|
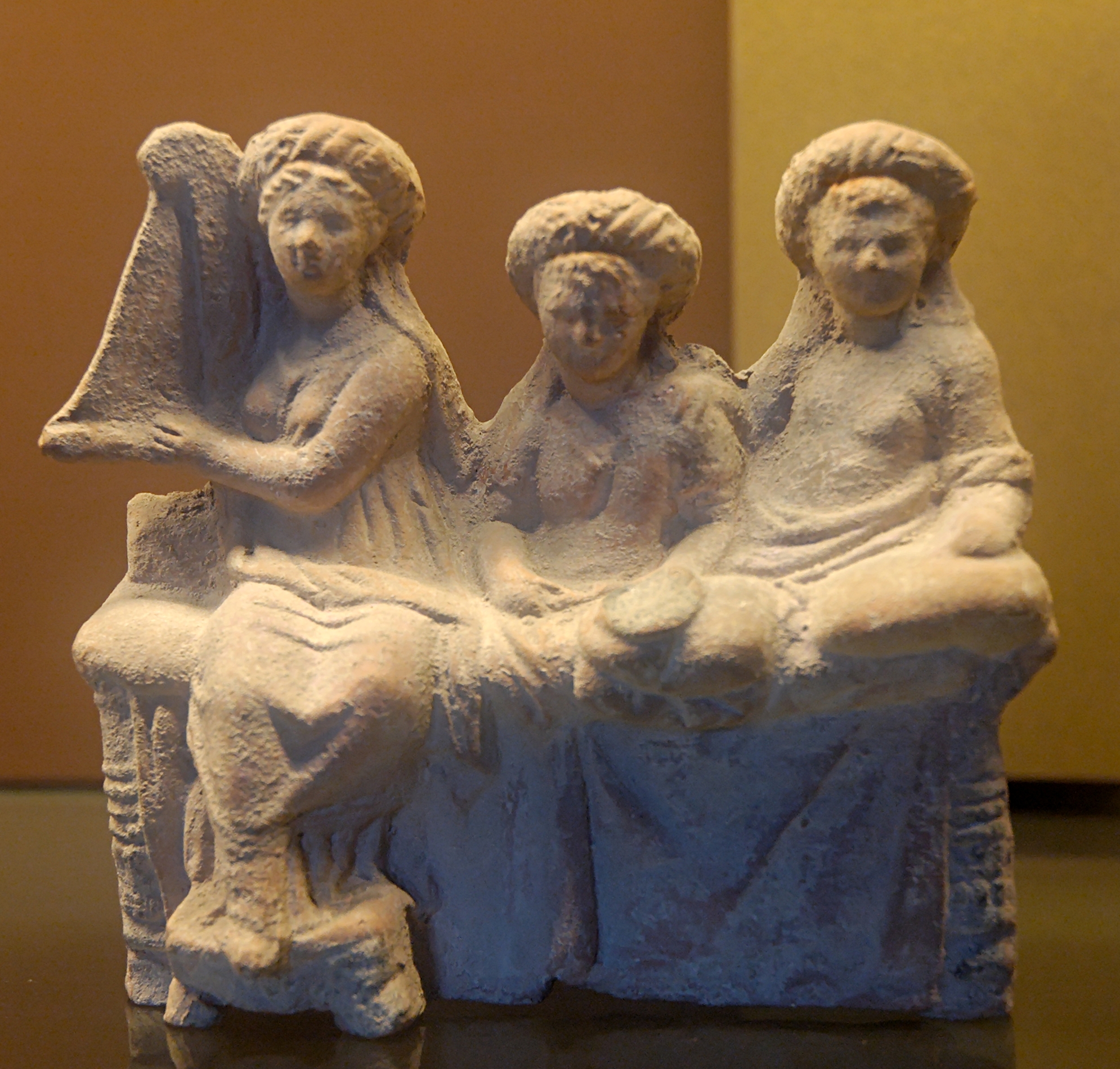
Hetairai
A (; , ; . , ), Latinized as ( ), was a type of highly educated female companion in ancient Greece who served as an artist, entertainer, and conversationalist. Historians have often classed them as courtesans, but the extent to which they were sex workers is a matter of dispute. Custom excluded the wives and daughters of Athenian citizens from the symposium, but this prohibition did not extend to , who were often foreign-born and could be well-versed in arts, philosophy, and culture. Other female entertainers might appear in the otherwise male domain, but actively participated in conversations, including intellectual and literary discourse. Summary Traditionally, historians of ancient Greece have distinguished between and '' pornai'', another class of prostitute. In contrast to pornai, who provided sex for numerous clients in brothels or on the street, were thought to have had only a few men as clients at any one time, to have had long-term relationships with them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prostitutes And Courtesans Of Antiquity
The following is a list of prostitutes and courtesans of antiquity mentioned by ancient sources. Greece and Rome Middle East and India Notes References Sources * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Further reading * * * * * {{Authority control Prostitution in ancient Greece Prostitution in ancient Rome Courtesans of antiquity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetairai
A (; , ; . , ), Latinized as ( ), was a type of highly educated female companion in ancient Greece who served as an artist, entertainer, and conversationalist. Historians have often classed them as courtesans, but the extent to which they were sex workers is a matter of dispute. Custom excluded the wives and daughters of Athenian citizens from the symposium, but this prohibition did not extend to , who were often foreign-born and could be well-versed in arts, philosophy, and culture. Other female entertainers might appear in the otherwise male domain, but actively participated in conversations, including intellectual and literary discourse. Summary Traditionally, historians of ancient Greece have distinguished between and '' pornai'', another class of prostitute. In contrast to pornai, who provided sex for numerous clients in brothels or on the street, were thought to have had only a few men as clients at any one time, to have had long-term relationships with them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostitution In Ancient Greece
Prostitution was a common aspect of ancient Greece.This article was originally translated from the French Wikipedia article '' Prostitution en Grèce antique'' 22 May 2006. In the more important cities, and particularly the many ports, it employed a significant number of people and represented a notable part of economic activity. It was far from being clandestine; cities did not condemn brothels, but rather only instituted regulations on them. In Athens, the legendary lawmaker Solon is credited with having created state brothels with regulated prices. Prostitution involved both sexes differently; women of all ages and young men were prostitutes, for a predominantly male clientele. Simultaneously, extramarital relations with a free woman were severely dealt with. In the case of adultery, the cuckold had the legal right to kill the offender if caught in the act; the same went for rape. Female adulterers, and by extension prostitutes, were forbidden to marry or take part in publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phryne
Phryne (, before 370 – after 316 BC) was an ancient Greek hetaira (courtesan). Born Mnesarete, she was from Thespiae in Boeotia, but seems to have lived most of her life in Athens. Apparently, she grew up poor but became one of the richest women in Greece. Phryne is best known for her trial for impiety, in which she was defended by the orator Hypereides. According to legend, she was acquitted after baring her breasts to the jury, though the historical accuracy of this episode is doubtful. She also modeled for the artists Apelles and Praxiteles: the Aphrodite of Knidos was said to be based on her. Phryne was largely ignored during the Renaissance, but artistic interest in her began to grow from the end of the eighteenth century. Her trial was depicted by Jean-Léon Gérôme in the 1861 painting '' Phryne Before the Areopagus'', which influenced many subsequent depictions of her, and according to Laura McClure made her an "international cultural icon". Sources The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetair-
Hetair- or latinicized Hetaer- is a Greek linguistic root bearing the meaning of ''companion'' (cf. Latin Socii and societas). It is used in the following terms: {{tocright Ancient Greece *Hetairoi (sing. Hetairos), the name of the Macedonian aristocracy and later Companion cavalry *Hetaira (plural Hetairai), female sophisticated companions, courtesans * Hetairideia, a festival of Magnesians and Macedonians *Hetairiai or Ancient Greek clubs, associations of ancient Greeks who were united by a common interest or goal *Hetairia or Andreia, the Cretan terms for Doric Syssitia (common meals) *Hetaireios, an epithet of Zeus Modern Greece *Filiki Eteria, a secret 19th century organization whose purpose was to overthrow Ottoman rule over Greece and to establish an independent Greek state *The Greek term for company, found in many business names such as Jumbo Anonymi Etairia Entomology * '' Hetaeria'', or hairy jewel orchids, a genus in the family Orchidaceae * ''Hetaerina'': a genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
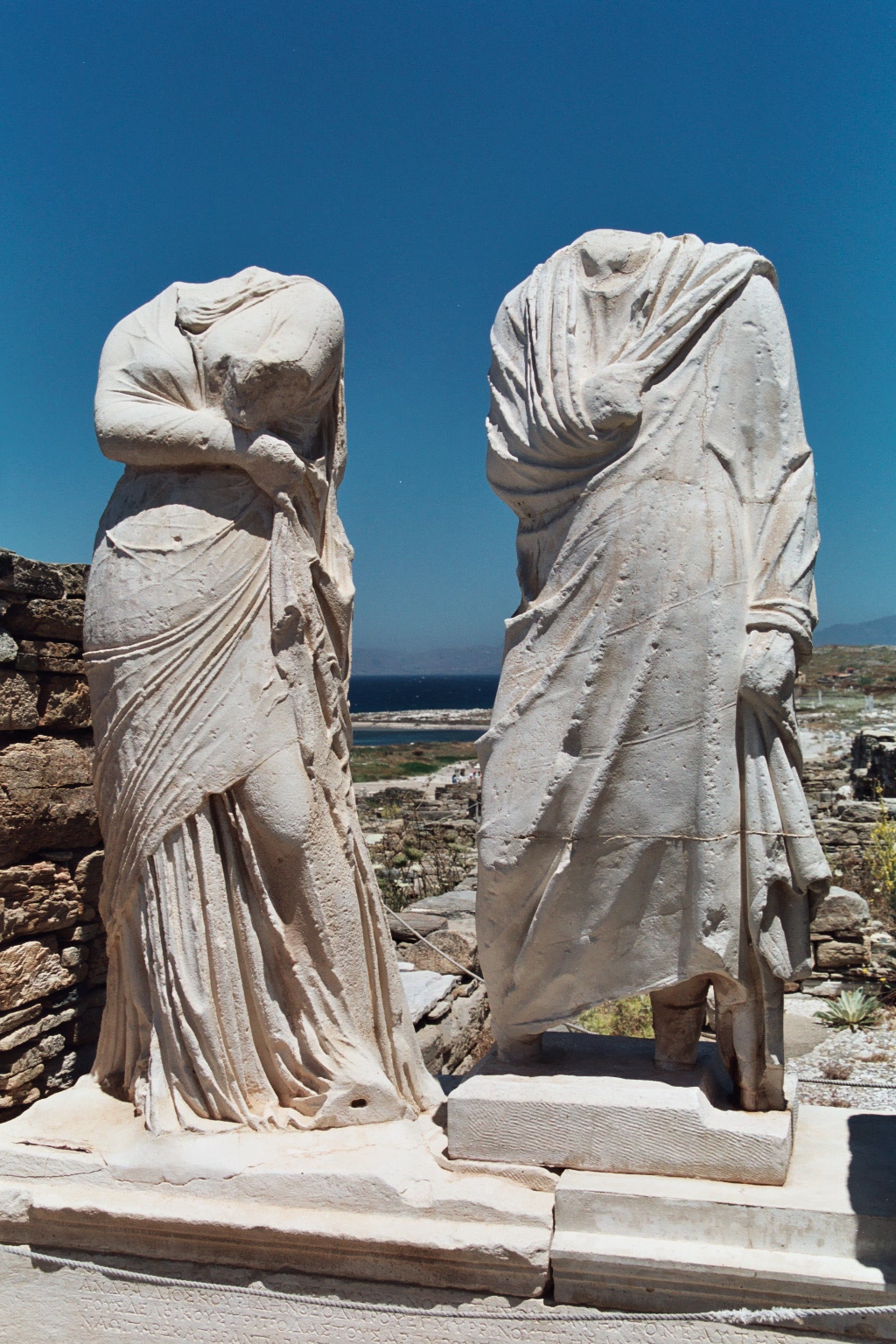
Himation
A himation ( , ) was a type of clothing, a mantle (clothing), mantle or Wrap (clothing), wrap worn by ancient Greek men and women from the Archaic Greece, Archaic period through the Hellenistic period ( BC). It was usually worn over a Chiton (garment), chiton and/or peplos, but was made of heavier drape and played the role of a cloak or shawl. When the himation was used alone, without a chiton, it served both as a chiton and as a cloak. The himation was markedly less voluminous than the Roman toga. Many vase paintings depict women wearing a himation as a veil covering their faces. The himation continued into the Byzantine dress, Byzantine era as "iconographic dress" used in art and by the lower classes, worn by Christ, the Mary, mother of Jesus, Virgin Mary, and biblical figures. Origins While there are no physical remains of himation that have been recovered, it is known that himation was worn by Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks as early as the 6th century BCE. Through differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsolete Occupations
Obsolescence is the process of becoming antiquated, out of date, old-fashioned, no longer in general use, or no longer useful, or the condition of being in such a state. When used in a biological sense, it means imperfect or rudimentary when compared with the corresponding part of other organisms. The international standard IEC 62402:2019 Obsolescence Management defines obsolescence as the "transition from available to unavailable from the manufacturer in accordance with the original specification". Obsolescence frequently occurs because a replacement has become available that has, in sum, more advantages compared to the disadvantages incurred by maintaining or repairing the original. Obsolete also refers to something that is already disused or discarded, or antiquated. Typically, obsolescence is preceded by a gradual decline in popularity. Consequences Driven by rapid technological changes, new components are developed and launched on the market with increasing speed. The resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexuality In Ancient Greece
The human sexuality and Human sexual activity, sexual behavior—along with its taboos, regulation, and sociology, social and politics, political impact—has had a profound effect on the various cultures of the world since Prehistory, prehistoric times. The study of the history of human sexuality The work of Swiss jurist Johann Bachofen made a major impact on the study of the history of sexuality. Many authors, notably Lewis Henry Morgan and Friedrich Engels, were influenced by Bachofen, and criticized Bachofen's ideas on the subject, which were almost entirely drawn from a close reading of ancient mythology. In his 1861 book ''Mother Right: An Investigation of the Religious and Juridical Character of Matriarchy in the Ancient World'' Bachofen writes that in the beginning human sexuality was chaotic and promiscuous. This "aphroditic" stage was replaced by a matriarchal "demeteric" stage, which resulted from the mother being the only reliable way of establishing descendants. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostitution In Ancient Rome
Prostitution in ancient Rome was legal and licensed. Men of any social status were free to engage prostitutes of either sex without incurring moral disapproval, as long as they demonstrated self-control and moderation in the frequency and enjoyment of sex. Brothels were part of the culture of ancient Rome, as popular places of entertainment for Roman men. Most prostitutes were female slaves or freedwomen. The balance of voluntary to forced prostitution can only be guessed at. Privately held slaves were considered property under Roman law, so it was legal for an owner to employ them as prostitutes. Pimping and prostitution were, however, considered disgraceful and dishonourable activities, and their practitioners were considered “ infamous” ('' infames''); for citizens, this meant loss of reputation and many of the rights and privileges attached to citizenship. Slave-owning patrons and investors may have sought to avoid loss of privilege by appointing slaves or freedmen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qiyan
(, ; singular , , ) were a social class of women, trained as entertainers, which existed in the pre-modern Islamic world. The term has been used for women who were both free, including some of whom came from nobility, and non-free women. It has been suggested that "the geisha of Japan are perhaps the most comparable form of socially institutionalized female companionship and entertainment for male patrons, although, of course, the differences are also myriad". Historically, the flourished under the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, and in Al-Andalus. Terminology is often rendered in English as or , but these translations do not reflect the fact that might be of any age, and were skilled entertainers whose training extended well beyond singing, including for example, dancing, composing music and verse, reciting historical or literary anecdotes (), calligraphy, or shadow play. Other translations include ,Matthew S. Gordon, 'Introduction: Producing Songs and Sons', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |