|
Flair Records Artists
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is a magnetic resonance imaging sequence with an inversion recovery set to null fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) effects on the image, so as to bring out the periventricular hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) plaques. It was invented by Graeme Bydder, Joseph Hajnal, and Ian Young in the early 1990s. FLAIR can be used with both three-dimensional imaging (3D FLAIR) or two dimensional imaging (2D FLAIR). Technique By carefully choosing the inversion time (TI), the signal from any particular tissue can be nulled. The appropriate TI depends on the tissue via the formula: :\textrm = \ln(2) \cdot T_1,\, in other words, one should typically use a TI of around 70% of the ''T1'' value. In the case of CSF suppression, one aims for ''T1''-weighted images, which prioritize the signal of fat over that of water. Therefore, if the long TI (inversion time) is adjusted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLAIR MRI Of Meningitis
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is a MRI sequence, magnetic resonance imaging sequence with an inversion recovery set to null fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) effects on the image, so as to bring out the periventricular Hyperintensity, hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) plaques. It was invented by Graeme Bydder, Joseph Hajnal, and Ian Young in the early 1990s. FLAIR can be used with both three-dimensional imaging (3D FLAIR) or two dimensional imaging (2D FLAIR). Technique By carefully choosing the inversion time (TI), the signal from any particular tissue can be nulled. The appropriate TI depends on the tissue via the formula: :\textrm = \ln(2) \cdot T_1,\, in other words, one should typically use a TI of around 70% of the Spin-lattice relaxation time, ''T1'' value. In the case of CSF suppression, one aims for Spin-lattice relaxation time, ''T1''-weighted images, which prioritize the signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
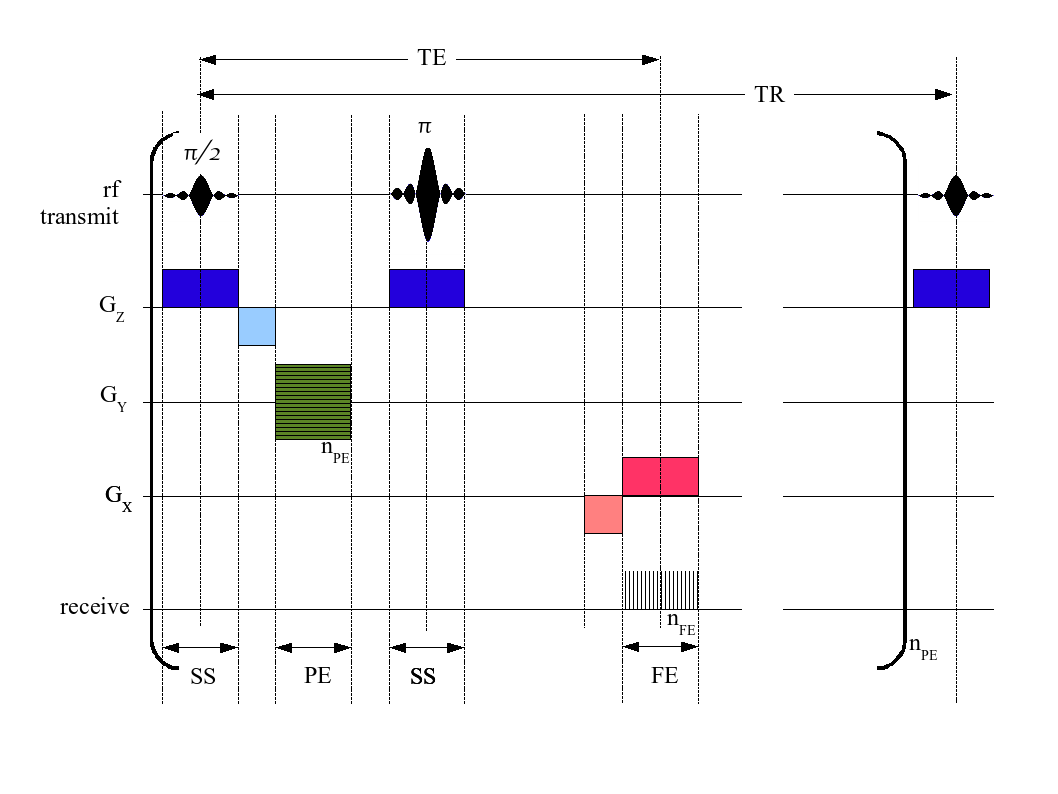
MRI Sequence
An MRI pulse sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance. A multiparametric MRI is a combination of two or more sequences, and/or including Magnetic resonance imaging#Other specialized configurations, other specialized MRI configurations such as In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy, spectroscopy. Spin echo T1 and T2 Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent relaxation processes of T1 (Spin–lattice relaxation, spin-lattice; that is, magnetization in the same direction as the static magnetic field) and T2 (Spin-spin relaxation time, spin-spin; transverse to the static magnetic field). To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characteriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversion Recovery
Inversion recovery is a magnetic resonance imaging sequence that provides high contrast between tissue and lesion. It can be used to provide high T1 weighted image, high T2 weighted image, and to suppress the signals from fat, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is an inversion-recovery pulse sequence used to nullify the signal from fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid so as to bring out periventricular hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis plaques. By carefully choosing the inversion time TI (the time between the inversion and excitation pulses), the signal from any particular tissue can be suppressed. Turbo inversion recovery magnitude Turbo inversion recovery magnitude (TIRM) measures only the magnitude of a turbo spin echo after a preceding inversion pulse, thus is phase insensitive. TIRM is superior in the assessment of osteomyeliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain. CSF is mostly produced by specialized Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. It is also produced by ependymal cells in the lining of the ventricles. In humans, there is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperintensity
A hyperintensity or T2 hyperintensity is an area of high intensity on types of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the brain of a human or of another mammal that reflect lesions produced largely by demyelination and axonal loss. These small regions of high intensity are observed on T2 weighted MRI images (typically created using 3D FLAIR) within cerebral white matter (white matter lesions, white matter hyperintensities or WMH) or subcortical gray matter (gray matter hyperintensities or GMH). The volume and frequency is strongly associated with increasing age. They are also seen in a number of neurological disorders and psychiatric illnesses. For example, deep white matter hyperintensities are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to occur in bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder than control subjects. WMH volume, calculated as a potential diagnostic measure, has been shown to correlate to certain cognitive factors. Hyperintensities appear as "bright signals" (bright areas) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graeme Bydder
Graham or Graeme may refer to: People * Graham (given name), an English-language given name * Graham (surname), an English-language surname * Graeme (surname), an English-language surname * Graham (musician) (born 1979), Burmese singer * Clan Graham, a Scottish clan * George Graham (clockmaker), an English clockmaker, inventor, and geophysicist * Graham baronets Fictional characters * Graham Aker, in the anime ''Gundam 00'' * Project Graham, what a human would look like to survive a car crash * Graham, the head of the royal in bridge incidents ''King's Quest'' series of video games Places Canada * Graham, Sudbury District, Ontario * Graham Island, part of the Charlotte Island group in British Columbia * Graham Island (Nunavut), Arctic island in Nunavut United States * Graham, Alabama * Graham, Arizona * Graham, Florida * Graham, Georgia * Graham, Kentucky * Graham, Missouri * Graham, North Carolina * Graham, Oklahoma * Graham, Texas * Graham, Washington Elsewhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System Disease
Central nervous system diseases or central nervous system disorders are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS). These disorders may be caused by such things as infection, injury, blood clots, age related degeneration, cancer, autoimmune disfunction, and birth defects. The symptoms vary widely, as do the treatments. Central nervous system tumors are the most common forms of pediatric cancer. Brain tumors are the most frequent and have the highest mortality. Some disorders, such as substance addiction, autism, and ADHD may be regarded as CNS disorders, though the classifications are not without dispute. Signs and symptoms Every disease has different signs and symptoms. Some of them are persistent headache; pain in the face, back, arms, or legs; an inability to concentrate; loss of feeling; memory loss; loss of muscle strength; tremors; seizures; increased reflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacunar Stroke
Lacunar stroke or lacunar cerebral infarct (LACI) is the most common type of ischemic stroke, resulting from the Vascular occlusion, occlusion of small penetrating artery, arteries that provide blood to the brain's deep structures. Patients who present with symptoms of a lacunar stroke, but who have not yet had diagnostic imaging performed, may be described as having lacunar stroke syndrome (LACS). Much of the current knowledge of lacunar strokes comes from C. Miller Fisher's cadaver dissections of post-mortem stroke patients. He observed "lacunae" (empty spaces) in the deep brain structures after occlusion of 200–800 μm penetrating arteries and connected them with five classic syndromes. These syndromes are still noted today, though lacunar infarcts are diagnosed based on clinical judgment and radiology, radiologic imaging. Signs and symptoms Each of the five classical lacunar syndromes has a relatively distinct symptom complex. Symptoms may occur suddenly, progressiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit signals, resulting in a range of signs and symptoms, including physical, cognitive disability, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. Symptoms include double vision, vision loss, eye pain, muscle weakness, and loss of Sensation (psychology), sensation or coordination. MS takes several forms, with new symptoms either occurring in isolated attacks (relapsing forms) or building up over time (progressive forms). In relapsing forms of MS, symptoms may disappear completely between attacks, although some permanent neurological problems often remain, especially as the disease advances. In progressive forms of MS, bodily function slowly deteriorates once symptoms manifest and will steadily worsen if left untreated. While its cause is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid (brain), arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the human brain, brain. Symptoms may include a thunderclap headache, severe headache of rapid onset, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, fever, weakness, numbness, and sometimes seizures. Neck stiffness or neck pain are also relatively common. In about a quarter of people a small bleed with resolving symptoms occurs within a month of a larger bleed. SAH may occur as a result of a head injury or spontaneously, usually from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Risk factors for spontaneous cases include high blood pressure, smoking, family history, alcoholism, and cocaine use. Generally, the diagnosis can be determined by a computed tomography, CT scan of the head if done within six hours of symptom onset. Occasionally, a lumbar puncture is also required. After confirmation further tests are usually performed to determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |