|
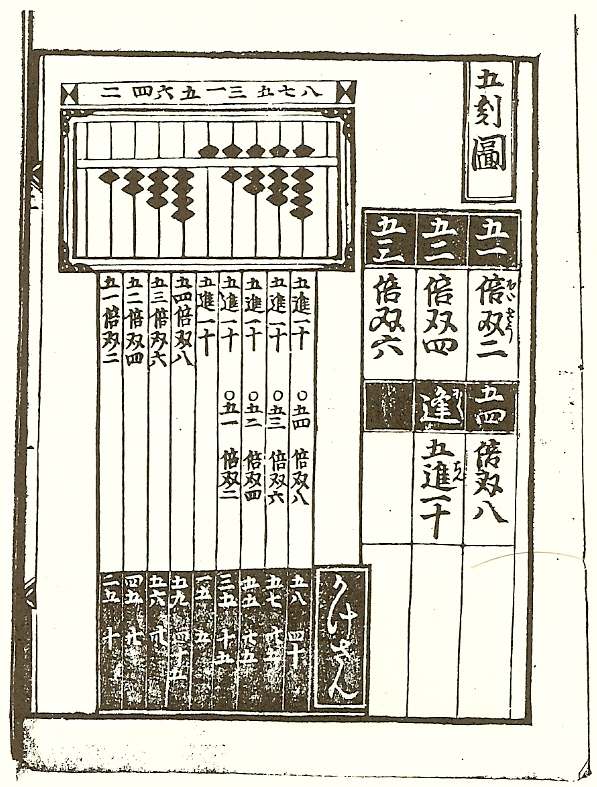
Japanese Mathematics
denotes a distinct kind of mathematics which was developed in Japan during the Edo period (1603–1867). The term ''wasan'', from ''wa'' ("Japanese") and ''san'' ("calculation"), was coined in the 1870s and employed to distinguish native Japanese mathematical theory from Western mathematics (洋算 ''yōsan''). In the history of mathematics, the development of ''wasan'' falls outside the Western realm. At the beginning of the Meiji period (1868–1912), Japan and its people opened themselves to the West. Japanese scholars adopted Western mathematical technique, and this led to a decline of interest in the ideas used in ''wasan''. History Pre-Edo period (552-1600) Records of mathematics in the early periods of Japanese history are nearly nonexistent. Though it was at this time that a large influx of knowledge from China reached Japan, including that of reading and writing, little sources exist of usage of mathematics within Japan. However, it is suggested that this period saw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventeen-article Constitution
The is, according to the '' Nihon Shoki'' of 720, a document authored by Prince Shōtoku in 604. It was adopted in the reign of Empress Suiko. The emphasis of the document is not so much on the basic laws by which the state was to be governed, such as one may expect from a modern constitution, but rather it was a highly Buddhist and Confucian document that focused on the morals and virtues that were to be expected of government officials and the emperor's subjects to ensure a smooth running of the state, where the emperor was to be regarded as the highest authority. It is one of the earliest constitutions in history. Contents The first article calls for harmony ( ''wa'') to be valued, a response to the lack of peace in Japan at the time. The second article places the Buddhist faith ahead of the authority of the emperor. Validity The degree to which the document matches the definition of a "constitution" is debated. While it introduces principles of governance much like the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floruit
''Floruit'' ( ; usually abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for 'flourished') denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicating the time when someone flourished. Etymology and use is the third-person singular perfect active indicative of the Latin verb ', ' "to bloom, flower, or flourish", from the noun ', ', "flower". Broadly, the term is employed in reference to the peak of activity for a person or movement. More specifically, it often is used in genealogy and historical writing when a person's birth or death dates are unknown, but some other evidence exists that indicates when they were alive. For example, if there are Will (law), wills Attestation clause, attested by John Jones in 1204 and 1229, as well as a record of his marriage in 1197, a record concerning him might be written as "John Jones (fl. 1197–1229)", even though Jones was born before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matsunaga Ryohitsu
Matsunaga (written: ) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Daniel Matsunaga, Japanese-Brazilian model, actor and football player currently based in the Philippines * Enzo Matsunaga, author *Futoshi Matsunaga, Japanese serial killer *Hikaru Matsunaga, Japanese legislator and finance minister * Hisahide Matsunaga, daimyō of the Matsunaga clan in the Sengoku period *Mari Matsunaga, founder of i-mode mobile service and Seiko Epson board director * Masahiro Matsunaga, racing driver * Masatoshi Matsunaga, Imperial Army Lieutenant General and Baron, Second Class *, Japanese professional wrestler * Sadaichi Matsunaga, Imperial Japanese Navy Vice Admiral *, Japanese sport wrestler *Spark Matsunaga, United States Senator from Hawaii *, Japanese footballer * Toh Matsunaga, Chairman of the 45th House of Representative *, Japanese professional wrestler * Yoshisuke Matsunaga, Japanese mathematician of the 18th century *, Japanese voice actress Fictional characters * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Takebe Kenkō
, also known as Takebe Kenkō, was a Japanese mathematician and cartographer during the Edo period.Smith, David. (1914). Biography Takebe was the favorite student of the Japanese mathematician Seki Takakazu Takebe is considered to have extended and disseminated Seki's work. In 1706, Takebe was offered a position in the Tokugawa shogunate's department of ceremonies. In 1719, Takebe's new map of Japan was completed; and the work was highly valued for its quality and detail. ''Shōgun'' Yoshimune honored Takebe with rank and successively better positions in the shogunate. Legacy Takebe played a critical role in the development of the Enri (, "circle principle") - a crude analogon to the western calculus. He also created charts for trigonometric functions. Mathematical Society of Japan [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoshida Mitsuyoshi
, also known as Yoshida Kōyū, was a Japanese mathematician in the Edo period. List of Japanese mathematicians -- Clark University, Dept. of Mathematics and Computer Science His popular and widely disseminated published work made him the most well known writer about mathematics in his lifetime. He was a student of Kambei Mori (also known as Kambei Mori, Mōri Shigeyoshi). Along with Imamura Chishō and Takahara Kisshu, Yoshida became known to his contemporaries as one of "the Three Arithmeticians." Yoshida was the author of the oldest extant Japanese mathematical text. The 1627 work was named ''Jinkōki''. The work dealt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seki Kowa Katsuyo Sampo Bernoulli Numbers
Seki may refer to: Places * Seki, Gifu, a city in Japan * Seki River, a river in Japan * Şəki, a city and provincial capital in Azerbaijan * Şəki (village), a village and municipality in Azerbaijan * Šeki, a small town in Slovenia * Seki, Bismil * Seki, Ilgaz, a village in Turkey * Seki, İskilip * Seki, Osmancık * Seki, Tavas Other uses * Seki, a term in the game of Go *SEKI, an acronym for Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks in California * Seki language, a Bantu language of Equatorial Guinea and Gabon * Sushi Seki, a Japanese sushi restaurant in New York City People with the surname *, Japanese soprano * Atsuko Seki (born 1964), Japanese pianist * Deniz Seki (born 1970), Turkish female pop singer * , Japanese politician *, Japanese businessman *, Japanese ice hockey player *, Japanese ''daimyō'' *, Japanese handball player * , Japanese politician * Koji Seki (other), multiple people *, Imperial Japanese Navy officer *, Japanese table tennis player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richardson Extrapolation
In numerical analysis, Richardson extrapolation is a Series acceleration, sequence acceleration method used to improve the rate of convergence of a sequence of estimates of some value A^\ast = \lim_ A(h). In essence, given the value of A(h) for several values of h, we can estimate A^\ast by extrapolating the estimates to h=0. It is named after Lewis Fry Richardson, who introduced the technique in the early 20th century, though the idea was already known to Christiaan Huygens in Christiaan_Huygens#De_Circuli_Magnitudine_Inventa, his calculation of \pi. In the words of Garrett Birkhoff, Birkhoff and Gian-Carlo Rota, Rota, "its usefulness for practical computations can hardly be overestimated."Page 126 of Practical applications of Richardson extrapolation include Romberg integration, which applies Richardson extrapolation to the trapezoid rule, and the Bulirsch–Stoer algorithm for solving ordinary differential equations. General formula Notation Let A_0(h) be an approximation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler
Leonhard Euler ( ; ; ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss polymath who was active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, logician, geographer, and engineer. He founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics, such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He also introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy, and music theory. Euler has been called a "universal genius" who "was fully equipped with almost unlimited powers of imagination, intellectual gifts and extraordinary memory". He spent most of his adult life in Saint Petersburg, Russia, and in Berlin, then the capital of Prussia. Euler is credited for popularizing the Greek letter \pi (lowercase pi) to denote the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Series
In mathematics, a power series (in one variable) is an infinite series of the form \sum_^\infty a_n \left(x - c\right)^n = a_0 + a_1 (x - c) + a_2 (x - c)^2 + \dots where ''a_n'' represents the coefficient of the ''n''th term and ''c'' is a constant called the ''center'' of the series. Power series are useful in mathematical analysis, where they arise as Taylor series of infinitely differentiable functions. In fact, Borel's theorem implies that every power series is the Taylor series of some smooth function. In many situations, the center ''c'' is equal to zero, for instance for Maclaurin series. In such cases, the power series takes the simpler form \sum_^\infty a_n x^n = a_0 + a_1 x + a_2 x^2 + \dots. The partial sums of a power series are polynomials, the partial sums of the Taylor series of an analytic function are a sequence of converging polynomial approximations to the function at the center, and a converging power series can be seen as a kind of generalized polynom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |