|
Geology Of Cornwall
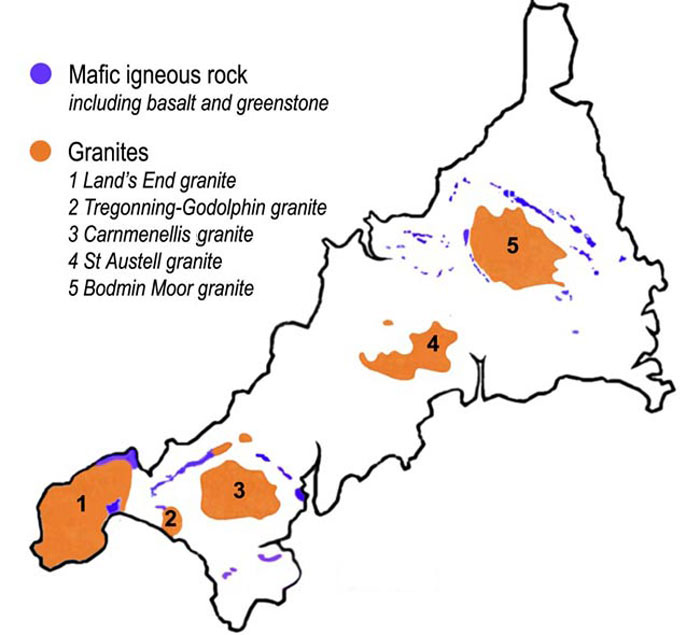
The geology of Cornwall, England, is dominated by its granite backbone, part of the Cornubian batholith, formed during the Variscan orogeny. Around this is an extensive metamorphic aureole (known locally as killas) formed in the mainly Devonian slates that make up most of the rest of the county. There is an area of sandstone and shale of Carboniferous age in the north east, and the Lizard peninsula is formed of a rare section of uplifted oceanic crust. Coasts Cornwall forms the tip of the south-west peninsula of the island Great Britain, and is therefore exposed to the full force of the prevailing winds that blow in from the Atlantic Ocean. The coastline is composed mainly of resistant rocks that give rise in many places to impressive cliffs. The north and south coasts have different characteristics. The north coast is more exposed and therefore has a wilder nature. The prosaically-named ''High Cliff'', between Boscastle and St Gennys, is the highest sheer-drop cliff i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boscastle
Boscastle () is a village and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England, in the civil parish of Forrabury and Minster (where the 2011 Census population was included) . It is south of Bude and northeast of Tintagel. The harbour is a natural inlet protected by two stone harbour walls built in 1584 by Sir Richard Grenville and is the only significant harbour for along the coast. The village extends up the valleys of the River Valency and River Jordan. Heavy rainfall on 16 August 2004 caused extensive damage to the village. Boscastle lies within the Cornwall National Landscape (formerly Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, or AONB). The South West Coast Path passes through the village. History Boscastle was first inhabited by the Bottreaux family around 1080, and the name of the village comes from Bottreaux Castle (pronounced "Botro"), a 12th-century motte-and-bailey fortress, of which few remains survive. The castle, built sometime between 1154 and 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Austell
Saint Austell (, ; ) is a town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, south of Bodmin and west of the border with Devon. At the 2021 Census in the United Kingdom, census it had a population of 20,900. History St Austell was a village centred around the parish church, until the arrival of significant tin mining in the 18th century turned it into a town. St Austell is named after the 6th-century Cornish saint, St Austol, a disciple of St Mewan. In a Vatican manuscript there is a 10th-century list of Cornish parish saints. This includes Austoll, which means that the church and village existed at that time, shortly after 900. St Austell is not mentioned in Domesday Book (1086). However, A. L. Rowse, in his book ''St. Austell: Church, Town, and Parish'', cites records which show a church was dedicated on 9 October 1262 by Bishop Bronescombe, and other records show a church there in 1169, dedicated to "Sanctus Austolus". The current church dates from the 13th–14th centuries, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor () is a granite moorland in north-eastern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous period of geology, geological history. It includes Brown Willy, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough Tor, a slightly lower peak. Many of Cornwall's rivers have their sources here. It has been inhabited since at least the Neolithic era, when early farmers started clearing trees and farming the land. They left their megalithic monuments, hut circles and cairns, and the Bronze Age culture that followed left further cairns, and more stone circles and stone rows. By medieval and modern times, nearly all the forest was gone and livestock rearing predominated. The name Bodmin Moor is relatively recent. An early mention is in the ''Royal Cornwall Gazette'' of 28 November 1812. The upland area was formerly known as Fowey Moor after the River Fowey, which rises within it. Geology Bodmin Moor is one of five granite plutons in Cornwall that make up pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RoughTor
Rough Tor (), or Roughtor, is a tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The site comprises the tor summit and logan stone, a Neolithic tor enclosure, many Bronze Age hut circles, and some contemporary monuments. Toponymy In the 19th century, the hill was known as ''Router,'' and even into the late 20th century, some locals used this pronunciation. Geography Rough Tor is approximately one mile northwest of Brown Willy, Cornwall's highest point, on Bodmin Moor. Its summit is 1313 ft (400m) above mean sea level, making it the second highest point in Cornwall. Both hills are in the civil parish of St Breward and near Camelford. The De Lank River rises nearby and flows between the two hills. Rough Tor and Little Rough Tor are twin summits of a prominent ridge of granite, though there are actually three tors at the site: Showery Tor (Also known as Flat Cap Ned), Little Rough Tor, and Rough Tor. Crowdy Reservoir and the Lowermoor Water Treatment Works are not fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
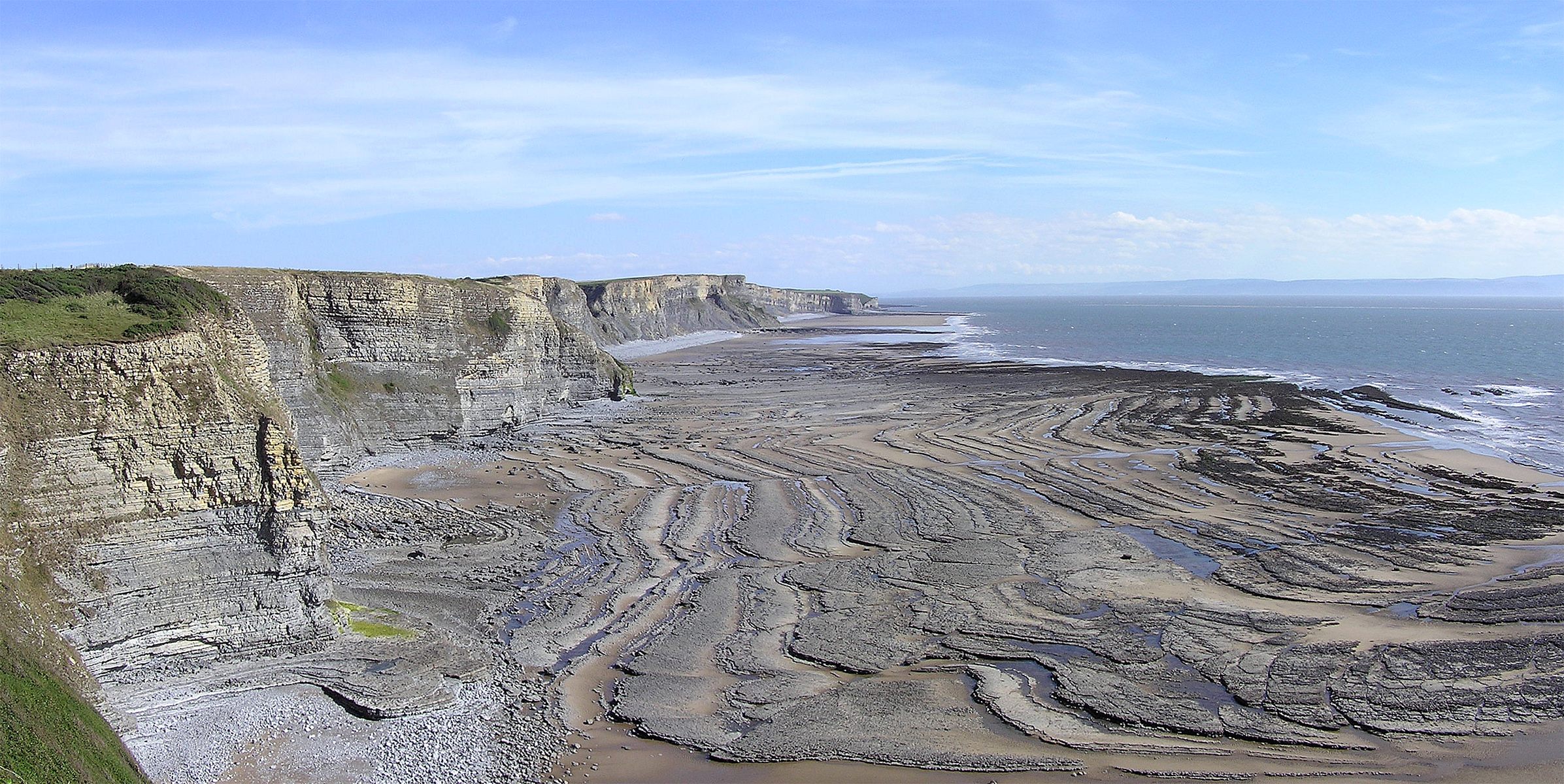
Wave-cut Platform
A wave-cut platform, shore platform, coastal bench, or wave-cut cliff is the narrow flat area often found at the base of a sea cliff or along the shoreline of a lake, bay, or sea that was created by erosion. Wave-cut platforms are often most obvious at low tide when they become visible as huge areas of flat rock. Sometimes the landward side of the platform is covered by sand, forming the beach, and then the platform can only be identified at low tides or when storms move the sand. __TOC__ Formation Wave-cut platforms form when destructive waves hit against the cliff face, causing an undercut between the high and low water marks, mainly as a result of abrasion, corrosion and hydraulic action, creating a wave-cut notch. This notch then enlarges into a cave. The waves undermine this portion until the roof of the cave cannot hold due to the pressure and freeze-thaw or biological weathering acting on it, and collapses, resulting in the cliff retreating landward. The base of the cave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
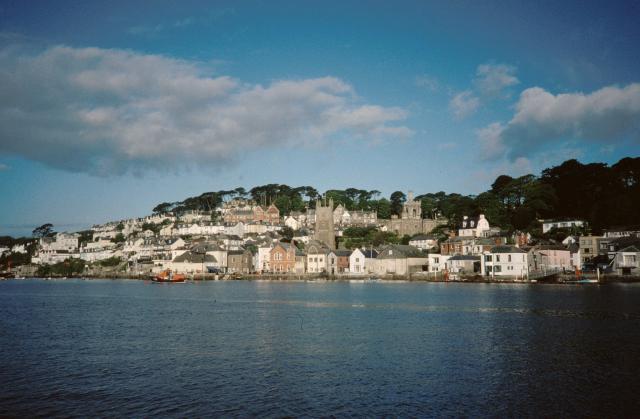
Fowey
Fowey ( ; , meaning ''beech trees'') is a port town and civil parishes in England, civil parish at the mouth of the River Fowey in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town has been in existence since well before the Norman invasion, with the local church first established some time in the 7th century; the estuary of the River Fowey forms a natural harbour which enabled the town to become an important trading centre. Privateers also made use of the sheltered harbourage. The Lostwithiel and Fowey Railway brought China clay here for export. History Early history The Domesday Book survey at the end of the 11th century records manors at Penventinue and Trenant, and a priory was soon established nearby at Tywardreath. the prior granted a charter to people living in Fowey itself. This medieval town ran from a north gate near Boddinick Passage to a south gate at what is now Lostwithiel Street; the town extended a little way up the hillside and was bounded on the other side b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falmouth, Cornwall
Falmouth ( ; ) is a town, civil parish and port on the River Fal on the south coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Falmouth was founded in 1613 by the Killigrew family on a site near the existing Pendennis Castle. It developed as a port on the Carrick Roads harbour, overshadowing the earlier town of Penryn, Cornwall, Penryn. In the 19th century after the arrival of the railways, tourism became important to its economy. In modern times, both industries maintain a presence in Falmouth and the town is also home to the National Maritime Museum Cornwall, a campus of Falmouth University and Falmouth Art Gallery. Etymology The name Falmouth is of English language, English origin, a reference to the town's situation on the mouth (river), mouth of the River Fal. The Cornish language name, or , is of identical meaning. History Early history In 1540, Henry VIII of England, Henry VIII built Pendennis Castle in Falmouth to defend Carrick Roads. The main town of the distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padstow
Padstow (; ) is a town, civil parishes in England, civil parish and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town is situated on the west bank of the River Camel estuary, approximately northwest of Wadebridge, northwest of Bodmin and northeast of Newquay. The population of Padstow civil parish was 3,162 in the United Kingdom Census 2001, 2001 census, reducing to 2,993 at the 2011 census. In addition Padstow (electoral division), an electoral ward with the same name exists but extends as far as Trevose Head. The population for this ward is 4,434. The geology of the low plateau west of Padstow has resulted in such features as Tregudda Gorge where erosion along the faultline has caused sheer cliffs to form; and Marble Cliffs which has alternating dark grey and light grey strata. The Round Hole is a collapsed sea cave. History In English, Padstow was originally named after Æthelstan who was reported by John Leland (antiquary), John Leland to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Camel
The River Camel (, meaning ''crooked river'') is a river in Cornwall, England. It rises on the edge of Bodmin Moor and with its tributaries its catchment area covers much of North Cornwall. The river flows into the eastern Celtic Sea between Stepper Point and Pentire Point having covered about making it the second longest river wholly in Cornwall. The river is tidal upstream to Egloshayle and is popular for sailing, birdwatching and fishing. The name ''Camel'' comes from the Cornish language for 'the crooked one', a reference to its winding course. Historically the river was divided into three named stretches. Heyl (, meaning ''estuary'') was the name for the estuary up to Egloshayle, the River Allen (, meaning ''shining river'') was the stretch between Egloshayle and Trecarne, whilst the Camel was reserved for the stretch of river between its source and Trecarne. Geology and hydrology The River Camel rises on Hendraburnick Down (UK Grid Reference SX135875) on the edge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newquay
Newquay ( ; ) is a town on the north coast in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is a civil parishes in England, civil parish, seaside resort, regional centre for aerospace industries with an airport and a spaceport, and a fishing port on the North Atlantic coast of Cornwall, approximately north of Truro and west of Bodmin. The town is bounded to the south by the River Gannel and its associated salt marsh, and to the north-east by the Porth Valley. The western edge of the town meets the Atlantic at Fistral Bay. The town has been expanding inland (south) since the former fishing village of New Quay began to grow in the second half of the nineteenth century. In 2001, the census recorded a permanent population of 19,562, increasing to 20,342 at the 2011 census and 23,600 in 2021. Recent estimates suggest that the total population for the wider Newquay area (Newquay and St Columb Community Network Area) was 27,682 in 2017, projected to rise to 33,463 by 2025. History Prehis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perranporth
Perranporth () is a seaside resort town on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is 2.1 miles east of the St Agnes Heritage Coastline, and around 7 miles south-west of Newquay. Perranporth and its long beach face the Atlantic Ocean.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 204 ''Truro & Falmouth'' It has a population of 3,066, and is the largest settlement in the civil parish of Perranzabuloe. It has an electoral ward in its own name whose population was 4,270 in the 2011 census. The town's modern name comes from ''Porth Peran'', the Cornish for The Cove of Saint Piran who is the patron saint of Cornwall. He founded the St Piran's Oratory on Penhale Sands, near Perranporth, in the 7th century. The Oratory was buried under sand dunes for many centuries, being unearthed in the 19th century (reference required). History John Woodward (1688-1728) recorded that iron ore was mined from a large vein on the beach. In the 1860s ore was moved up the cliff by a 'pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |