|
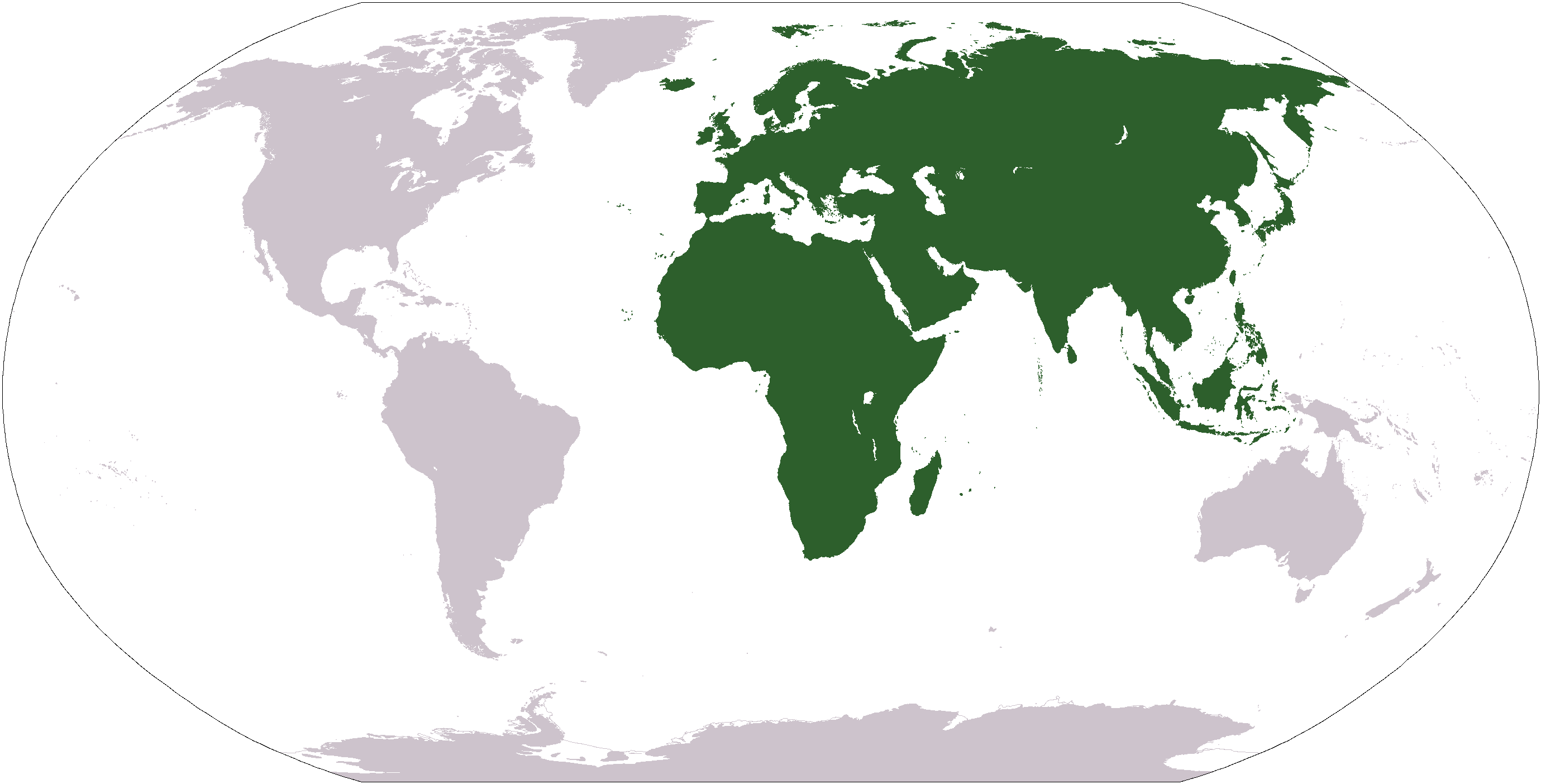
Elatinaceae
Elatinaceae is a family of flowering plants with ca 35 (to perhaps 50) species in two genera: ''Elatine'' and ''Bergia''. The ''Elatine'' are mostly aquatic herbs, and the ''Bergia'' are subshrubs to shrubs. ''Elatine'' species are widely distributed throughout the world from temperate to tropical zones, with its greatest diversity found in temperate zones. ''Bergia'' is found in temperate to tropical Eurasia and Africa, with two tropical and one tropical to temperate species in the Americas. The center for biodiversity of ''Bergia'' is the Old World tropics, and this is also the center for biodiversity for the family. Neither genus is found in arctic ecosystems. Member of the family have bisexual flowers, usually small flowers, single, or in cymes, with two to five overlapping petals. The plants have opposite or whorled leaves, which may have glands along their margins, and have stipules. The aquatic herbs in the genus ''Elatine'' often have reduced characteristics as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elatine Hexandra
''Elatine hexandra'', the six-stamened waterwort, is flowering plant of the family Elatinaceae, which grows in shallow water around lakes and pools in Europe from Ireland to Romania. It is declining due to drainage and water pollution and is therefore protected in several countries. Description Six-stamened waterwort is a small annual to short-lived perennial herb with creeping stems up to about 8 cm long, which root at the nodes. It is entirely glabrous, with opposite pairs of elliptical to spathulate leaves about 7 mm long, which are borne on short petioles. At the tip of each leaf is a tiny, black hydathode. There are also minute stipules at the base of the leaf stalks. The stems and leaves are usually yellowy-green under water, becoming bright green or reddish when exposed on bare mud. The flowers are usually solitary or sometimes in short Cyme (botany), cymes arising at the leaf nodes. Each flower has three (sometimes 4) sepals and the same number of pinkish-white petals. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elatinaceae
Elatinaceae is a family of flowering plants with ca 35 (to perhaps 50) species in two genera: ''Elatine'' and ''Bergia''. The ''Elatine'' are mostly aquatic herbs, and the ''Bergia'' are subshrubs to shrubs. ''Elatine'' species are widely distributed throughout the world from temperate to tropical zones, with its greatest diversity found in temperate zones. ''Bergia'' is found in temperate to tropical Eurasia and Africa, with two tropical and one tropical to temperate species in the Americas. The center for biodiversity of ''Bergia'' is the Old World tropics, and this is also the center for biodiversity for the family. Neither genus is found in arctic ecosystems. Member of the family have bisexual flowers, usually small flowers, single, or in cymes, with two to five overlapping petals. The plants have opposite or whorled leaves, which may have glands along their margins, and have stipules. The aquatic herbs in the genus ''Elatine'' often have reduced characteristics as par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elatine
''Elatine'' is one of only two genera in the plant family Elatinaceae, the waterwort family. It contains about 25 species of aquatic plants known generally as waterworts. These are annual or perennial plants found in wet areas worldwide. , Plants of the World Online accepted the following species: *'' Elatine alsinastrum'' L. *'' Elatine ambigua'' Wight - Asian waterwort *'' Elatine americana'' (Pursh) Arn. - American waterwort *'' Elatine brachysperma'' A.Gray - shortseed waterwort *'' Elatine brochonii'' Clavaud *'' Elatine californica'' A.Gray - California waterwort *'' Elatine campylosperma'' Seub. *'' Elatine chilensis'' Gay - Chilean waterwort *'' Elatine ecuadoriensis'' Molau *'' Elatine fassettiana'' Steyerm. *'' Elatine fauquei'' Monod *'' Elatine glaziovii'' Nied. *'' Elatine gratioloides'' A.Cunn. *'' Elatine gussonei'' (Sommier) Brullo, Lanfr., Pavone & Ronsisv. *'' Elatine heterandra'' H.Mason - mosquito waterwort *''Elatine hexandra'' (Lapierre) DC. - six-stamen wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elatine Hydropiper
''Elatine hydropiper'', known as the eight-stamened waterwort, is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Elatinaceae. Its native range is Europe to Russian Far East. It was first described by Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus in 1753. References External links ''Elatine hydropiper'' images & occurrence data at Global Biodiversity Information Facility, GBIF {{Taxonbar, from=Q163322 Elatinaceae Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Plants described in 1753 Flora of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterwort
''Elatine'' is one of only two genera in the plant family Elatinaceae, the waterwort family. It contains about 25 species of aquatic plants known generally as waterworts. These are annual or perennial plants found in wet areas worldwide. , Plants of the World Online accepted the following species: *'' Elatine alsinastrum'' L. *'' Elatine ambigua'' Wight - Asian waterwort *'' Elatine americana'' (Pursh) Arn. - American waterwort *'' Elatine brachysperma'' A.Gray - shortseed waterwort *'' Elatine brochonii'' Clavaud *'' Elatine californica'' A.Gray - California waterwort *'' Elatine campylosperma'' Seub. *'' Elatine chilensis'' Gay - Chilean waterwort *'' Elatine ecuadoriensis'' Molau *'' Elatine fassettiana'' Steyerm. *'' Elatine fauquei'' Monod *'' Elatine glaziovii'' Nied. *'' Elatine gratioloides'' A.Cunn. *'' Elatine gussonei'' (Sommier) Brullo, Lanfr., Pavone & Ronsisv. *'' Elatine heterandra'' H.Mason - mosquito waterwort *''Elatine hexandra'' (Lapierre) DC. - six-stamen wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bergia
''Bergia'' is one of the two genera of plants composing the waterwort family, Elatinaceae. These are tropical to subtropical plants and sometimes aquatic in nature. Species include: *'' Bergia ammannioides'' *'' Bergia aquatica'' *'' Bergia auriculata'' *'' Bergia capensis'' *'' Bergia decumbens'' *'' Bergia glutinosa'' *''Bergia henshallii'' *'' Bergia pedicellaris'' *'' Bergia pentherana'' *'' Bergia perennis'' *'' Bergia polyantha'' *'' Bergia pusilla'' *''Bergia serrata ''Bergia'' is one of the two genera of plants composing the waterwort family, Elatinaceae. These are tropical to subtropical plants and sometimes aquatic plant, aquatic in nature. Species include: *''Bergia ammannioides'' *''Bergia aquatica'' * ...'' *'' Bergia suffruticosa'' *'' Bergia texana'' References External links Jepson Manual Treatment''Bergia'' of Zimbabwe''Bergia'' of Western Australia Elatinaceae Malpighiales genera {{Malpighiales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously thought of by the Europeans as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
An aquarium (: aquariums or aquaria) is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. fishkeeping, Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian era, Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854. Small aquariums are k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stipule
In botany, a stipule is an outgrowth typically borne on both sides (sometimes on just one side) of the base of a leafstalk (the petiole (botany), petiole). They are primarily found among dicots and rare among monocots. Stipules are considered part of the anatomy of the leaf of a typical flowering plant, although in many species they may be inconspicuous —or sometimes entirely absent, and the leaf is then termed ''exstipulate''. At the other end of the scale are species like ''Artocarpus elasticus'' where the stipules can be up to eight inches (twenty cm) in length. (In some older botanical writing, the term "stipule" was used more generally to refer to any small leaves or leaf-parts, notably prophylls.) The word ''stipule'' was coined by Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus''Concise English Dictionary'' Wordsworth Editions Ltd. 1994, from Latin ''stipula'', straw, stalk. Types of stipules General characteristics The position of stipules on a plant varies widely from species to species, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petal
Petals are modified leaves that form an inner whorl surrounding the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corolla''. Petals are usually surrounded by an outer whorl of modified leaves called sepals, that collectively form the ''calyx'' and lie just beneath the corolla. The calyx and the corolla together make up the perianth, the non-reproductive portion of a flower. When the petals and sepals of a flower are difficult to distinguish, they are collectively called tepals. Examples of plants in which the term ''tepal'' is appropriate include genera such as '' Aloe'' and '' Tulipa''. Conversely, genera such as '' Rosa'' and '' Phaseolus'' have well-distinguished sepals and petals. When the undifferentiated tepals resemble petals, they are referred to as "petaloid", as in petaloid monocots, orders of monocots with brightly coloured tepals. Since they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |