council of Europe is an official United Nations General Assembly observers, United Nations observer. Unlike the EU, the Council of Europe cannot make binding laws; however, the council has produced a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia And Montenegro
The State Union of Serbia and Montenegro or simply Serbia and Montenegro, known until 2003 as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and commonly referred to as FR Yugoslavia (FRY) or simply Yugoslavia, was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the Breakup of Yugoslavia, breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFR Yugoslavia). The state was founded on 27 April 1992 as a federation comprising the Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Republic of Serbia and the Republic of Montenegro (1992–2006), Republic of Montenegro. In February 2003, it was transformed from a federal republic to a Confederation, political union until Montenegro seceded from the union in June 2006, leading to the full independence of both Serbia and Montenegro. Its aspirations to be the sole legal successor state to SFR Yugoslavia were not recognized by the United Nations, following the passing of United Nations Security Council Resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Charter For Regional Or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the charter does not provide any criterion or definition for an idiom to be a minority or a regional language, and the classification stays in the hands of the national state. The preparation for the charter was undertaken by the predecessor to the current Congress of Local and Regional Authorities, the Standing Conference of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe because involvement of local and regional government was essential. The actual charter was written in the Parliamentary Assembly based on the Congress' Recommendations. It only applies to languages traditionally used by the nationals of the State Parties (thus excluding languages used by recent immigrants from other states, see immigrant languages), which significantly diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani Language
Romani ( ; also Romanes , Romany, Roma; ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani people. The largest of these are Vlax Romani language, Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself. The differences between the various varieties can be as large as, for example, the differences between the Slavic languages. Name Speakers of the Romani language usually refer to the language as ' "the Romani language" or '' (adverb)'' "in a Rom way". This derives from the Romani word ', meaning either "a member of the (Romani) group" or "husband". This is also the origin of the term "Roma" in English, although some Roma groups refer to themselves using other demonyms (e.g. 'Kaale', 'Sinti'). C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |