|
Geothermal Power Stations
Geothermal is related to energy and may refer to: * Geothermal energy, useful energy generated and stored in the Earth * Geothermal activity, the range of natural phenomena at or near the surface, associated with release of the Earth's internal heat. * Earth's internal heat budget, accounting of the flows of energy at and below the surface of the planet's crust * Geothermal gradient, down which heat flows within the Earth * Geothermal exploration, the search for commercially usable geothermal energy Uses of geothermal energy * Earth sheltering, constructing a building into a hill side or Earth berm to reduce heating and cooling requirements * Earth cooling tubes, using ambient Earth temperature to cool and dehumidify air * Geothermal desalination, the production of fresh water using heat energy extracted from underground rocks * Geothermal heating, methods of heating and cooling a building using underground heat * Geothermal power, electricity generated from naturally occurring geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is thermal energy extracted from the crust (geology), crust. It combines energy from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay. Geothermal energy has been exploited as a source of heat and/or electric power for millennia. Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since Roman times. Geothermal power (generation of electricity from geothermal energy), has been used since the 20th century. Unlike wind and solar energy, geothermal plants produce power at a constant rate, without regard to weather conditions. Geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs. Most extraction occurs in areas near tectonic plate boundaries. The cost of generating geothermal power decreased by 25% during the 1980s and 1990s. Technological advances continued to reduce costs and thereby expand the amount of viable resources. In 2021, the US ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Activity
Geothermal activity is a group of natural heat transfer processes, occurring on Earth's surface, caused by the presence of excess heat in the subsurface of the affected area, usually caused by the presence of an igneous intrusion underground. Geothermal activity can manifest itself in a variety of different phenomena, including, among others, elevated surface temperatures, various forms of hydrothermal activity, and the presence of Fumarole, fumaroles that emit hot Volcanic gas, volcanic gases. Background physics Geothermal activity mostly appears in volcanic provinces, where it is fueled by the presence of a magma chamber. In some rare cases it can be caused by Coal-seam fire, underground fires or by large deposits of radioactive elements. Other sources of internal heating can be Planetary differentiation, gravitational differentiation of substances, tidal friction, metamorphism, or phase transitions. The release of heat to the surface occurs either in the form of a conductive h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
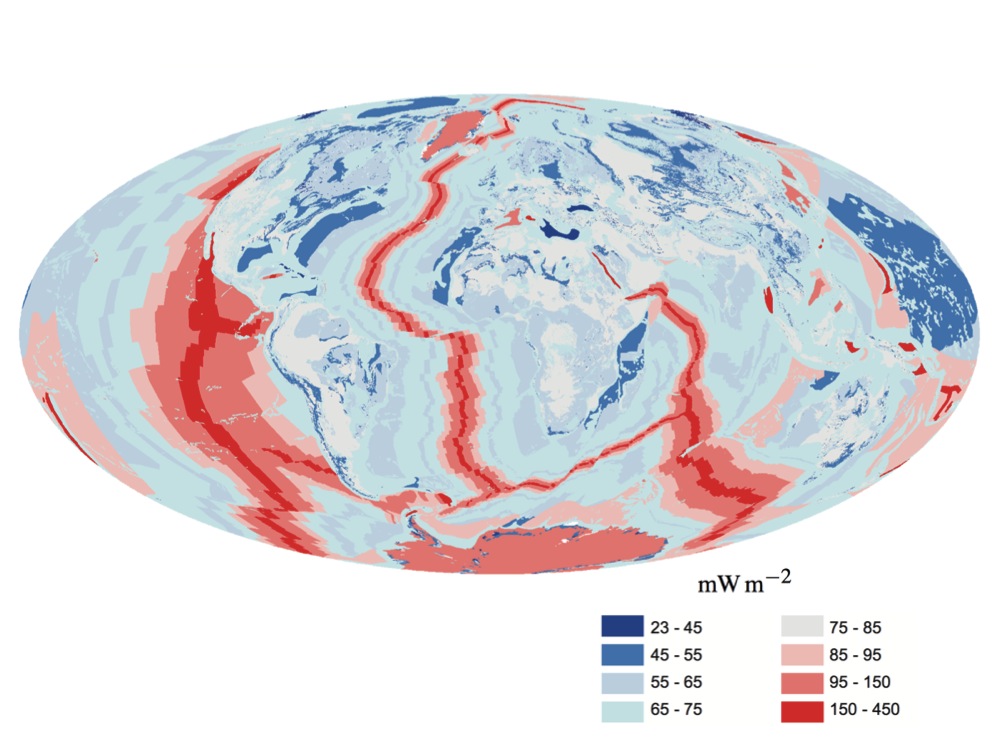
Earth's Internal Heat Budget
Earth's internal heat budget is fundamental to the thermal history of the Earth. The flow of heat from Earth's interior to the surface is estimated at 47±2 terawatts (TW) and comes from two main sources in roughly equal amounts: the ''radiogenic heat'' produced by the radioactive decay of isotopes in the mantle and crust, and the ''primordial heat'' left over from the formation of Earth. Earth's internal heat travels along geothermal gradients and powers most geological processes. It drives mantle convection, plate tectonics, mountain building, rock metamorphism, and volcanism. Convective heat transfer within the planet's high-temperature metallic core is also theorized to sustain a geodynamo which generates Earth's magnetic field. Despite its geological significance, Earth's interior heat contributes only 0.03% of Earth's total energy budget at the surface, which is dominated by 173,000 TW of incoming solar radiation. This external energy source powers most of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
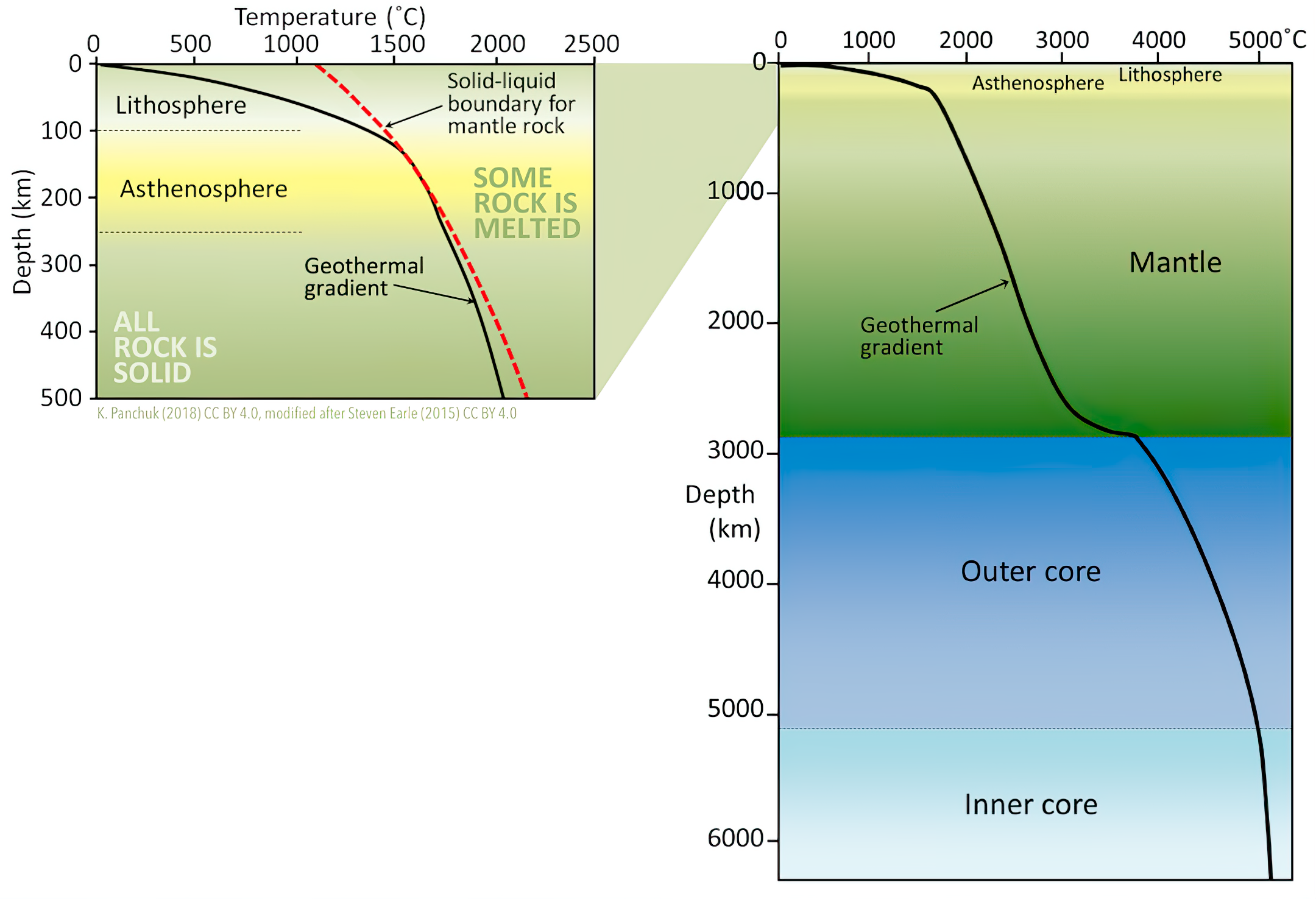
Geothermal Gradient
Geothermal gradient is the rate of change in temperature with respect to increasing depth in Earth's interior. As a general rule, the crust temperature rises with depth due to the heat flow from the much hotter mantle; away from tectonic plate boundaries, temperature rises in about 25–30 °C/km (72–87 °F/mi) of depth near the surface in the continental crust. However, in some cases the temperature may drop with increasing depth, especially near the surface, a phenomenon known as or geothermal gradient. The effects of weather, the Sun, and season only reach a depth of roughly . Strictly speaking, ''geo''-thermal necessarily refers to Earth, but the concept may be applied to other planets. In SI units, the geothermal gradient is expressed as °C/km, K/km, or mK/m. These are all equivalent. Earth's internal heat comes from a combination of residual heat from planetary accretion, heat produced through radioactive decay, latent heat from core crystallization, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
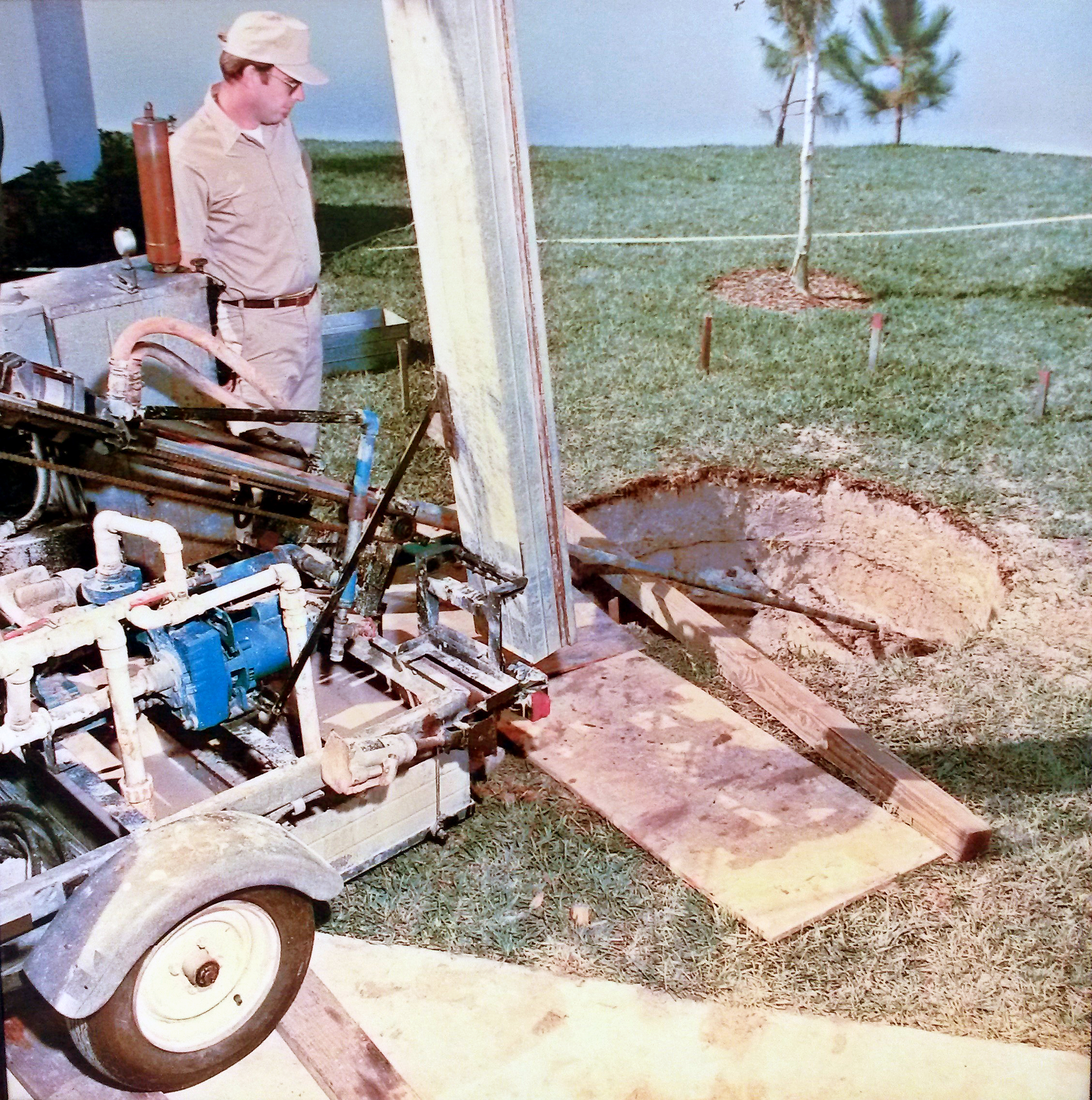
Geothermal Exploration
Geothermal exploration is the exploration of the subsurface in search of viable active geothermal regions with the goal of building a geothermal power plant, where hot fluids drive turbines to create electricity. Exploration methods include a broad range of disciplines including geology, geophysics, geochemistry and engineering. Geothermal regions with adequate heat flow to fuel power plants are found in rift zones, subduction zones and mantle plumes. Hotspot (geology), Hot spots are characterized by four geothermal elements. An active region will have: # Heat Source - Shallow magmatic body, decaying radioactive elements or ambient heat from high pressures # Reservoir - Collection of hot rocks from which heat can be drawn # Geothermal Fluid - Gas, vapor and water found within the reservoir # Recharge Area - Area surrounding the reservoir that rehydrates the geothermal system. Exploration involves not only identifying hot geothermal bodies, but also low-density, cost effective r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Sheltering
An earth shelter, also called an earth house, earth-bermed house, earth-sheltered house, earth-covered house, or underground house, is a structure (usually a house) with earth (soil) against the walls and/or on the roof, or that is entirely buried underground. Earth acts as thermal mass, making it easier to maintain a steady indoor air temperature and therefore reduces energy costs for heating or cooling. Earth sheltering became relatively popular after the mid-1970s, especially among environmentalists. However, the practice has been around for nearly as long as humans have been constructing their own shelters. Definition * "Earth-sheltering is ../nowiki> a generic term with the general meaning: building design in which soil plays an integral part." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Cooling Tubes
A ground-coupled heat exchanger is an underground heat exchanger that can capture heat from and/or dissipate heat to the ground. They use the Earth's near constant subterranean temperature to warm or cool air or other fluids for residential, agricultural or industrial uses. If building air is blown through the heat exchanger for heat recovery ventilation, they are called earth tubes (or Canadian well, Provençal well, Solar chimney, also termed earth cooling tubes, earth warming tubes, earth-air heat exchangers (EAHE or EAHX), air-to-soil heat exchanger, earth channels, earth canals, earth-air tunnel systems, ground tube heat exchanger, hypocausts, subsoil heat exchangers, thermal labyrinths, underground air pipes, and others). Earth tubes are often a viable and economical alternative or supplement to conventional central heating or air conditioning systems since there are no compressors, chemicals or burners and only blowers are required to move the air. These are used for eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Desalination
Geothermal desalination refers to the process of using geothermal energy to power the process of converting salt water to fresh water. The process is considered economically efficient, and while overall environmental impact is uncertain, it has potential to be more environmentally friendly compared to conventional desalination options. Geothermal desalination plants have already been successful in various regions, and there is potential for further development to allow the process to be used in an increased number of water scarce regions. Process explanation Desalination is the process of removing minerals from seawater to convert it into fresh water. Desalination is divided into two categories in terms of processes: processes driven by thermal energy and processes driven by mechanical energy. Geothermal desalination uses geothermal energy as the thermal energy source to drive the desalination process. There are two types of geothermal desalination: direct and indirect. Direct ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Heating
Geothermal heating is the direct use of geothermal energy for some heating applications. Humans have taken advantage of geothermal heat this way since the Paleolithic era. Approximately seventy countries made direct use of a total of 270 PJ of geothermal heating in 2004. As of 2007, 28 GW of geothermal heating capacity is installed around the world, satisfying 0.07% of global primary energy consumption. Thermal efficiency is high since no energy conversion is needed, but capacity factors tend to be low (around 20%) since the heat is mostly needed in the winter. Geothermal energy originates from the heat retained within the Earth since the original formation of the planet, from radioactive decay of minerals, and from solar energy absorbed at the surface. Most high temperature geothermal heat is harvested in regions close to tectonic plate boundaries where volcanic activity rises close to the surface of the Earth. In these areas, ground and groundwater can be found with temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Power
Geothermal power is electricity generation, electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 countries,Geothermal Energy AssociationGeothermal Energy: International Market Update May 2010, p. 4-6. while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries. As of 2019, worldwide geothermal power capacity amounts to 15.4 gigawatts (GW), of which 23.9% (3.68 GW) are installed in the geothermal energy in the United States, United States. International markets grew at an average annual rate of 5 percent over the three years to 2015, and global geothermal power capacity is expected to reach 14.5–17.6 GW by 2020. Based on current geologic knowledge and technology the Geothermal Energy Association (GEA) publicly discloses, the GEA estimates that only 6.9% of total global potential has been tapped so far, while the In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Source Heat Pump
A ground source heat pump (also geothermal heat pump) is a heating/cooling system for buildings that use a type of heat pump to transfer heat to or from the ground, taking advantage of the relative constancy of temperatures of the earth through the seasons. Ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs)or geothermal heat pumps (GHP), as they are commonly termed in North Americaare among the most energy-efficient technologies for providing HVAC and water heating, using less energy than can be achieved by use of resistive electric heaters. Efficiency is given as a coefficient of performance (CoP) which is typically in the range 3-6, meaning that the devices provide 3-6 units of heat for each unit of electricity used. Setup costs are higher than for other heating systems, due to the requirement of installing ground loops over large areas or of drilling bore holes, hence ground source is often installed when new blocks of flats are built. Air-source heat pumps have lower set-up costs but have a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Exchange Geothermal Heat Pump
A direct exchange (DX) geothermal heat pump is a type of ground source heat pump in which refrigerant circulates through copper tubing placed in the ground unlike other ground source heat pumps where refrigerant is restricted to the heat pump itself with a secondary loop in the ground filled with a mixture of water and anti-freeze. The simplicity of the DX designs is that high efficiencies can be reached using a shorter and smaller amount of buried tubing thereby reducing both the footprint and installation cost. Other appellations The technology has many different others names and designations: * Direct exchange geothermal heat pump * DX * Direct Geoexchange heat pumps – used by thAir-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) and is abbreviated DGX * Direct-expansion ground source heat pumps – used bThe American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers(ASHRAE) * Direct geothermal heat pumps * Refrigerant-based geothermal systems * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |