|
Enzymes Of Known Structure
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes described as a ''type'' of enzyme rather than being ''like'' an enzyme, but even in the decades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucosidase Enzyme
Glucosidases are the glycoside hydrolase enzymes categorized under the Enzyme Commission number, EC number 3.2.1. Function Alpha-glucosidases are enzymes involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into their monomers. They catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates including alpha- or beta-linked polymers of glucose. This enzyme convert complex sugars into simpler ones. Members Different sources include different members in this class. Members marked with a "#" are considered by Medical Subject Headings, MeSH to be glucosidases. Clinical significance Alpha-glucosidases are targeted by alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose and miglitol to control diabetes mellitus type 2. See also * DNA glycosylases * Mucopolysaccharidoses References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Hydrolases Carbohydrates EC 3.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
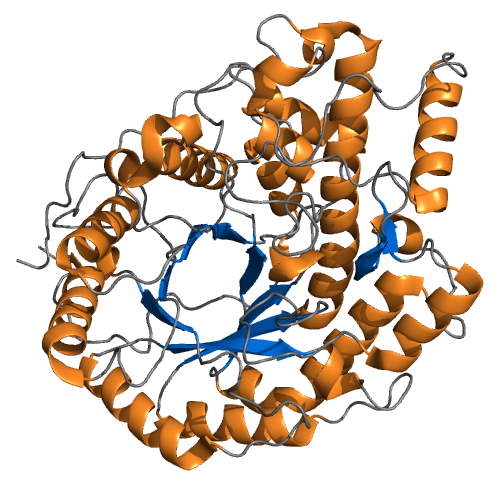
Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detergent Enzymes
Detergent enzymes are biological enzymes that are used with detergents. They catalyze the reaction between stains and the water solution, thus aiding stain removal and improving efficiency. Laundry detergent enzymes are the largest application of industrial enzymes. They can be a part of both liquid and powder detergents. History Otto Röhm introduced the use of enzymes in detergent by using trypsin extracted from the tissues of slaughtered animals. Röhm's formula, though more successful than German household cleaning methods, was considered unstable when used with alkali and bleach. In 1959, yields were improved by microbial synthesis of proteases. Properties Laundry enzymes must be able to function normally in a wide array of conditions: water temperatures ranging from 0 to 60 °C; alkaline and acidic environments; solutions with high ionic strength; and the presence of surfactants or oxidizing agents. Types The six classes of enzymes found in laundry deterge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, treatment and antibiotic prophylaxis, prevention of such infections. They may either bactericide, kill or bacteriostatic agent, inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the ones which cause the common cold or influenza. Drugs which inhibit growth of viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals. Antibiotics are also not effective against fungi. Drugs which inhibit growth of fungi are called antifungal drugs. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek language, Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |