|
Explosive Detection
Explosive detection is a non-destructive inspection process to determine whether a container contains explosive material. Explosive detection is commonly used at airports, ports and for border control. Detection tools Colorimetrics & automated colorimetrics The use of colorimetric test kits for explosive detection is one of the most simple methods for officers, and widely used method for the detection of explosives. Colorimetric detection of explosives involves applying a chemical reagent to an unknown material or sample and observing a color reaction. Common color reactions are known and indicate to the user if there is an explosive material present and in many cases the group of explosives from which the material is derived. The major groups of explosives are nitroaromatic, nitrate ester, and nitramine explosives, as well as inorganic nitrate-based explosives. Other groups include chlorates and peroxides which are not nitro based explosives. Since explosives usually contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Detection Dog, CBP
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An explosive charge is a measured quantity of explosive material, which may either be composed solely of one ingredient or be a mixture containing at least two substances. The potential energy stored in an explosive material may, for example, be: * chemical energy, such as nitroglycerin or Dust explosion, grain dust * pressure, pressurized gas compressor, gas, such as a gas cylinder, aerosol can, or boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion * nuclear weapon, nuclear energy, such as in the fissile isotopes uranium-235 and plutonium-239 Explosive materials may be categorized by the speed at which they expand. Materials that detonate (the front of the chemical reaction moves faster through the material than the speed of sound) are said to be "high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dodd, Mead & Co
Dodd, Mead and Company was one of the pioneer publishing houses of the United States, based in New York City. Under several names, the firm operated from 1839 until 1990. History Origins In 1839, Moses Woodruff Dodd (1813–1899) and John S. Taylor, at that time a leading publisher in New York, formed the company of Taylor and Dodd as a publisher of religious books. In 1840, Dodd bought out Taylor and renamed the company as M.W. Dodd. Frank Howard Dodd (1844–1916) joined his father in business in 1859 and became increasingly involved in the publishing company's operation. With the retirement of founder Moses Dodd in 1870, control passed to his son Frank Howard Dodd, who joined in partnership with his cousin Edward S. Mead (1847–1894), and the company was reorganized as Dodd and Mead. In 1876, Bleecker Van Wagenen became a member of the firm and the name was changed to Dodd, Mead and Company. Tebbel, John, ''Between Covers: The Rise and Transformation of Book Publishin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for Separation process, separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without Chemical decomposition, decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an Reactivity (chemistry), unreactive gas such as helium, arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
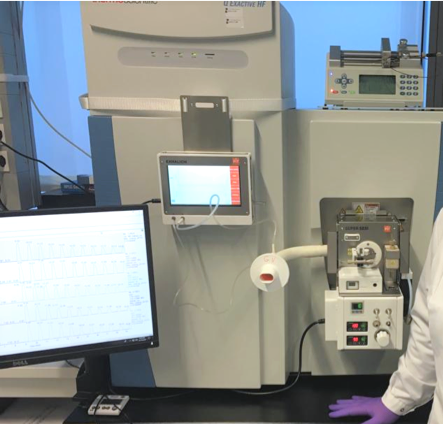
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionization, ionized, for example by bombarding it with a Electron ionization, beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Mobility Spectrometry
Ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) It is a method of conducting analytical research that separates and identifies ionized molecules present in the gas phase based on the mobility of the molecules in a carrier buffer gas. Even though it is used extensively for military or security objectives, such as detecting drugs and explosives, the technology also has many applications in laboratory analysis, including studying small and big biomolecules. IMS instruments are extremely sensitive stand-alone devices, but are often coupled with mass spectrometry, gas chromatography or high-performance liquid chromatography in order to achieve a multi-dimensional separation. They come in various sizes, ranging from a few millimetres to several metres depending on the specific application, and are capable of operating under a broad range of conditions. IMS instruments such as microscale high-field asymmetric-waveform ion-mobility spectrometry, high-field asymmetric-waveform ion mobility spectrometry ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service has over 5,500 journalists working across its output including in 50 foreign news bureaus where more than 250 foreign correspondents are stationed. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscentinel
Inscentinel was a British firm based at Rothamsted Experimental Station in Hertfordshire. They specialise in the development of insect olfaction technologies for the detection of trace chemicals, specifically Hymenoptera training techniques and technologies. History Inscentinel was founded in 2000, and was a spin-out resulting from a joint venture project between Unilever and Rothamsted Research. The firm was backed with venture capital, funding from the British Government, and other investment. Technology Conventionally, detection of chemicals at low vapour pressures has been based on mass spectrometry, gas chromatography and the use of sniffer dogs. Insect olfaction is sensitive down to parts per trillion and the use of insects to conduct searches for illegal drugs, and explosives—particularly in security applications such as demining—is envisaged. The technology has been tested by QinetiQ for Geneva International Centre for Humanitarian Demining. Potential health uses ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanning, 3D scanner, 3D point clouds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honey Bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to mainland Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosmopolitan distribution of honey bees, introducing multiple subspecies into South America (early 16th century), North America (early 17th century), and Australia (early 19th century). Honey bees are known for their construction of perennial colonial nests from wax, the large size of their colonies, and surplus production and storage of honey, distinguishing their hives as a prized foraging target of many animals, including honey badgers, bears and human hunter-gatherers. Only 8 surviving species of honey bees are recognized, with a total of 43 subspecies, though historically 7 to 11 species are recognized. Honey bees represent only a small fraction of the roughly 20,000 known species of bees. The best-known honey bee is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry (journal)
''Analytical Chemistry'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published since 1929 by the American Chemical Society. Articles address general principles of chemical measurement science and novel analytical methodologies. Topics commonly include chemical reactions and selectivity, chemometrics and data processing, electrochemistry, elemental and molecular characterization, imaging, instrumentation, mass spectrometry, microscale and nanoscale systems, -omics, sensing, separations, spectroscopy, and surface analysis. It is abstracted and indexed in Chemical Abstracts Service, CAB International, EBSCOhost, ProQuest, PubMed, Scopus, and the Science Citation Index Expanded. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', it has a 2022 impact factor of 7.4. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all depart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Electrospray Ionization
Secondary electro-spray ionization (SESI) is an ambient ionization technique for the analysis of trace concentrations of vapors, where a Nanoelectrospray, nano-electrospray produces charging agents that collide with the analyte molecules directly in gas-phase. In the subsequent reaction, the charge is transferred and vapors get ionized, most molecules get protonated (in positive mode) and deprotonated (in negative mode). SESI works in combination with mass spectrometry or ion-mobility spectrometry. History The fact that trace concentrations of gases in contact with an electrospray plume were efficiently ionized was first observed by John Fenn (chemist), Fenn and colleagues when they noted that tiny concentrations of plasticizers produced intense peaks in their mass spectra. However, it was not until 2000 when this problem was reframed as a solution, when Hill and coworkers used an electrospray to ionize molecules in the gas phase, and named the technique Secondary Electrospray Ioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explosive Vapor Detector
Explosive vapor detectors (EVD) are explosives detection instruments whose principle of operation is the selective analysis of collected vapor samples from the air, in contrast to explosives trace detectors (ETD) which require the physical collection of particulate samples from surfaces. EVDs are not limited to explosives, and may also be used to detect narcotics and other illicit or dangerous substances such as biological agents or chemical warfare agents. EVDs can be classified into two types: portable EVDs, and pre-concentrated sample EVDs. Portable units have detection limits in the ranges of parts per million or parts per billion, similar to those of ETDs or explosive detection dogs. Pre-concentrated sample EVDs have sensitivities in the range of parts per quadrillion (10−15). Principle of operation The detection process is based on two broad steps: sampling and analysis. In portable instruments, sampling and the analysis are done on the same device. Sampling A samp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |