|
Javelins
A javelin is a light spear designed primarily to be thrown, historically as a ranged weapon. Today, the javelin is predominantly used for sporting purposes such as the javelin throw. The javelin is nearly always thrown by hand, unlike the sling, bow, and crossbow, which launch projectiles with the aid of a hand-held mechanism. However, devices do exist to assist the javelin thrower in achieving greater distances, such as spear-throwers or the amentum. A warrior or soldier armed primarily with one or more javelins is a javelineer. The word javelin comes from Middle English and it derives from Old French ''javelin'', a diminutive of ''javelot'', which meant spear. The word ''javelot'' probably originated from one of the Celtic languages. Prehistory There is archaeological evidence that javelins and throwing sticks were already in use by the last phase of the Lower Paleolithic. Seven spear-like objects were found in a coal mine in the city of Schöningen, Germany. Stratigraphy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amentum
An ''amentum'' (Greek: ''αγκύλη'', ankyle,) was a leather strap attached to a javelin used in ancient Greek athletics, hunting, and warfare, which helped to increase the range and the stability of the javelin in flight. Stability in flight was important because it allowed the javelin to land on its point, which was the only way the throw could be accurately recorded in competition or be useful against a live target. An ''amentum'' also increased the effective length of the throwing arm, as does a spear-thrower, so enhanced speed. It is very similar to the Swiss arrow. Throwing technique The javelin was held at ear level and released after a short run. The ''amentum'' was looped over the first two fingers of the throwing hand so as to slip off when the throw was made. In competition throwing for distance, including the Ancient Olympic pentathlon at Olympia, Greece, a blunt javelin would be launched at about 45 degrees, but in war or the chase, a sharp weapon was thrown muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the soldiers from acting alone, for this would compromise the formation and minimize its strengths. The hoplites were primarily represented by free citizens – propertied farmers and artisans – who were able to afford a linen or bronze armour suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population). Some states maintained a small elite professional unit, known as the '' epilektoi'' or logades ('the chosen') because they were picked from the regular citizen infantry. These existed at times in Athens, Sparta, Argos, Thebes, and Syracuse, among other places. Hoplite soldiers made up the bulk of ancient Greek armies. In the 8th or 7th century BC, Greek armies adopted the phalanx formation. The formatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skirmishers
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They may be deployed in a skirmish line, an irregular open formation that is much more spread out in depth and in breadth than a traditional line formation. Their purpose is to harass the enemy by engaging them in only light or sporadic combat to delay their movement, disrupt their attack, or weaken their morale. Such tactics are collectively called skirmishing. An engagement with only light, relatively indecisive combat is sometimes called a skirmish even if heavier troops are sometimes involved. Skirmishers can be either regular army units that are temporarily detached to perform skirmishing or specialty units that were specifically armed and trained for such low-level irregular warfare tactics. Light infantry, light cavalry (historically), and irregular units often specialize in ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peltast
A ''peltast'' (, ) was a type of light infantry originating in Thracians, Thrace and Paeonia (kingdom), Paeonia and named after the kind of shield he carried.Williams, Mary Frances. "Philopoemen's special forces: Peltasts and a new kind of greek light-armed warfare (Livy 35.27) " ''Historia: Zeitschrift Für Alte Geschichte'' H. 3 (2004): 257-277. Thucydides mentions the Thracian peltasts, while Xenophon in the Anabasis (Xenophon), Anabasis distinguishes the Thracian and Greek peltast troops. The peltast often served as a skirmisher in Hellenistic period, Hellenistic armies. In the Middle Ages, the same term was used for a type of Byzantine Empire, Byzantine infantryman. Description ''Pelte'' shield ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chariotry In Ancient Egypt
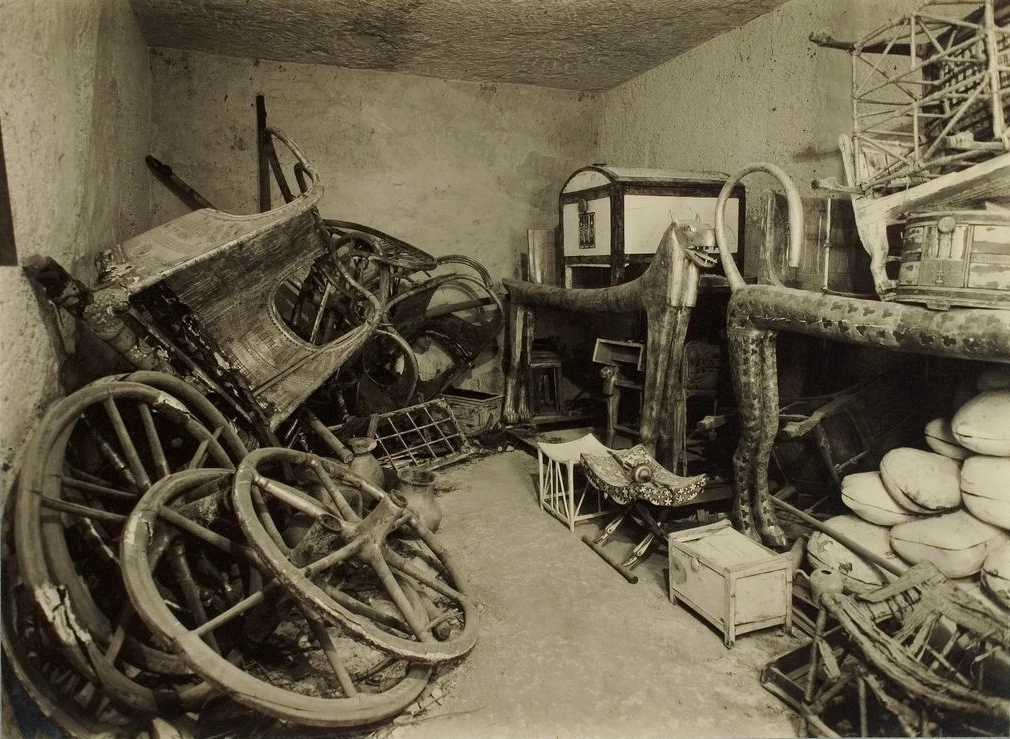
In ancient Egyptian society, primarily during the New Kingdom, chariotry stood as an independent unit in the king’s military force. It is thought that chariots came to Egypt with the Hyksos people as a weapon during the 16th century.Hyskos introduced chariots to ancient Egypt The Egyptians later developed their own chariot design, which when compared to the Hyksos counterpart was lighter. Beyond their role in warfare, chariots seem to have a role in royal power both in and out of Egypt. Design Archaeologist Joost Crouwel writes that "chariots were not sudden inventions but developed out of earlier vehicles that were mounted on disk or cross-bar wheels. This development can best be traced in the Near East, where spoke-wheeled and horse-drawn ‘tr ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidearm (weapon)
A sidearm is an individual-served weapon that is kept at one's side and can be rapidly accessed if needed. A sidearm may be carried alone or as an ancillary weapon to a more frequently-used primary weapon. The term historically referred to swords, daggers, and similar small weapons kept at one's side in a sheath, and in modern combat dominated by guns, sidearms are often defined as handguns that are similarly kept in a holster. A sidearm is typically required equipment for military officers and may be carried by law enforcement personnel. Usually, uniformed personnel of these services wear their weapons openly, while plainclothes personnel have their sidearms concealed under their clothes. Uses In many contemporary armies, the issue of a sidearm in the form of a service pistol is a clear sign of authority and is the mark of a commissioned officer or senior NCO. In the protocol of courtesy, the surrender of a commander's sidearm is the final act in the general surrender o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatchet
A hatchet (from the Old French language, Old French , a diminutive form of ''hache'', 'axe' of Germanic origin) is a Tool, single-handed striking tool with a sharp blade on one side used to cut and split wood, and a hammerhead on the other side. Hatchets may also be used for hewing when making flattened surfaces on logs; when the hatchet head is optimized for this purpose it is called a hewing hatchet. The earliest known use of the noun hatchet is in the Middle English period (1150—1500) Although 'hand axe' and 'hatchet' are often used interchangeably in contemporary usage, 19th and 20th century American manufacturers and retailers (Collins, Kelly, Vaughan, Warren, Mann; Simmons, Shapleigh, Sears, et al.) unanimously distinguished hatchets from hand axes in their product catalogs, listing them in separate groupings. A ''hand axe'' (also known by terms including "camp axe", "belt axe", "hunters axe" and others) is a short-handled woods tool. A ''hatchet'' is a short-handled co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Club (weapon)
A club (also known as a cudgel, baton, bludgeon, truncheon, cosh, nightstick, or impact weapon) is a short staff or stick, usually made of wood, wielded as a weapon or tool since prehistory. There are several examples of blunt trauma, blunt-force trauma caused by clubs in the past, including at the site of Nataruk in Turkana County, Turkana, Kenya, described as the scene of a prehistoric conflict between bands of hunter-gatherers 10,000 years ago. Most clubs are small enough to be swung with one hand, although larger clubs may require the use of two to be effective. Various specialized clubs are used in martial arts and other fields, including the Baton (law enforcement), law-enforcement baton. The military Mace (bludgeon), mace is a more sophisticated descendant of the club, typically made of metal and featuring a spiked, knobbed, or flanged head attached to a shaft. Examples of cultural depictions of clubs may be found in mythology, where they are associated with strong figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry like spears or long ranged projectiles such as arrows. They function as means of active blocks, as well as to provide passive protection by closing one or more lines of engagement during combat. Shields vary greatly in size and shape, ranging from large panels that protect the user's whole body to small models (such as the buckler) that were intended for hand-to-hand-combat use. Shields also vary a great deal in thickness; whereas some shields were made of relatively deep, absorbent, wooden planking to protect soldiers from the impact of spears and crossbow bolts, others were thinner and lighter and designed mainly for deflecting blade strikes (like the roromaraugi or qauata). Finally, shields vary greatly in shape, ranging in roundness to angularity, proportional length and wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |