|
History Of Leon County, Florida
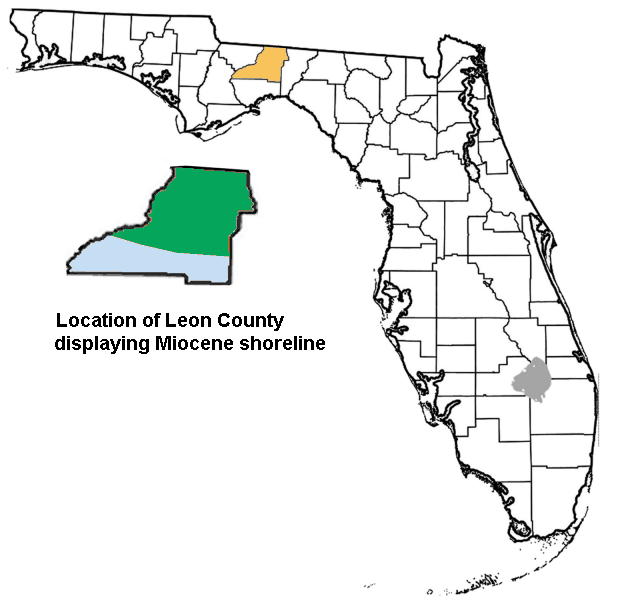
The history of Leon County, Florida, much like the History of Tallahassee, dates back to the settlement of the Americas. Beginning in the 16th century, the region was colonized by Europeans, becoming part of Spanish Florida. In 1819, the Adams–Onís Treaty ceded Spanish Florida, including modern-day Leon County, to the United States. Named for Spanish explorer Juan Ponce de León, Leon County became an official U.S. county in 1824; the American takeover led to the county's rapid expansion as growing numbers of cotton plantations began to spring up nearby, increasing Leon County's population significantly. Prehistoric Leon County, like most of North America, supported a variety of ancient and now extinct animals as far back as 33 million years ago. There are no fossils of dinosaurs in Florida. Prior to the Miocene, Florida was a submerged carbonate platform essentially cut off from the continent by the Gulf Trough. When this trough filled with sediments during the Eocene� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Tallahassee, Florida
The history of Tallahassee, Florida, much like the History of Leon County, Florida, history of Leon County, dates back to the settlement of the Americas. Beginning in the 16th century, the region was European colonization of the Americas, colonized by Europeans, becoming part of Spanish Florida. In 1819, the Adams–Onís Treaty ceded Spanish Florida, including modern-day Tallahassee, to the United States. Tallahassee became a city and the state capital of Florida in 1821; the American takeover led to the settlements' rapid expansion as growing numbers of Plantation complexes in the Southern United States, cotton plantations began to spring up nearby, increasing Tallahassees' population significantly. Early history Tallahassee is situated within the Apalachee Province, home of the Apalachee, a Mississippian culture of agrarian people who farmed vast tracts of land. Their capital, Anhaica, was located within Tallahassee's city limits. The name "Tallahassee" is a Muskogean lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group . The term is also used as a verb, to describe carbonation: the process of raising the concentrations of carbonate and bicarbonate ions in water to produce carbonated water and other carbonated beverageseither by the addition of carbon dioxide gas under pressure or by dissolving carbonate or bicarbonate salts into the water. In geology and mineralogy, the term "carbonate" can refer both to carbonate minerals and carbonate rock (which is made of chiefly carbonate minerals), and both are dominated by the carbonate ion, . Carbonate minerals are extremely varied and ubiquitous in chemically precipitated sedimentary rock. The most common are calcite or calcium carbonate, , the chief constituent of limestone (as well as the main component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megatherium
''Megatherium'' ( ; from Greek () 'great' + () 'beast') is an extinct genus of ground sloths endemic to South America that lived from the Early Pliocene through the end of the Late Pleistocene. It is best known for the elephant-sized type species ''Megatherium americanum'', primarily known from the Pampas, but ranging southwards to northernmost Patagonia and northwards to southern Bolivia during the late Middle Pleistocene and Late Pleistocene. Various other species belonging to the subgenus ''Pseudomegatherium'' ranging in size comparable to considerably smaller than ''M. americanum'' are known from the Andean region. The first (holotype) specimen of ''Megatherium'' was discovered in 1787 on the bank of the Luján River in what is now northern Argentina. The specimen was then shipped to Spain the following year wherein it caught the attention of the French paleontologist Georges Cuvier, who named the animal in 1796 and was the first to determine, by means of comparative anato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanotylopus
''Titanotylopus'' is an extinct genus of camel (tribe Camelini), endemic to North America from the late Hemphillian stage of the Miocene through the Irvingtonian stage of the Pleistocene. It was one of the last surviving North American camels; after its extinction, only ''Camelops'' remained. Its name is derived from the Greek words Τιτάν, τύλος and πούς — "Titan", "knob" and "foot"; thus, "giant knobby-foot". Paleobiology ''Titanotylopus'' is distinguished from other early large camelids by its large upper canines amongst other distinguishing dental characteristics, and absence of lacrimal vacuities in the skull. Unlike the smaller, contemporaneous ''Camelops'', ''Titanotylopus'' had relatively broad second phalanges, suggesting that it had true padded "cameltoes", like modern camels.Björn Kurtén and Elaine Anderson ''Pleistoceone Mammals of North America'' (New York : Columbia University Press, 1980), pp. 301–302 The species ''Titanotylopus spat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
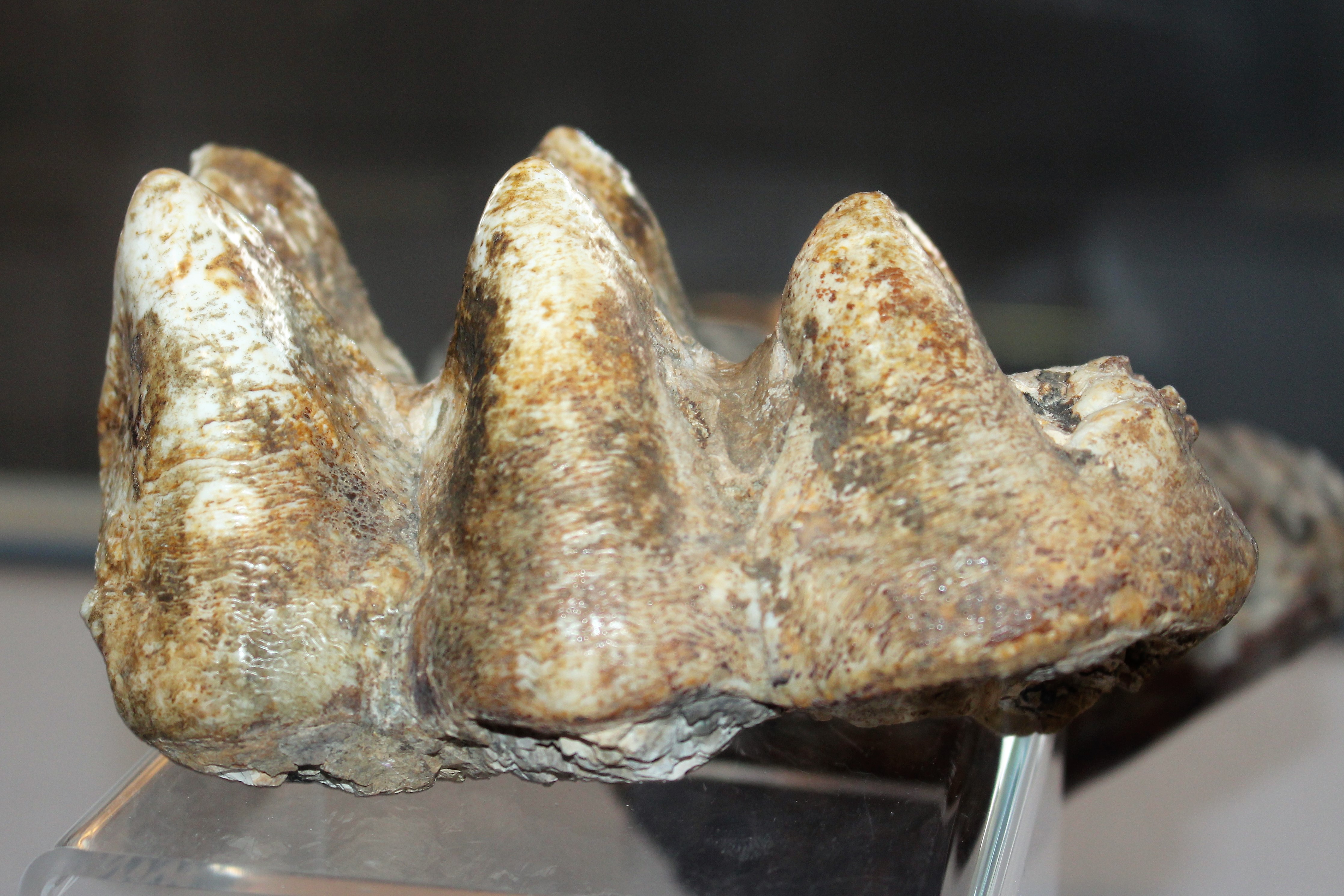
Mastodon
A mastodon, from Ancient Greek μαστός (''mastós''), meaning "breast", and ὀδούς (''odoús'') "tooth", is a member of the genus ''Mammut'' (German for 'mammoth'), which was endemic to North America and lived from the late Miocene to the early Holocene. Mastodons belong to the order Proboscidea, the same order as elephants and mammoths (which belong to the family Elephantidae). ''Mammut'' is the type genus of the extinct family Mammutidae, which diverged from the ancestors of modern elephants at least 27–25 million years ago, during the Oligocene. Like other members of Mammutidae, the molar (tooth), molar teeth of mastodons have zygodont morphology (where parallel pairs of cusp (anatomy), cusps are merged into sharp ridges), which strongly differ from those of elephantids. In comparison to its likely ancestor ''Zygolophodon'', ''Mammut'' is characterized by particularly long and upward curving upper tusks, reduced or absent tusks on the lower jaw, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Bison
''Bison antiquus'' is an extinct species of bison that lived in North America during the Late Pleistocene from over 60,000 years ago until around 10,000 years ago. ''Bison antiquus'' was one of the most common large herbivores in North America during this time period. It is the direct ancestor of the living American bison.C. G Van Zyll de Jong , 1986, A systematic study of recent bison, with particular consideration of the wood bison (Bison bison athabascae Rhoads 1898), p.53, National Museum of Natural Sciences History of discovery The first described remains of ''Bison antiquus'' were collected at Big Bone Lick, Kentucky in Pleistocene deposits in the 1850s and only consisted of a fragmentary posterior skull and a nearly complete horn core. The fossil ( ANSP 12990) was briefly described by Joseph Leidy in 1852. Although the original fossils were fragmentary, a complete skull of an old male was discovered in southern California and were described as a new species, ''B. cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans. It is followed by the Mesolithic. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. ''Homo sapiens'') are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago. It has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of Artefact (archaeology), artefacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to early human migrations, expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which may have contributed to the Neanderthal extinction, extinction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clovis Culture
The Clovis culture is an archaeological culture from the Paleoindian period of North America, spanning around 13,050 to 12,750 years Before Present (BP). The type site is Blackwater Draw locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, where stone tools were found alongside the remains of Columbian mammoths in 1929. Clovis sites have been found across North America. The most distinctive part of the Clovis culture toolkit are Clovis points, which are projectile points with a fluted, lanceolate shape.Fluted: Having a flake removed from the base, either on one or both sides.Lanceolate: Tapering to a point at one end, like the head of a lance. Clovis points are typically large, sometimes exceeding in length. These points were multifunctional, also serving as cutting tools. Other stone tools used by the Clovis culture include knives, scrapers, and bifacial tools, with bone tools including beveled rods and shaft wrenches, with possible ivory points also being identified. Hides, wood, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoindians
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in the Western Hemisphere and is distinct from the term ''Paleolithic''.''Paleolithic'' specifically refers to the period between million years ago and the end of the Pleistocene in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is not used in New World archaeology. Traditional theories suggest that big-animal hunters crossed the Bering Strait from North Asia into the Americas over a land bridge (Beringia). This bridge existed from 45,000 to 12,000 BCE (47,000–14,000 BP). Small isolated groups of hunter-gatherers migrated alongside herds of large herbivores far into Alaska. From BCE ( BP), ice-free corridors developed along the Pacific coast and valleys of North America. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protohistoric
Protohistory is the period between prehistory and written history, during which a culture or civilization has not yet developed writing, but other cultures that have developed writing have noted the existence of those pre-literate groups in their own writings. Protohistoric may also refer to the transition period between the advent of literacy in a society and the writings of the first historians. The preservation of oral traditions may complicate matters, as they can provide a secondary historical source for even earlier events. Colonial sites involving a literate group and a nonliterate group are also studied as protohistoric situations. The term can also refer to a period in which fragmentary or external historical documents, not necessarily including a developed writing system, have been found. For instance, the Proto–Three Kingdoms of Korea, the Yayoi, recorded by the Chinese, and the Mississippian groups, recorded by early European explorers, are protohistoric. Use o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leon County, Florida Paleontological Sites
The Leon County, Florida, Leon County Paleontological site, paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene Invertebrate, invertebrates and vertebrates of Leon County, Florida, United States. Age Era (geology), Era: Neogene. Period (geology), Period: Early Miocene. Faunal stage: Arikareean, ~23.1–21.9 Annum, Ma, calculates to a period of approximately . Geological Formation: Torreya Formation. Sites Leon County paleontological sites are represented by the following: *Griscom Plantation Site. Located in Killearn Lakes Plantation, south-southeast of Lake Iamonia on the southeast most section of Luna Plantation during a well drilling operation. Time period: ~23.6–18.8 Ma. (Appearance Event Ordination, AEO). Coordinates: *Seaboard Air Line Railroad Site. Location was south of the center of Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee during a dredging operation for a roadway. Time period: ~21.7 Ma. (AEO, Alroy). Coordinates: *St. Marks River site. Located along the St. Marks River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) and Capreolinae (which includes, among others reindeer (caribou), white-tailed deer, roe deer, and moose). Male deer of almost all species (except the water deer), as well as female reindeer, grow and shed new antlers each year. These antlers are bony extensions of the skull and are often used for combat between males. The musk deer ( Moschidae) of Asia and chevrotains ( Tragulidae) of tropical African and Asian forests are separate families that are also in the ruminant clade Ruminantia; they are not especially closely related to Cervidae. Deer appear in art from Paleolithic cave paintings onwards, and they have played a role in mythology, religion, and literature throughout history, as well as in heraldry, such as red deer that app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |