|
Genocide Perpetrators
In genocide studies, perpetrators, victims, and bystanders is an evolving typology for classifying the participants and observers of a genocide. The typology was first proposed by Raul Hilberg in the 1992 book '' Perpetrators Victims Bystanders: Jewish Catastrophe 1933–1945''. Anthropologist Alexander Hinton credits work on this theory with sparking widespread public intolerance of mass violence, calling it a "proliferation of a post-cold war human rights regime that demanded action in response to atrocity and accountability for culprits.". The triad is also used in studying the psychology of genocide. It has become a key element of scholarship on genocide, with subsequent researchers refining the concept and applying it to new fields. Initial analyses of atrocities such as the Holocaust discussed these events simply as violence by perpetrators against victims. Scholars added the category of "bystander" to include people who impact, and are impacted by, mass violence but who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bystander Intervention
Bystander intervention is a type of training used in post-secondary education institutions to prevent sexual assault or rape, binge drinking and harassment and unwanted comments of racist, homophobic, or transphobic nature. A bystander is a person who is present at an event, party, or other setting who notices a problematic situation, such as a someone making sexual advances on a drunk person. The bystander then takes on personal responsibility and takes action to intervene, with the goal of preventing the situation from escalating. The bystander who is intervening has several options, including distracting either of the people, getting help from others, checking in later, or directly intervening. There are risks to bystander intervention; it can lead to fights, it can ruin the mood for the people who were "intervened" into, and it can lead to confrontations. Bystander intervention may also be called "bystander education", because the model is based on a system of educating train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploitation (other)
{{disambig ...
Exploitation may refer to: *Exploitation of natural resources * Exploitation of Animals *Exploitation of labour **Forced labour *Exploitation colonialism *Slavery **Sexual slavery and other forms *Oppression *Psychological manipulation In arts and entertainment * Exploitation fiction *Exploitation film As a proper name * ''Exploitation'' (film), a 2012 film See also * * Exploit (other) * Overexploitation Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimes Against Humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as foreign nationals.Margaret M. DeGuzma"Crimes Against Humanity"''Research Handbook on International Criminal Law'', Bartram S. Brown, ed., Edgar Elgar Publishing, 2011. Together with war crimes, genocide, and the crime of aggression, crimes against humanity are one of the core crimes of international criminal law and, like other crimes against international law, have no temporal or jurisdictional limitations on prosecution (where universal jurisdiction is recognized). The first prosecution for crimes against humanity took place during the Nuremberg trials against defeated leaders of Nazi Germany. Crimes against humanity have been prosecuted by other international courts (such as the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugosl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abuse
Abuse is the act of improper usage or treatment of a person or thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, crimes, or other types of aggression. To these descriptions, one can also add the Kantian notion of the wrongness of using another human being as means to an end rather than as ends in themselves. Some sources describe abuse as "socially constructed", which means there may be more or less recognition of the suffering of a victim at different times and societies. Types and contexts of abuse Abuse of authority Abuse of authority includes harassment, interference, pressure, and inappropriate requests or favors. Abuse of corpse Necrophilia involves possessing a physical attraction to dead bodies that may led to acting upon sexual urges. As corpses are dead and cannot give consent, any manipulation, removal of parts, mutilation, or sexua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, religion, history or social treatment. Ethnicities may also have a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, with some groups having mixed genetic ancestry. ''Ethnicity'' is sometimes used interchangeably with ''nation'', particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism. It is also used interchangeably with '' race'' although not all ethnicities identify as racial groups. By way of assimilation, acculturation, amalgamation, language shift, intermarriage, adoption and religious conversion, individuals or groups may over time shift from one ethnic group to another. Ethnic groups may be divided into subgroups or tribes, which over time may become separate ethnic groups themselves due to endogamy or physical isolation from the parent gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistance Movement
A resistance movement is an organized group of people that tries to resist or try to overthrow a government or an occupying power, causing disruption and unrest in civil order and stability. Such a movement may seek to achieve its goals through either the use of violent or nonviolent resistance (sometimes called civil resistance), or the use of force, whether armed or unarmed. In many cases, as for example in the United States during the American Revolution, or in Norwegian resistance movement, Norway in the Second World War, a resistance movement may employ both violent and non-violent methods, usually operating under different organizations and acting in different phases or geographical areas within a country. Etymology The Oxford English Dictionary records use of the word "resistance" in the sense of organised opposition to an invader from 1862. The modern usage of the term "Resistance" became widespread from the self-designation of many movements during World War II, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
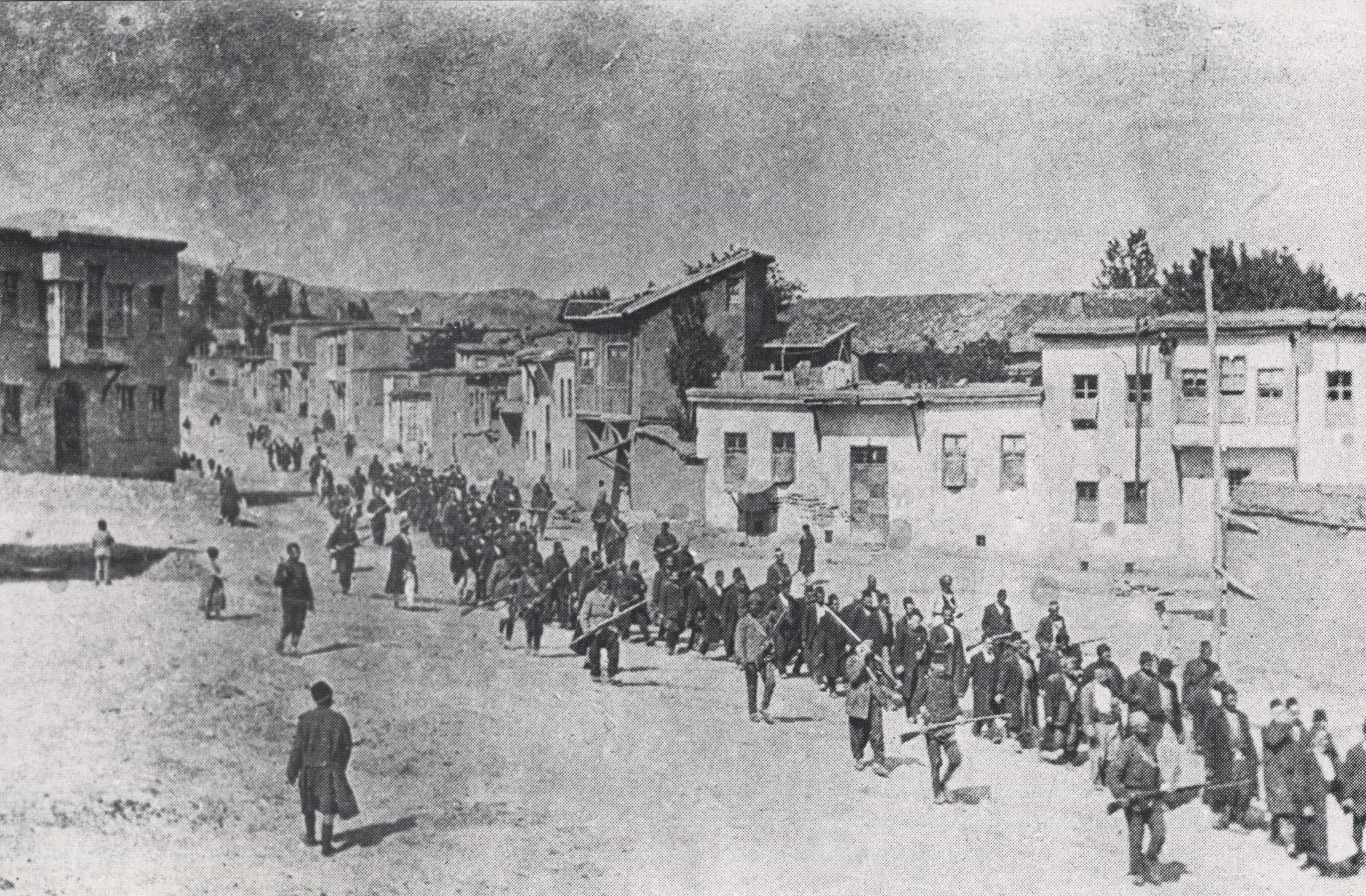
Genocide Definitions
Genocide definitions include many scholarly and international legal definitions of genocide, a word coined by Raphael Lemkin in 1944.Oxford English Dictionary "Genocide" citing Raphael Lemkin ''Axis Rule in Occupied Europe'' ix. 79 The word is a compound of the ancient Greek word (, 'genus', or 'kind') and the Latin word ("kill"). While there are various definitions of the term, almost all international bodies of law officially adjudicate the crime of genocide pursuant to the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide (CPPCG). This and other definitions are generally regarded by the majority of genocide scholars to have an " intent to destroy" as a requirement for any act to be labelled genocide; there is also growing agreement on the inclusion of the physical destruction criterion. Writing in 1998, Kurt Jonassohn and Karin Björnson stated that the CPPCG was a legal instrument resulting from a diplomatic compromise; the wording of the treaty is not in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
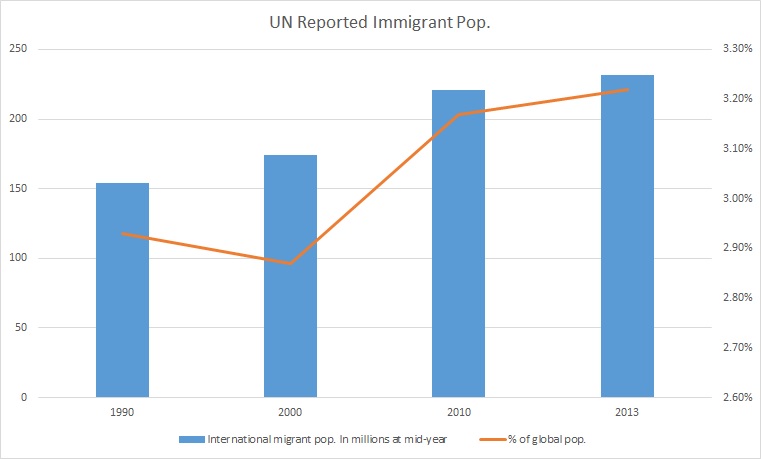
Assimilation Of Immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-born persons in criminal justice, business, the economy, ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Genocide
Cultural genocide or culturicide is a concept first described by Polish lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944, in the same book that coined the term ''genocide''. The destruction of culture was a central component in Lemkin's formulation of genocide. The precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, and the United Nations does not include it in the definition of ''genocide'' used in the 1948 Genocide Convention. The Armenian Genocide Museum defines culturicide as "acts and measures undertaken to destroy nations' or ethnic groups' culture through spiritual, national, and cultural destruction", which appears to be essentially the same as ethnocide. Some ethnologists, such as Robert Jaulin, use the term '' ethnocide'' as a substitute for ''cultural genocide'', although this usage has been criticized as risking the confusion between ethnicity and culture. Cultural genocide and ethnocide have in the past been utilized in distinct contexts. Cultural genocide without et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Other (philosophy)
In philosophy, the Other is a fundamental concept referring to anyone or anything perceived as distinct or different from oneself. This distinction is crucial for understanding how individuals construct their own identities, as the encounter with "otherness" helps define the boundaries of the "self."''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'' (1995) p. 673. In Phenomenology (philosophy), phenomenology, the Other plays a particularly important role in this self-formation, acting as a kind of mirror against which the self is reflected and understood. The Other is not simply a neutral observer but an active participant in shaping the individual's self-image. This includes the idea of the "Constitutive Other," which refers to the internal relationship between a person's essential nature (personality) and their physical embodiment (body), reflecting the interplay of internal differences within the self. Beyond this individual level, the concept of "the Other" extends to broader social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Identity (social Science)
Identity is the set of qualities, beliefs, personality traits, appearance, or expressions that characterize a person or a social group, group. Identity emerges during childhood as children start to comprehend their self-concept, and it remains a consistent aspect throughout different stages of life. Personal identity, Identity is shaped by social and cultural factors and how others perceive and acknowledge one's characteristics. The etymology of the term "identity" from the Latin noun ''identitas'' emphasizes an individual's "sameness with others". Identity encompasses various aspects such as occupational, Religion, religious, national, Ethnicity, ethnic or racial, Gender identity, gender, educational, generational, and political identities, among others. Identity serves multiple functions, acting as a "self-regulatory structure" that provides meaning, direction, and a sense of self-control. It fosters internal harmony and serves as a behavioral compass, enabling individuals to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |