|
Hypotheses
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific method, scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and Research ethics, warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ὑπόθεσις
A hypothesis (: hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis must be based on observations and make a testable and reproducible prediction about reality, in a process beginning with an educated guess or thought. If a hypothesis is repeatedly independently demonstrated by experiment to be true, it becomes a scientific theory. In colloquial usage, the words "hypothesis" and "theory" are often used interchangeably, but this is incorrect in the context of science. A working hypothesis is a provisionally-accepted hypothesis used for the purpose of pursuing further progress in research. Working hypotheses are frequently discarded, and often proposed with knowledge (and warning) that they are incomplete and thus false, with the intent of moving research in at least somewhat the right direction, especially when scientists are stuck on an issue and brainstorming ideas. A different meaning of the term ''hypothesis'' is used in formal logic, to den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and medieval world. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous skepticism, because Philosophy of science#Observation inseparable from theory, cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the Perception#Process and terminology, observation. Scientific inquiry includes creating a testable hypothesis through inductive reasoning, testing it through experiments and statistical analysis, and adjusting or discarding the hypothesis based on the results. Although procedures vary across Branches of science, fields, the underlying #Process, process is often similar. In more detail: the scientific method involves making conjectures (hypothetical explanations), predicting the logical consequences of hypothesis, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testable
Testability is a primary aspect of science and the scientific method. There are two components to testability: #Falsifiability or defeasibility, which means that counterexamples to the hypothesis are logically possible. #The practical feasibility of observing a reproducible series of such counterexamples if they do exist. In short, a hypothesis is testable if there is a possibility of deciding whether it is true or false based on experimentation by anyone. This allows anyone to decide whether a theory can be supported or refuted by data. However, the interpretation of experimental data may be also inconclusive or uncertain. Karl Popper introduced the concept that scientific knowledge had the property of falsifiability as published in '' The Logic of Scientific Discovery''.Karl Popper "The Logic of Scientific Discovery", 1934 (as ''Logik der Forschung'', English translation 1959), ISBN 0415278449 and 2002 ISBN 9780415278447, 0415278449 See also * Confirmability * Controlla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Working Hypothesis
A working hypothesis is a hypothesis that is provisionally accepted as a basis for further ongoing research in the hope that a tenable theory will be produced, even if the hypothesis ultimately fails.See in "hypothesis", ''Century Dictionary Supplement'', v. 1, 1909, New York: The Century Company. Reprintedv. 11, p. 616(via ''Internet Archive''] of the ''Century Dictionary and Cyclopedia'', 1911. Like all hypotheses, a working hypothesis is constructed as a statement of expectations, which can be linked to deductive, exploratory research Shields, Patricia and Rangarjan, N. (2013). ''A Playbook for Research Methods: Integrating Conceptual Frameworks and Project Management''. Stillwater, OK: New Forums Press. See Chapter 5. in empirical investigation and is often used as a conceptual framework in qualitative research. The term "working" indicates that the hypothesis is subject to change. History Use of the phrase "working hypothesis" goes back to at least the 1850s. Charles Sande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Of Ancient Greece
A Theatre, theatrical culture flourished in ancient Greece from 700 BC. At its centre was the Polis, city-state of Classical Athens, Athens, which became a significant cultural, political, and religious place during this period, and the theatre was institutionalised there as part of a festival called the Dionysia, which honoured the god Dionysus. Greek tragedy, Tragedy (late 500 BC), Ancient Greek comedy, comedy (490 BC), and the satyr play were the three dramatic genres emerged there. Athens exported the festival to its numerous colonies. Modern Western theatre comes, in large measure, from the theatre of ancient Greece, from which it borrows technical terminology, classification into genres, and many of its theme (arts), themes, stock characters, and plot elements. Etymology The word , from which the word "tragedy" is derived, is a compound (linguistics), compound of two Greek language, Greek words: or "goat" and meaning "song", from . This etymology indicates a link with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterfactual Conditional
Counterfactual conditionals (also ''contrafactual'', ''subjunctive'' or ''X-marked'') are conditional sentences which discuss what would have been true under different circumstances, e.g. "If Peter believed in ghosts, he would be afraid to be here." Counterfactuals are contrasted with indicatives, which are generally restricted to discussing open possibilities. Counterfactuals are characterized grammatically by their use of fake tense morphology, which some languages use in combination with other kinds of morphology including aspect and mood. Counterfactuals are one of the most studied phenomena in philosophical logic, formal semantics, and philosophy of language. They were first discussed as a problem for the material conditional analysis of conditionals, which treats them all as trivially true. Starting in the 1960s, philosophers and linguists developed the now-classic possible world approach, in which a counterfactual's truth hinges on its consequent holding at certai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
What If
What If may refer to: Film * ''What If'', a 2006 TV film starring Niall Buggy * What If... (2010 film), ''What If...'' (2010 film), an American film * What If... (2012 film), ''What If...'' (2012 film), a Greek film * What If (2013 film), ''What If'' (2013 film) or ''The F Word'', a Canadian-Irish film * ''Yun Hota Toh Kya Hota'', or ''What If...?'', a 2006 Indian film Television * ''What/If'', a 2019 American thriller streaming miniseries * What If... (web series), ''What If...'' (web series), a 2010 American soap-opera crossover series * What If...? (TV series), ''What If...?'' (TV series), a 2021 American animated series by Marvel Studios * What If... (Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D.), "What If..." (''Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D.''), a 2017 episode * What If (Doctors), "What If" (''Doctors''), a 2004 episode * What If (Drop Dead Diva), "What If" (''Drop Dead Diva''), a 2009 episode * What If? (JAG), "What If?" (''JAG''), a 2004 episode Literature * Alternate history, fiction based on wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothesis (drama)
In its ancient usage, a hypothesis is a summary of the plot of a classical drama.Easterling (1997, 202) and Gregory (2005, 271-272, 384). These hypotheses were often copied as a preface to the text of the surviving Athenian tragedies in Medieval manuscripts. They also indicated whether any other tragic poets had dramatised the story, gave its setting, identified the chorus and the character who delivered the prologue A prologue or prolog (from Ancient Greek πρόλογος ''prólogos'', from πρό ''pró'', "before" and λόγος ''lógos'', "speech") is an opening to a story that establishes the context and gives background details, often some earlier st ..., and indicated the date of its first production and the titles of the poet's other plays performed that year, as well as the poet's rivals in the dramatic competition and the prize awarded.Gregory (2005, 384-385). References Sources * Easterling, P. E., ed. 1997. ''The Cambridge Companion to Greek Tragedy''. Camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
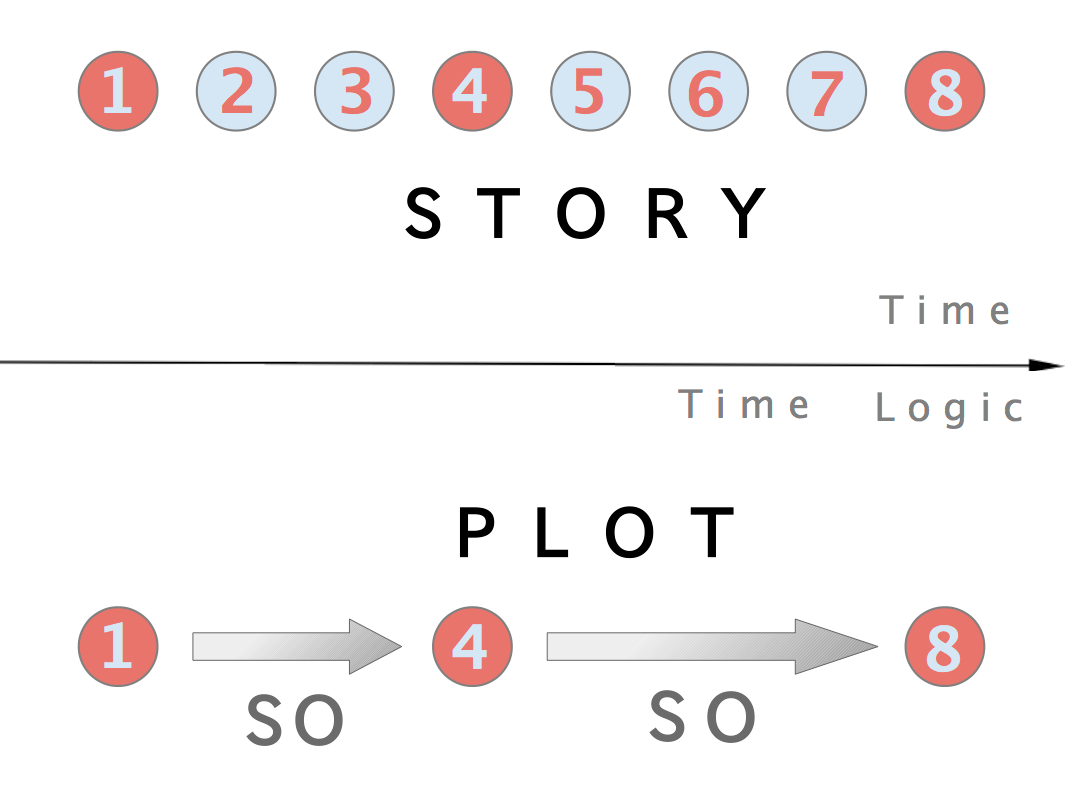
Plot (narrative)
In a literary work, film, or other narrative, the plot is the mapping of events in which each one (except the final) affects at least one other through the principle of Causality, cause-and-effect. The causal events of a plot can be thought of as a selective collection of events from a narrative, all linked by the connector "and so". Simple plots, such as in a traditional ballad, can be linearly sequenced, but plots can form complex interwoven structures, with each part sometimes referred to as a subplot. Plot is similar in meaning to the term ''storyline''. In the narrative sense, the term highlights important points which have consequences within the story, according to American science fiction writer Ansen Dibell. The Premise (narrative), premise sets up the plot, the Character (arts), characters take part in events, while the Setting (narrative), setting is not only part of, but also influences, the final story. An can convolute the plot based on a misunderstanding. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellarius Harmonia Macrocosmica - Hypothesis Ptolemaica
Cellarius may refer to: Surname Cellarius is the Latin form of cellarer, an office within a medieval Benedictine abbey. As a surname it is usually a Latinized form of the German name ''Keller (surname), Keller''. Notable people with the surname include: * Andreas Cellarius, 1596–1665, German-Dutch mathematician and cartographer * Christoph Cellarius, 1638–1707, Christoph Keller, Weimar, classical scholar * Ludwig Cellarius, died 1526, Ludwig Keller of Basel, first husband of Wibrandis Rosenblatt * Martin Cellarius, 1499–1564, Martin Borrhaus, anti-Trinitarian reformer Other * 12618 Cellarius, a minor planet named after Andreas Cellarius * ''Cellarius'', a pseudonym used by Samuel Butler (novelist), Samuel Butler in his 1863 letter ''Darwin among the Machines'' {{disambig, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consequent
A consequent is the second half of a hypothetical proposition. In the standard form of such a proposition, it is the part that follows "then". In an implication, if ''P'' implies ''Q'', then ''P'' is called the antecedent and ''Q'' is called the consequent. In some contexts, the consequent is called the ''apodosis''.See Conditional sentence. Examples: * If P, then Q. Q is the consequent of this hypothetical proposition. * If X is a mammal, then X is an animal. Here, "X is an animal" is the consequent. * If computers can think, then they are alive. "They are alive" is the consequent. The consequent in a hypothetical proposition is not necessarily a consequence of the antecedent. * If monkeys are purple, then fish speak Klingon. "Fish speak Klingon" is the consequent here, but intuitively is not a consequence of (nor does it have anything to do with) the claim made in the antecedent that "monkeys are purple". See also * Antecedent (logic) * Conjecture * Necessity and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |