|
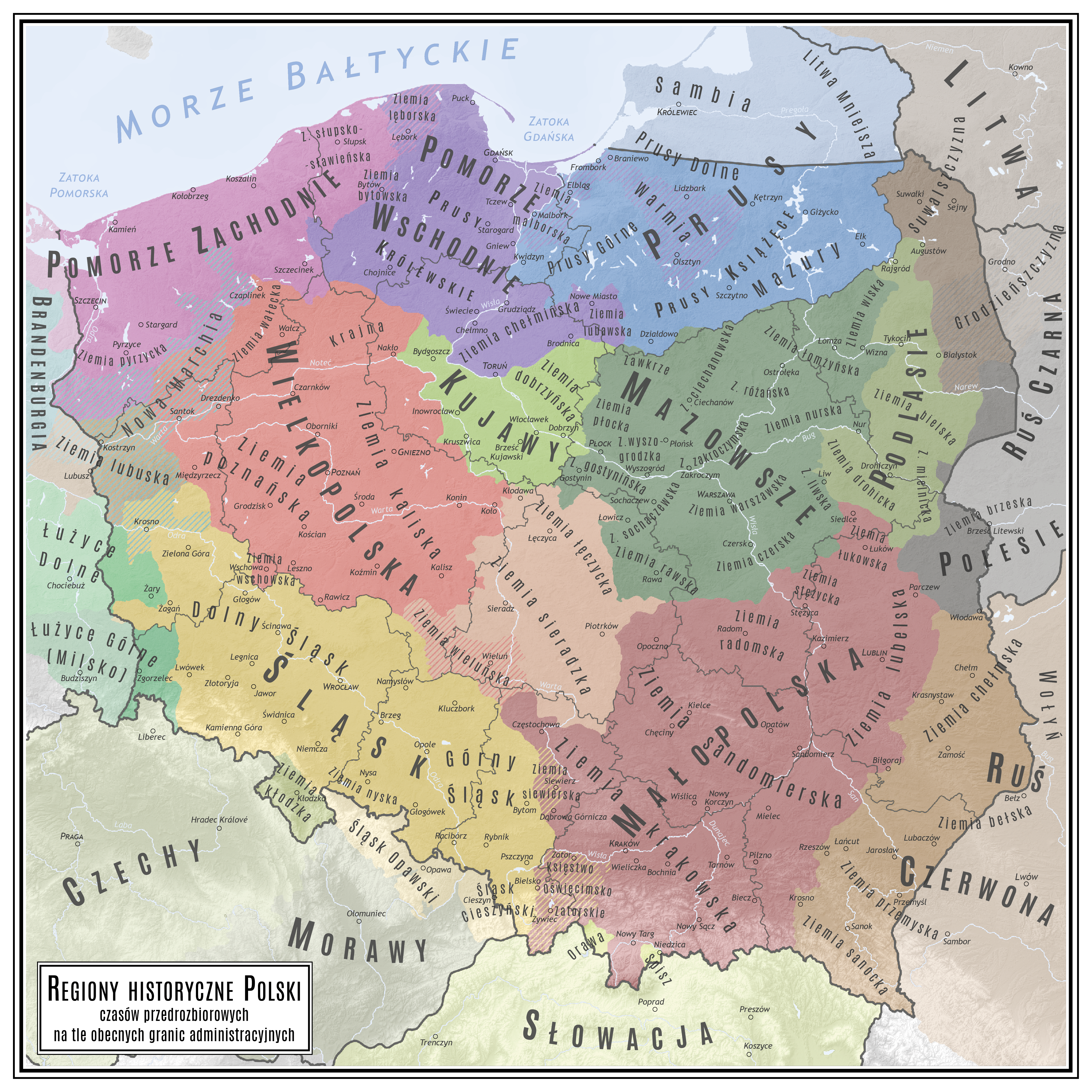
Historical Regions In Poland
Polish historic regions are regions that were related to a Territorial evolution of Poland, former Polish state, or are within present-day Poland, with or without being identified in its administrative divisions. There are several historic and cultural regions in Poland that are called ethnography, ethnographic regions. Their exact borders cannot be drawn, as the regions are not official political or administrative units. They are delimited by culture, such as country traditions, traditional lifestyle, songs, tales, etc. To some extent, the regions correspond to the zones of Polish language, Polish language dialects. The correspondence, however, is by no means strict. Historical regions within the current Polish state The following historical regions, historic regions within Poland's modern borders belonged to the Polish state during most of its existence, inhabited by a majority or a sizeable Polish- or Cashubian-speaking population, thus forming the core Polish territory: *G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
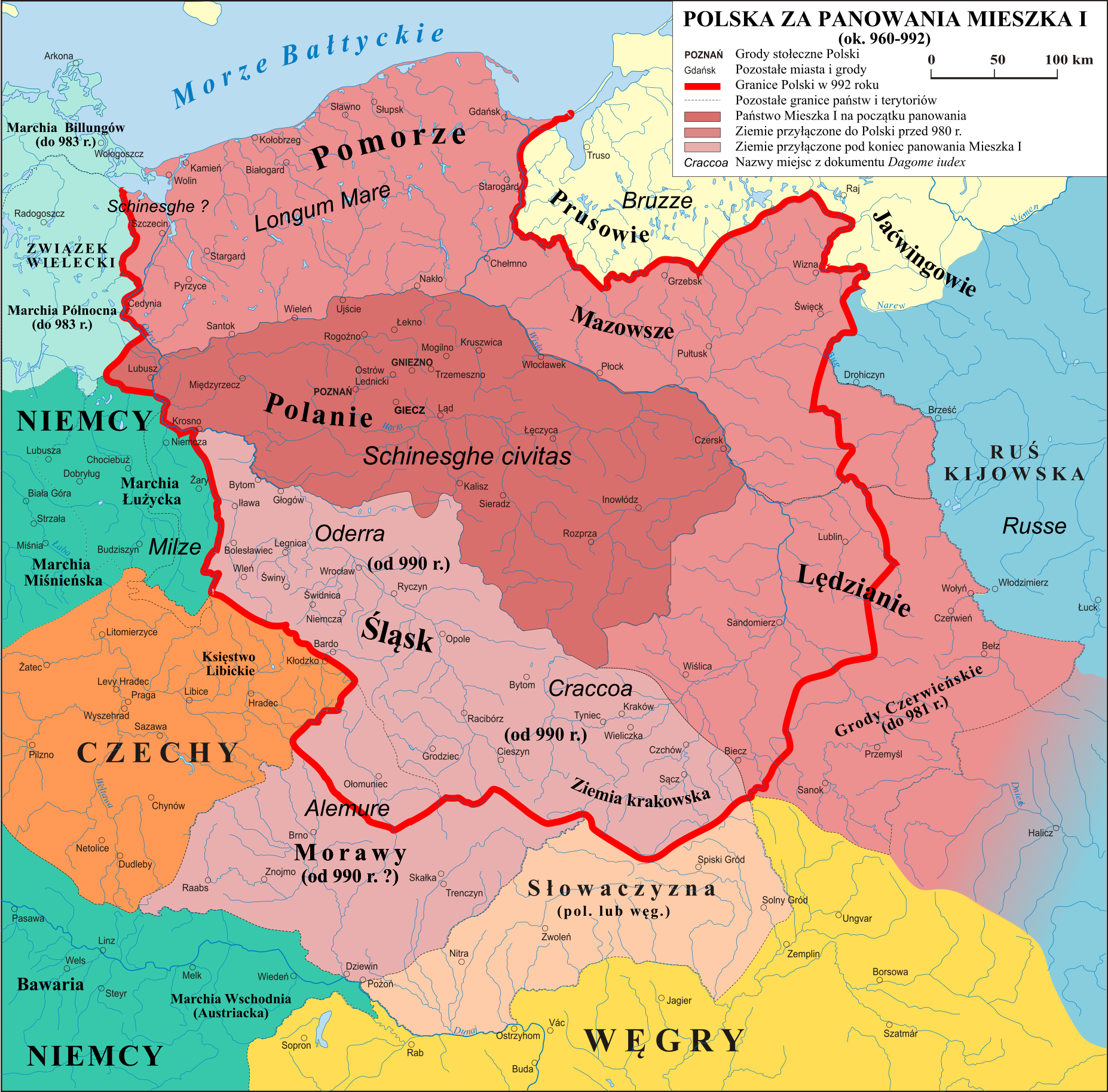
Territorial Evolution Of Poland
Poland is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus, and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian Enclave and exclave, exclave, to the north. The total area of Poland is , making it the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 69th largest country in the world and the List of European countries by area, ninth largest in Europe. From a nucleus between the Oder and Vistula rivers on the North European Plain, North-Central European Plain, Poland has at its largest extent expanded as far as the Baltic Sea, Baltic, the Dnieper River, Dnieper and the Carpathian Mountains, Carpathians, while in periods of weakness it has shrunk drastically or even ceased to exist. Territorial history In 1492, the territory of Poland-Lithuania – not counting the fiefs of Mazovia, Moldavia, and State of the Teutonic Order, Prussia – covered , making it the largest ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piła
Piła (; ) is a city in northwestern Poland and the capital of Piła County, situated in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. Its population was 71,846, making it the city in the voivodeship after Poznań and Kalisz and the largest city in the northern part of Greater Poland. Founded in the 14th century, Piła was a royal city of Poland, whose prosperity came from crafts and trade. The city is located on the Gwda river and is famous for its green areas, parks and dense forests nearby. It is an important road and railway hub, located at the intersection of two main lines: Poznań–Szczecin and Bydgoszcz–Krzyż Wielkopolski. Piła is the center of light industry, culture and education in northern Greater Poland, and is particularly known for motorcycle speedway racing. City name ''Piła'' is a Polish language, Polish word meaning "saw". This was a typical name denoting a village of Lumberjack, woodcutters belonging to a local noble. The German name ''Schneidemühl'' means "sawmill" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rypin
Rypin is a town in north-central Poland, in Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, about 50 km east of Toruń. It is the capital of Rypin County. Population is 16,528 (2010). History Rypin was founded in the Middle Ages, and was part of Poland since the establishment of the state in the 10th century. From the 11th century it was the seat of a local castellany, and from the 14th century it was a county seat. It was granted town rights in the early 14th century, and afterwards it was a royal city in Poland, royal town of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Polish Crown, administratively located in the Dobrzyń Land in the Inowrocław Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Greater Poland Province. In the early 14th century, local dukes of the Polish Piast dynasty founded a hospital in Rypin to commemorate their deceased father Duke Siemowit of Dobrzyń. In 1352, the hospital was granted various privilege (law), privileges by Duke Władysław the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobrzyń Nad Wisłą
Dobrzyń nad Wisłą (; ) is a town in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It lies on the Vistula River in the vicinity of Włocławek. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 2,025. History Foundations The settlement of Dobrzyń dates back to the Middle Ages. A stronghold existed at the site since 9th century, and later also a castle was erected. It became part of the emerging Polish state in the 10th century. The oldest known mention of Dobrzyń (as Dobrin) comes from 1065. In the 11th century there was a castellan stronghold here. From 1228, Konrad I of Masovia allowed the military knights called the Dobrzyń brothers. The crusading Order of Dobrzyń was granted Dobrzyń as a base in 1228, although the knights were later incorporated into the Teutonic Order.Marian Biskup , Gerard Labuda , History of the Teutonic Order in Prussia , Gdańsk: Wydawnictwo Morskie, 1986, p. 91, , OCLC 831220291 . High Middle Ages The 13th and 14th century was tumultuous t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobrzyń Land
Dobrzyń Land () is a historical region in central-northern Poland. It lies northeast of the Vistula River, south of the Drwęca, and west of the Skrwa. The territory approximately corresponds with the present-day powiats of Lipno, Rypin, and half of Golub-Dobrzyń within the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, although it encompasses parts of other counties as well. Totally, it has about 3,000 km2 and 200,000 inhabitants. Its historic capital is Dobrzyń nad Wisłą, which gave its name to the entire region. Its largest town is Rypin. History The region became part of the emerging Polish state under duke Mieszko I of Poland (960–992). Upon the death of his descendant Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth in 1138, it was allocated to the newly established Duchy of Masovia, a provincial duchy of Poland. In his Prussian Crusade, Duke Konrad I of Masovia in 1228 established the Order of Dobrzyń of German knights (''fratribus militiae Christi in Prussia''), whom he vested with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship
The Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship (, ) was a unit of administrative division and local government in the Kingdom of Poland (later Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth), from the 14th century to the Second Partition of Poland in 1793. It was part of the historic Kuyavia region and the Greater Poland Province. Originally, its name was Brzesc Voivodeship (''Województwo brzeskie''), but after the 1569 Union of Lublin, it was renamed into Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship, to distinguish it from Lithuanian Brest Litovsk Voivodeship (Polish: ''Województwo brzesko-litewskie''). Geography Its area was 3,276 sq. kilometers, divided into five counties. The seat of the voivode was at Brześć Kujawski, while local sejmiks for both Brześć Kujawski and Inowrocław Voivodeships took place at Radziejów. It was one of the smallest and most densely populated voivodeships of the Commonwealth. Zygmunt Gloger in his monumental book Historical Geography of the Lands of Old Poland provides this des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inowrocław Voivodeship
Inowrocław Voivodeship () was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from the 14th century to the First Partition of Poland in 1772. Together with the neighbouring Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship it was part of the Kuyavia region and the Greater Poland Province. With size of some 2,900 km2 (together with Dobrzyn Land, its area was 5,877 km2.), it was one of the smallest voivodeships of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In early years after its creation (14th century), it was called ''Gniewkowo Voivodeship'' (''Województwo gniewkowskie''), from the town of Gniewkowo, the seat of local Piast princes. Last mention of Gniewkowo Voivodeship was in 1420. Even though the capital of the voivodeship was in Inowrocław, its biggest urban center was Bydgoszcz. Local sejmiks, together with Brzesc Kujawski Voivodeship, took place in Radziejów. The Inowroclaw Voivodeship with Dobrzyn Land had six senators (Voivode and Castellan of Inowrocław, Castella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brześć Kujawski
Brześć Kujawski (Polish pronunciation: ; ) is a town in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship in central Poland. Once a royal seat of Kuyavia, the town has been the seat of one of two small duchy, duchies into which Kuyavia had been temporarily divided. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 4,527. It is situated on the Zgłowiączka (river), Zgłowiączka River. Etymology The name Brześć comes from the word Brzost, which is a species of elm that the area was originally covered in, while the name Kujawski is derived from the region of Kuyavia and was assigned to distinguish the town from Brześć Litewski, now capital of the Brest Region of Belarus. History The earliest traces of Brześć Kujawski date back to Neolithic settlements, but it wasn't until the thirteenth century that the area became of significant importance as it was the site of a stronghold that was the seat of the Dukes of Kuyavia. Brześć was a part of fragmented Piast dynasty, Piast-ruled Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Włocławek
Włocławek (; or ''Alt Lesle'', Yiddish: וולאָצלאַוועק, romanized: ''Vlatzlavek'') is a city in the Kuyavian–Pomeranian Voivodeship in central Poland along the Vistula River, bordered by the Gostynin-Włocławek Landscape Park. As of December 2021, the population of the city is 106,928. Founded in the 9th century, Włocławek is located in the historical region of Kuyavia, and was its administrative center and main city in the Middle Ages. Nowadays, Włocławek is the third largest city of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (after Bydgoszcz and Toruń) and the main cultural and economic center of eastern Kuyavia. It is the seat of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Włocławek, one of the oldest dioceses in Poland, since the 12th century, with the landmark Gothic Włocławek Cathedral listed as a Historic Monument of Poland. Poland's largest hydroelectric power plant is also located there. History Włocławek's history dates back to the late Bronze Age – ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz is a city in northern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Kuyavia. Straddling the confluence of the Vistula River and its bank (geography), left-bank tributary, the Brda (river), Brda, the strategic location of Bydgoszcz has made it an inland port and a vital centre for trade and transportation. With a city population of 339,053 as of December 2021, Bydgoszcz is the eighth-largest city in Poland. Today, it is the seat of Bydgoszcz County and one of the two capitals of the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship as a seat of its centrally appointed governor, a voivode. Bydgoszcz metropolitan area comprising the city and several adjacent communities is inhabited by half a million people, and forms a part of an extended polycentric Bydgoszcz-Toruń metropolitan area with a population of approximately 0.8 million inhabitants. Since the Middle Ages, Bydgoszcz served as a Royal city in Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, royal city of the Crown of the Kingdom of Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuyavia
Kuyavia (; ), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with the capital in Bydgoszcz, ethnographically distinct), central (the capital in Inowrocław or Kruszwica), and south-eastern (the capital in Włocławek or Brześć Kujawski). Etymology The name Kuyavia first appeared in written sources in the 1136 Bull of Gniezno (, Latin: ''Ex commisso nobis'') issued by Pope Innocent II, and was then mentioned in many documents from medieval times. It is also mentioned in the chronicles of Wincenty Kadłubek. Geography and boundaries In the north, Kuyavia borders with the historic regions of Gdańsk Pomerania (Pomerelia) and Chełmno Land, in the west with proper (exact) Greater Poland, in the south with Łęczyca Land and in the east with Masovia and Dobrzyń Land. The borders of Kuyavia stretch out on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |