|
Ermelo, Netherlands
Ermelo (, Dutch Low Saxon: ''Armelo'' or ''Armel'') is a Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality and town in the Netherlands; found within Gelderland province and the forest-rich Veluwe area. The population was . Etymology ''Ermelo'' comes from ''lo'', meaning "woods"Maurits Gysseling, M. Gysseling (1960), Toponymisch Woordenboek van België, Nederland, Luxemburg, Noord-Frankrijk en West-Duitsland (vóór 1226)', blz. 327, George Michiels N.V., Tongeren and ''irmin'' for which several explanations are given. Some of those are "great", "divine" or it refers to an old Germanic god called Irminism, Irmin. Population centres History The town has been known to exist since at least 855, when the name ''Irminlo'' first appeared in a legal document. Human presence in the area goes back further however, with many archaeological finds of the Beaker culture, Bell-Beaker culture having been made in the area. Two Roman Empire, Roman marching camps have been found on the push mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities Of The Netherlands
Since 1 January 2023, there have been 342 regular municipalities ( ; Grammatical number#Overview, sing. ) and three Caribbean Netherlands, special municipalities ( ) in the Netherlands. The latter is the status of three of the six island territories that make up the Dutch Caribbean. Municipalities are the second-level administrative division, or public body (Netherlands), public bodies (), in the Netherlands and are subdivisions of their respective provinces of the Netherlands, provinces. Their duties are delegated to them by the Cabinet of the Netherlands, central government and they are ruled by a municipal council (Netherlands), municipal council that is elected every four years. Municipal merger (politics), mergers have reduced the total number of municipalities by two-thirds since the first official boundaries were created in the mid 19th century. Municipalities themselves are informally subdivided into districts and neighbourhoods for administrative and statistical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farms
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used for specialized units such as arable farms, vegetable farms, fruit farms, dairy, pig and poultry farms, and land used for the production of natural fiber, biofuel, and other biobased products. It includes ranches, feedlots, orchards, plantations and estates, smallholdings, and hobby farms, and includes the farmhouse and agricultural buildings as well as the land. In modern times, the term has been extended to include such industrial operations as wind farms and fish farms, both of which can operate on land or at sea. There are about 570 million farms in the world, most of which are small and family-operated. Small farms with a land area of fewer than 2 hectares operate on about 12% of the world's agricultural land, and family farms comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
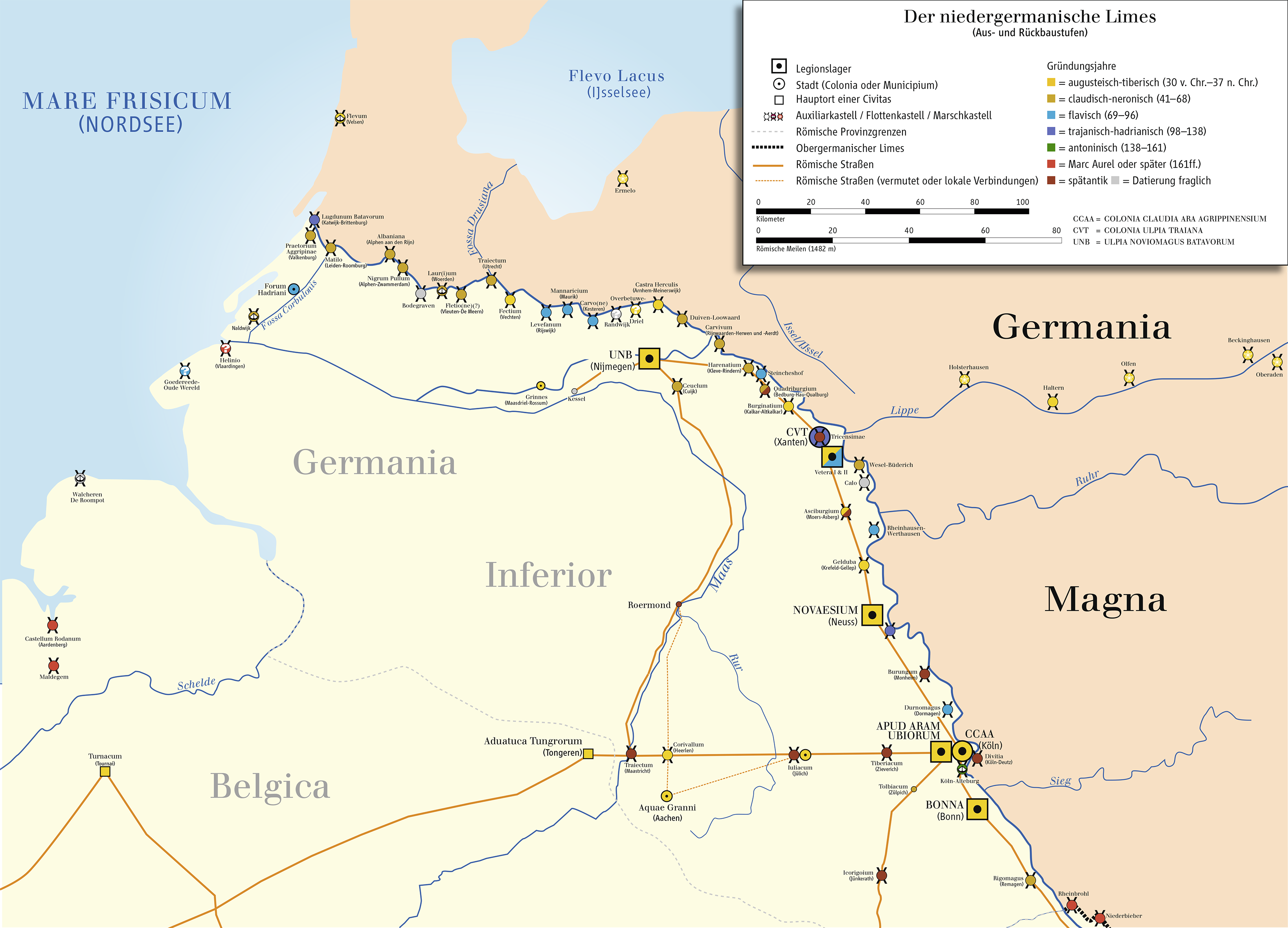
Roman Ermelo
Roman Ermelo was a big roman camp (and possible fortification) in what is now Netherland. It was created under Augustus in the short-lived roman province of Germania. History A Roman marching camp has been found on the push moraine east of Ermelo: Roman camp Ermelo. It has been found together with a smaller one. They were far in hostile territory for the Romans, on the route between the Limes and the ancient Lake Flevo. The largest camp of 6 hectares offered space for 4000-6000 legionaries. The diamond-shaped earthen defensive walls of this marching camp can still be partly seen in the landscape and were partly restored in 2006. A second smaller camp was not found until 2017. In 2020, excavations confirmed that it was of Roman origin. See also * Flevum Flevum was a castrum and port of the Romans in Frisia (actual northern Netherlands), built when emperor Augustus wanted to conquer the German populated territories between the Rhine river and the Elbe river. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legionary
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius''; : ''legionarii'') was a citizen soldier of the Roman army. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the Republic and Principate eras, alongside auxiliary and cavalry detachments. At its height, Roman Legionnaires were viewed as the foremost fighting force in the Roman world, with commentators such as Vegetius praising their fighting effectiveness centuries after the classical Roman legionary disappeared. Roman legionnaires were recruited from Roman citizens under age 45. They were first predominantly made up of recruits from Roman Italy, but more were recruited from the provinces as time went on. As legionnaires moved into newly conquered provinces, they helped Romanize the native population and helped integrate the disparate regions of the Roman Empire into one polity. They enlisted in a legion for 25 years of service, a change from the early practice of enlisting only for a campaign. Legionna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Flevo
The Zuiderzee or Zuider Zee (; old spelling ''Zuyderzee'' or ''Zuyder Zee''), historically called Lake Almere and Lake Flevo, was a shallow bay of the North Sea in the northwest of the Netherlands. It extended about 100 km (60 miles) inland and at most 50 km (30 miles) wide, with an overall depth of about 4 to 5 metres (13–16 feet) and a coastline of about 300 km (200 miles). It covered . Its name is Dutch for "southern sea", indicating that the name originates in Friesland, to the north of the Zuiderzee (cf. North Sea). In the 20th century the majority of the Zuiderzee was closed off from the North Sea by the construction of the Afsluitdijk, leaving the mouth of the inlet to become part of the Wadden Sea. The salt water inlet changed into a fresh water lake now called the IJsselmeer (IJssel Lake) after the river that drains into it, and by means of drainage and polders, an area of some was reclaimed as land. This land eventually became the province of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin; , : ) is a term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting system of ancient Rome marking the borders of the Roman Empire. The term has been extended in modern times to refer to the Roman military frontiers and fortifications, frontier defences in other parts of the empire, such as in the east and in Africa. Overview The Roman frontier stretched for more than from the Atlantic coast of northern Roman Britain, Britain, through Europe to the Black Sea, and from there to the Red Sea and across North Africa to the Atlantic coast. The positions of the borders changed especially during the main periods of Roman expansion and contraction, and first became more stable during the early Roman Empire, Empire period under Augustus, but the borders continued to change with time in different provinces. The borders had different constituents depending on local needs; often they consisted of natural boundaries (e.g. rivers) with roads behind for easier movement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Moraine
A push moraine or pushed moraine is in geomorphology a moraine (a landform formed by glacial processes) that forms when the terminus advance of a lowland glacier pushes unstratified glacial sediment into a pile or linear ridge in front of it. A push moraine is identified by its ability to push sediment upwards from its original horizontal position. Push moraines are limited in size by the advance of a glacier front and its tendency to shear over the top of any ridge large enough to resist the movement of ice. Pushed moraines generally occur in low, flat plains at higher latitudes and were formed during the glacial stages of the Quaternary ice age. They can be up to 100 km long and several hundreds of metres in height. Pushed moraines can be found in the North American plains, in Siberia and in Northern Europe. They were formed during cool, glacial stages, when glaciers advanced and covered large parts of North America and Eurasia. In some regions pushed moraines of more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marching Camp
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English language, English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large Roman legion, legionary fortresses, smaller forts for Cohort (military unit), cohorts or for auxiliary forces, military camp, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan language, Oscan and Umbrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beaker Culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell Beaker (archaeology), beaker drinking vessel used at the beginning of the European Bronze Age, arising from around 2800 BC. The term's English translation ''Bell Beaker'' was introduced by John Abercromby, 5th Baron Abercromby, John Abercromby in 1904.''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Archaeology'' Bell Beaker culture lasted in Bronze Age Britain, Britain from BC, with the appearance of single burial graves,Armit, Ian, and David Reich, (2022)"What do we know about the Beaker Folk" in: Antiquity Journal, Youtube, min: 1:11: "So, the Beaker Complex in terms of Great Britain and Ireland is from ... around 2450 BC, when we see in Britain the appearance of single inhumation graves ...." until as late as 1800 BC, but in continental Europe only until 2300 BC, when it was succeeded by the Únětice culture. The culture was wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |