|
Fictional Characters From Illinois
Fiction is any creative work, chiefly any narrative work, portraying individuals, events, or places that are imaginary or in ways that are imaginary. Fictional portrayals are thus inconsistent with fact, history, or plausibility. In a traditional narrow sense, fiction refers to written narratives in prose often specifically novels, novellas, and short stories. More broadly, however, fiction encompasses imaginary narratives expressed in any medium, including not just writings but also live theatrical performances, films, television programs, radio dramas, comics, role-playing games, and video games. Definition and theory Typically, the fictionality of a work is publicly expressed, so the audience expects a work of fiction to deviate to a greater or lesser degree from the real world, rather than presenting for instance only factually accurate portrayals or characters who are actual people. Because fiction is generally understood as not adhering to the real world, the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alice Par John Tenniel 25
Alice may refer to: * Alice (name), most often a feminine given name, but also used as a surname Literature * Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland), Alice (''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''), a character in books by Lewis Carroll * Alice (novel series), ''Alice'' series, children's and teen books by Phyllis Reynolds Naylor * Alice (Hermann book), ''Alice'' (Hermann book), a 2009 short story collection by Judith Hermann Computers * Alice (computer chip), a graphics engine chip in the Amiga computer in 1992 * Alice (programming language), a functional programming language designed by the Programming Systems Lab at Saarland University * Alice (software), an object-oriented programming language and IDE developed at Carnegie Mellon * Alice (Microsoft), an AI project at Microsoft for improving decision-making in economics * Alice mobile robot * Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity, an open-source chatterbot * Matra Alice, a home micro-computer marketed in France * Alice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
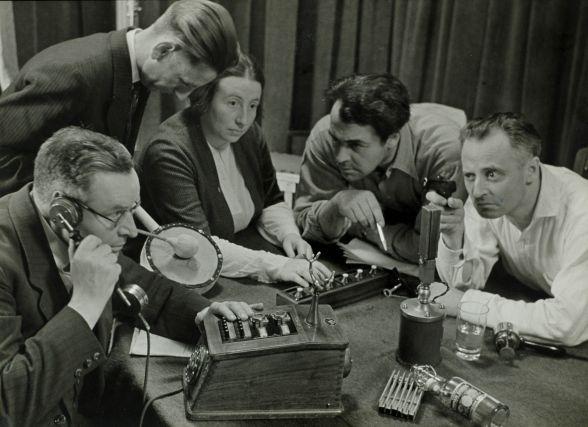
Radio Dramas
Radio drama (or audio drama, audio play, radio play, radio theatre, or audio theatre) is a dramatised, purely acoustic performance. With no visual component, radio drama depends on dialogue, music and sound effects to help the listener imagine the characters and story: "It is auditory in the physical dimension but equally powerful as a visual force in the psychological dimension." Radio drama includes plays specifically written for radio, docudrama, dramatised works of fiction, as well as plays originally written for the theatre, including musical theatre, and opera. Radio drama achieved widespread popularity within a decade of its initial development in the 1920s. By the 1940s, it was a leading international popular entertainment. With the advent of television in the 1950s, radio drama began losing its audience. However, it remains popular in much of the world. Recordings of OTR ( old-time radio) survive today in the audio archives of collectors, libraries and museums, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verisimilitude (narrative)
Verisimilitude () is the "lifelikeness" or believability of a work of fiction. The word comes from meaning truth and ''similis'' meaning similar. Language philosopher Steve Neale distinguishes between two types: cultural verisimilitude, meaning plausibility of the fictional work within the cultural and/or historical context of the real world, outside of the work; and generic verisimilitude, meaning plausibility of a fictional work within the bounds of its own genre (so that, for example, characters regularly singing about their feelings is a believable action within the fictional universe of a musical). Original roots Verisimilitude has its roots in both the Platonic and Aristotelian dramatic theory of mimesis, the imitation or representation of nature. For a piece of art to hold significance or persuasion for an audience, according to Plato and Aristotle, it must have grounding in reality. This idea laid the foundation for the evolution of mimesis into verisimilitude in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wood (critic)
James Douglas Graham Wood (born 1 November 1965) is an English literary critic, essayist and novelist. Wood was ''The Guardian''s chief literary critic between 1992 and 1995. He was a senior editor at '' The New Republic'' between 1995 and 2007. , he is Professor of the Practice of Literary Criticism at Harvard University and a staff writer at '' The New Yorker''. Early life and education James Wood was born in Durham, England, to Dennis William Wood (born 1928), a Dagenham-born minister and professor of zoology at Durham University, and Sheila Graham Wood, née Lillia, a schoolteacher from Scotland. Wood was raised in Durham in an evangelical wing of the Church of England, an environment he describes as austere and serious. He was educated at Durham Chorister School (on a music scholarship) and at Eton College (with the support of a bursary based on his parents' "demonstrated financial need"; his older brother attended Eton as a King's Scholar). He read English Litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worldbuilding
Worldbuilding is the process of constructing an imaginary world or setting (narrative), setting, sometimes associated with a fictional universe. Developing the world with coherent qualities such as a history, geography, culture and ecology is a key task for many science fiction or fantasy writers. Worldbuilding often involves the Fantasy map, creation of geography, a backstory, flora, fauna, inhabitants, technology, and often if writing speculative fiction, different peoples. This may include social norms, social customs as well as invented languages (often called ''conlangs'') for the world. The world could encompass different planets spanning vast distances of space or be limited in scope to a single small village. Worldbuilding exists in novels, tabletop role-playing games, and visual media such as film, films, video games, and comics. Prior to 1900, most worldbuilding was conducted by novelists, who could leave imagination of the fictional setting in part to the reader. Some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fictional Universe
A fictional universe, also known as an imagined universe or a constructed universe, is the internally consistent fictional setting used in a narrative or a work of art. This concept is most commonly associated with works of fantasy and science fiction, and can be found in various forms such as novels, comics, films, television shows, video games, and other creative works. In science fiction, a fictional universe may be a remote alien planet or galaxy with little apparent relationship to the real world (as in '' Star Wars''). In fantasy, it may be a greatly fictionalized or invented version of Earth's distant past or future (as in ''The Lord of the Rings''). Fictional continuity In a 1970 article in '' CAPA-alpha'', comics historian Don Markstein defined the fictional ''universe'' as meant to clarify the concept of fictional continuities. According to the criteria he imagined: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre Criticism
Theatre criticism is a genre of arts criticism, and the act of writing or speaking about the performing arts such as a play or opera. Theatre criticism is distinct from drama criticism, as the latter is a division of literary criticism whereas the former is a critique of the theatrical performance. Dramas or plays as long as they stay in the print form remain a part of literature. They become a part of the performing arts as soon as the written words of the drama are transformed into performance on the stage or any arena suitable for viewers to see. So the literary craft gives birth to a stage production. Likewise a criticism of a written play has a different character from that of a theatre performance. Criticism vs review There is a distinctive dissimilarity between theatre criticism and a theatre review. Both of them deal with the dramatic arts as they are performed. But they are done in different ways and for different purposes. Both have strong rationalities to support the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Criticism
Film criticism is the analysis and evaluation of films and the film medium. In general, film criticism can be divided into two categories: Academic criticism by film studies, film scholars, who study the composition of film theory and publish their findings and essays in books and journals, and general Journalism, journalistic criticism that appears regularly in press newspapers, magazines and other popular mass-media outlets. Academic film criticism rarely takes the form of a review; instead it is more likely to analyse the film and its place in the history of its genre, the industry and History of film, film history as a whole. Film criticism is also labeled as a type of writing that perceives films as possible achievements and wishes to convey their differences, as well as the films being made in a level of quality that is satisfactory or unsatisfactory. Film criticism is also associated with the journalistic type of criticism, which is grounded in the media's effects being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Criticism
A genre of arts criticism, literary criticism or literary studies is the study, evaluation, and interpretation of literature. Modern literary criticism is often influenced by literary theory, which is the philosophical analysis of literature's goals and methods. Although the two activities are closely related, literary critics are not always, and have not always been, theorists. Whether or not literary criticism should be considered a separate field of inquiry from literary theory is a matter of some controversy. For example, ''The Johns Hopkins Guide to Literary Theory and Criticism'' draws no distinction between literary theory and literary criticism, and almost always uses the terms together to describe the same concept. Some critics consider literary criticism a practical application of literary theory, because criticism always deals directly with particular literary works, while theory may be more general or abstract. Literary criticism is often published in essay or book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Theory
Literary theory is the systematic study of the nature of literature and of the methods for literary analysis. Culler 1997, p.1 Since the 19th century, literary scholarship includes literary theory and considerations of intellectual history, moral philosophy, social philosophy, and interdisciplinary themes relevant to how people interpret meaning. In the humanities in modern academia, the latter style of literary scholarship is an offshoot of post-structuralism. Searle, John. (1990)"The Storm Over the University" ''The New York Review of Books'', December 6, 1990. Consequently, the word ''theory'' became an umbrella term for scholarly approaches to reading texts, some of which are informed by strands of semiotics, cultural studies, philosophy of language, and continental philosophy, often witnessed within Western canon along with some postmodernist theory. History The practice of literary theory became a profession in the 20th century, but it has historical roots that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetic Interpretation
In the philosophy of art, an interpretation is an explanation of the meaning of a work of art.} An aesthetic interpretation expresses a particular emotional or experiential understanding most often used in reference to a poem or piece of literature, and may also apply to a work of visual art or performance. Aims of interpretation Readers may approach reading a text from different starting points. A student assigned to interpret a poem for class comes at reading differently from someone on the beach reading a novel for escapist pleasure. "Interpretation" implies the conscious task of making sense out of a piece of writing that may not be clear at first glance or that may reward deeper reading even if it at first appears perfectly clear. The beach reader will probably not need to interpret what she or he reads, but the student will. Professor Louise Rosenblatt, a specialist in the study of the reading process, distinguished between two reading ''stances'' that occupy opposite ends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theme (narrative)
In contemporary literary studies, a theme is a central topic, subject, or message within a narrative. Themes can be divided into two categories: a work's ''thematic concept'' is what readers "think the work is about" and its ''thematic statement'' being "what the work says about the subject". The most common contemporary understanding of theme is an idea or point that is central to a story, which can often be summed in a single abstract noun (for example, love, death, betrayal, patriotism, or parenthood) or noun phrase (for example, coming of age, grief during wartime, or the importance of community). Typical examples of themes of this type are conflict between the individual and society; coming of age; humans in conflict with technology; nostalgia; and the dangers of unchecked ambition. A theme may be exemplified by the actions, utterances, or thoughts of a character in a novel. An example of this would be the thematic idea of loneliness in John Steinbeck's '' Of Mice and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |