|
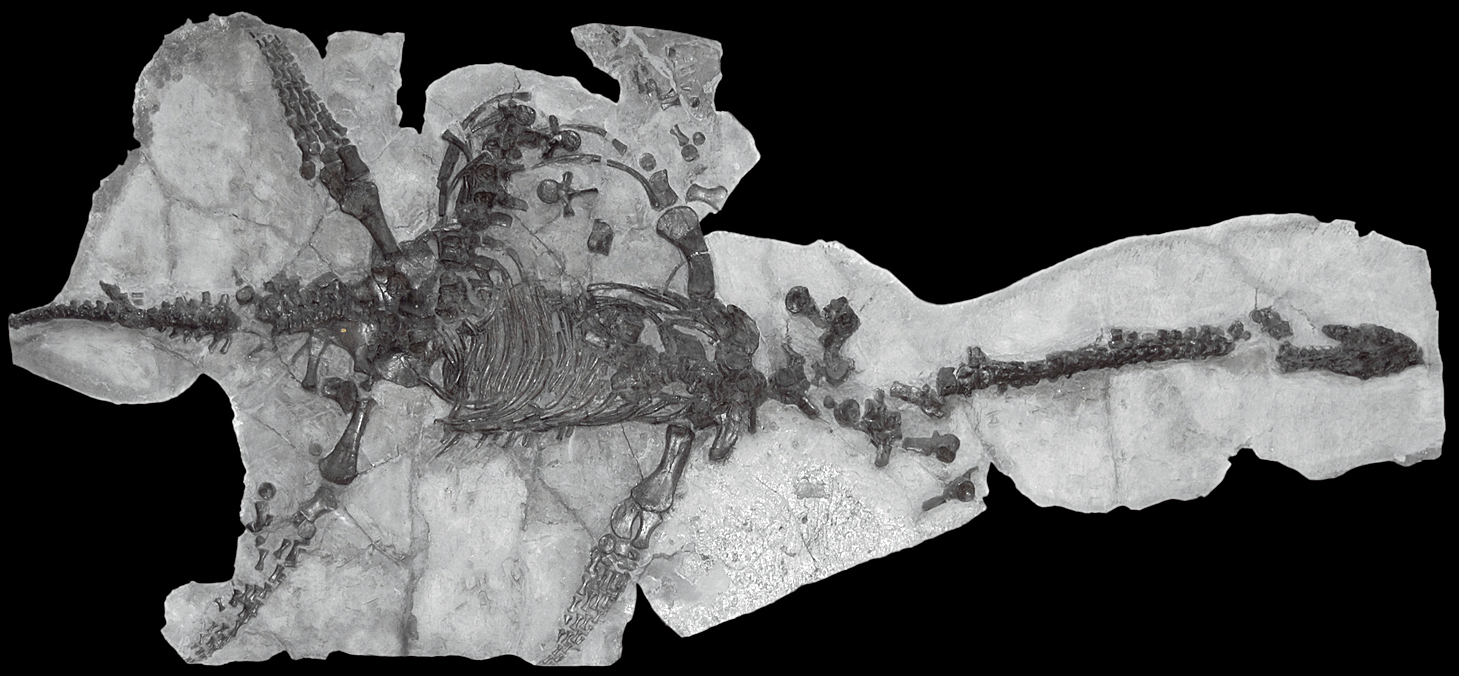
Guanling Formation
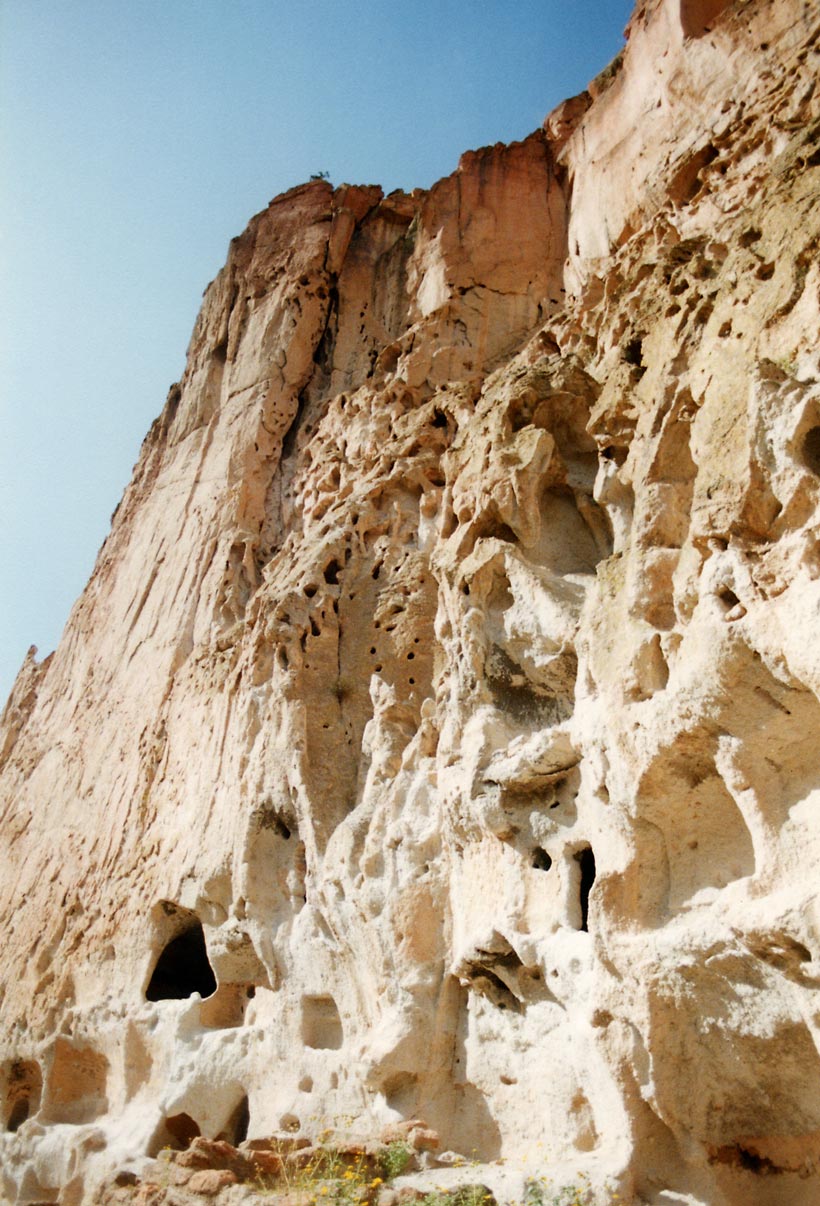
The Guanling Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian or Pelsonian in the regional chronostratigraphy) geologic Formation (geology), formation in southwestern China. Geology The formation encompasses two members. The first member is primarily calcareous mudstone and dolomite (rock), dolomite, indicative of a coastal environment. The second member is a thicker marine sequence of dark Micrite, micritic limestone with some dolomite. Two distinct fossil assemblages are found in the second member. The older Luoping biota preserves abundant arthropods (including Isopoda, isopods, decapods, mysidaceans and thylacocephalans) along with fossils from other invertebrates and vertebrates, which are rare but well-preserved. The slightly younger Panxian fauna has a more diverse and common assortment of marine reptiles such as sauropterygians. A tuff bed in the Luoping biota has been dated to 244.5 ± 2.2 Ma via Uranium–lead dating, U-Pb Sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe, SHRIMP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics (lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness (geology), thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrite
Micrite is a limestone constituent formed of calcareous particles ranging in diameter up to four μm formed by the recrystallization of lime mud. Flügel, Erik, ''Microfacies of Carbonate Rocks: Analysis, Interpretation and Application,'' Springer, pp 74-94, 2004 The term was coined in 1959 by Robert L. Folk for his carbonate rock classification system. Micrite is derived from MICRocrystalline calcITE. In the Folk classification micrite is a carbonate rock dominated by fine-grained calcite Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on .... Carbonate rocks that contain fine-grained calcite in addition to allochems are named ''intramicrite'', ''oomicrite'', ''biomicrite'' or ''pelmicrite'' under the Folk classification depending on the dominant allochem. Micrite is lime mud, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proxy (climate)
In the study of past climates ("paleoclimatology"), climate proxies are preserved physical characteristics of the past that stand in for direct meteorological measurements and enable scientists to reconstruct the climatic conditions over a longer fraction of the Earth's history. Reliable global records of climate only began in the 1880s, and proxies provide the only means for scientists to determine climatic patterns before record-keeping began. A large number of climate proxies have been studied from a variety of geologic contexts. Examples of proxies include stable isotope measurements from ice cores, growth rates in tree rings, species composition of sub-fossil pollen in lake sediment or foraminifera in ocean sediments, temperature profiles of boreholes, and stable isotopes and mineralogy of corals and carbonate speleothems. In each case, the proxy indicator has been influenced by a particular seasonal climate parameter (e.g., summer temperature or monsoon intensity) at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclostratigraphy
Cyclostratigraphy is a subdiscipline of stratigraphy that studies astronomically forced climate cycles within sedimentary successions. Orbital changes Astronomical cycles (also known as Milankovitch cycles) are variations of the Earth's orbit around the Sun due to the gravitational interaction with other masses within the Solar System. Due to this cyclicity, solar irradiation differs through time on different hemispheres and seasonality is affected. These insolation variations have influence on Earth's climate and on the deposition of sedimentary rocks. The main orbital cycles are precession with main periods of 19 and 23 kyr, obliquity with main periods of 41 kyr, and 1.2 Myr, and eccentricity with main periods of around 100 kyr, 405 kyr, and 2.4 Myr. Precession influences how much insolation each hemisphere receives. Obliquity controls the intensity of the seasons. Eccentricity influences how much insolation the Earth receives altogether. Varied insolation directly infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitive High-resolution Ion Microprobe
The sensitive high-resolution ion microprobe (also sensitive high mass-resolution ion microprobe or SHRIMP) is a large-diameter, double-focusing secondary ion mass spectrometer (SIMS) sector instrument that was produced by Australian Scientific Instruments in Canberra, Australia and now has been taken over by Chinese company Dunyi Technology Development Co. (DTDC) in Beijing. Similar to the IMS 1270-1280-1300 large-geometry ion microprobes produced by CAMECA, Gennevilliers, France and like other SIMS instruments, the SHRIMP microprobe bombards a sample under vacuum with a beam of primary ions that sputters secondary ions that are focused, filtered, and measured according to their energy and mass. The SHRIMP is primarily used for geological and geochemical applications. It can measure the isotopic and elemental abundances in minerals at a 10 to 30 μm-diameter scale and with a depth resolution of 1–5 μm. Thus, SIMS method is well-suited for the analysis of complex mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–lead Dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon crystals will contain no lead, meaning that any lead found in the mineral is radiogenic. Since the exact rate at which uranium decays into lead is known, the current ratio of lead to uranium in a sample of the mineral can be used to reliably determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Decay routes Uranium decays to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as ''tuffaceous'' (for example, ''tuffaceous sandstone''). A pyroclastic rock containing 25–75% volcanic bombs or volcanic blocks is called tuff breccia. Tuff composed of sandy volcanic material can be referred to as volcanic sandstone. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Because it is common in Italy, the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the ''moai'' statues on Easter Island. Tuff can be classified as either igneous or sedimentary rock. It is usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although it is sometimes described using sedimentological terms. Tuff is often erroneously called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic, when they became extinct as part of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Other than being diapsids, their affinities to other reptiles have long been contentious. Sometimes suggested to be closely related to turtles, other proposals have considered them most closely related to Lepidosauromorpha or Archosauromorpha, and/or the marine reptile groups Thalattosauria and Ichthyosauromorpha. Origins an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known Phylum, phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxon, taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 Micrometre, μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" para ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacocephala
The Thylacocephala (from the Greek or ', meaning " pouch", and or ' meaning "head") are group of extinct probable mandibulate arthropods, that have been considered by some researchers as having possible crustacean affinities. As a class they have a short research history, having been erected in the early 1980s. They typically possess a large, laterally flattened carapace that encompasses the entire body. The compound eyes tend to be large and bulbous, and occupy a frontal notch on the carapace. They possess three pairs of large raptorial limbs, and the abdomen bears a battery of small swimming limbs. Their size ranges from ~15 mm to potentially up to 250 mm. Inconclusive claims of thylacocephalans have been reported from the lower lower Cambrian ('' Zhenghecaris''), but later study considered that genus as radiodont or arthropod with uncertain systematic position. The oldest unequivocal fossils are Upper Ordovician and Lower Silurian in age. As a group, the Thylacocephala s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysidacea
The Mysidacea is a group of shrimp-like crustaceans in the superorder Peracarida, comprising the two extant orders Mysida and Lophogastrida Lophogastrida is an Order (biology), order of malacostracan crustaceans in the superorder Peracarida, comprising shrimp-like animals that mostly inhabit the relatively deep pelagic waters of the oceans throughout the world. Most lophogastridan s ... and the prehistoric Pygocephalomorpha. Current data indicate that despite their external similarities, the three orders are not closely related, and the taxon Mysidacea is not used in modern taxonomy. References {{Authority control Malacostraca taxonomy Obsolete arthropod taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |