|
Diterpenes
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary intermediate. Diterpenes form the basis for biologically important compounds such as retinol, retinal, and phytol. Some diterpenes are known to be antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory. Structures As with most terpenes a huge number of potential structures exists, which may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. Biosynthesis Diterpenes are derived from the addition of one IPP unit to FPP to form geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). From GGPP, structural diversity is achieved mainly by two classes of enzymes; the diterpene synthases and cytochromes P450. Several diterpenes are produced by plants and cyanobacteria. GGPP is also the precursor for the synthesis of the phytane by the action of the enzyme geran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terpenes
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. In plants, terpenes and terpenoids are important mediators of ecological interactions, while some insects use some terpenes as a form of defense. Other functions of terpenoids include cell growth modulation and plant elongation, light harvesting and photoprotection, and membrane permeability and fluidity control. Terpenes are classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), as examples. The terpene alpha-pinene is a major component of the common solvent, turpentine. The one terpene that has major applications is natural rubber (i.e., polyisoprene). The possibility that other terpenes could be used as precursors to produce synthetic polymers has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geranylgeranyl Pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and diterpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls. It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, which is its primary use in human cells. It is formed from farnesyl pyrophosphate by the addition of an isoprene unit from isopentenyl pyrophosphate. In ''Drosophila'', geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is synthesised by HMG-CoA encoded by the Columbus gene. Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is utilised as a chemoattractant for migrating germ cells that have traversed the midgut epithelia. The attractant signal is produced at the gonadal precursors, directing the germ cells to these sites, where they will differentiate into eggs and spermatozoa (sperm). Related compounds * Farnesyl pyrophosphate * Geranylgeraniol Geranylgeraniol is a diterpenoid alcohol. It is a colorless waxy solid. It is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
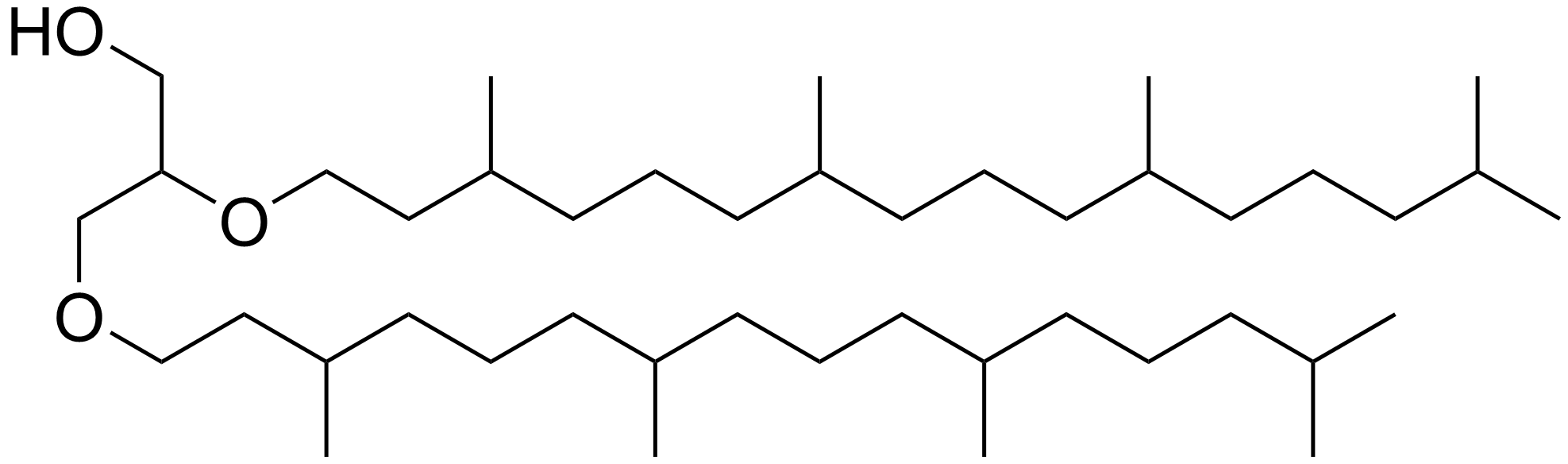
Phytane
Phytane is the Diterpenoid, isoprenoid alkane formed when phytol, a chemical substituent of chlorophyll, loses its Hydroxy group, hydroxyl group. When phytol loses one carbon atom, it yields pristane. Other sources of phytane and pristane have also been proposed than phytol. Pristane and phytane are common constituents in petroleum and have been used as Proxy (climate), proxies for Deposition (geology), depositional redox conditions, as well as for correlating oil and its source rock (i.e. elucidating where oil formed). In environmental studies, pristane and phytane are target compounds for investigating oil spills. Chemistry Phytane is a Chemical polarity, non-polar organic compound that is a clear and colorless liquid at room temperature. It is a wikibooks:Structural Biochemistry/Lipids/Isoprenoids#Structural Features and Some Isoprenoid Compounds, head-to-tail linked regular Terpenoid, isoprenoid with chemical formula C20H42. Phytane has List of straight-chain alkanes, many S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinol
Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes, immune function and reproductive development. Dietary sources include fish, dairy products, and meat. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. It is taken by mouth or by intramuscular injection, injection into a muscle. As an ingredient in skin-care products, it is used to reduce wrinkles and other effects of skin aging. Retinol at normal doses is well tolerated. High doses may cause hepatomegaly, enlargement of the liver, dry skin, and hypervitaminosis A. High doses during pregnancy may harm the fetus. The body converts retinol to retinal and retinoic acid, through which it acts. Retinol was discovered in 1909, isolated in 1931, and first m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytyl
Phytane is the isoprenoid alkane formed when phytol, a chemical substituent of chlorophyll, loses its hydroxyl group. When phytol loses one carbon atom, it yields pristane. Other sources of phytane and pristane have also been proposed than phytol. Pristane and phytane are common constituents in petroleum and have been used as proxies for depositional redox conditions, as well as for correlating oil and its source rock (i.e. elucidating where oil formed). In environmental studies, pristane and phytane are target compounds for investigating oil spills. Chemistry Phytane is a non-polar organic compound that is a clear and colorless liquid at room temperature. It is a head-to-tail linked regular isoprenoid with chemical formula C20H42. Phytane has many structural isomers. Among them, crocetane is a tail-to-tail linked isoprenoid and often co-elutes with phytane during gas chromatography (GC) due to its structural similarity. Phytane also has many stereoisomers because of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytane
Phytane is the Diterpenoid, isoprenoid alkane formed when phytol, a chemical substituent of chlorophyll, loses its Hydroxy group, hydroxyl group. When phytol loses one carbon atom, it yields pristane. Other sources of phytane and pristane have also been proposed than phytol. Pristane and phytane are common constituents in petroleum and have been used as Proxy (climate), proxies for Deposition (geology), depositional redox conditions, as well as for correlating oil and its source rock (i.e. elucidating where oil formed). In environmental studies, pristane and phytane are target compounds for investigating oil spills. Chemistry Phytane is a Chemical polarity, non-polar organic compound that is a clear and colorless liquid at room temperature. It is a wikibooks:Structural Biochemistry/Lipids/Isoprenoids#Structural Features and Some Isoprenoid Compounds, head-to-tail linked regular Terpenoid, isoprenoid with chemical formula C20H42. Phytane has List of straight-chain alkanes, many S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stemodene
Stemodene is a labdane-related diterpene whose corresponding class I terpene synthase has been discovered in rice and subsequently cloned and functionally characterized. The gene responsible for stemodene production has not been found in the completed rice genome, thus suggesting that perhaps other genes are as yet undiscovered in the "completed" genome. Stemarene synthase demonstrates high sequence homology with stemodene synthase, thus accounting for the latter's discovery by Dana Morrone in 2005. Additionally, the corresponding olefin In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins. The International Union of Pu ... produced by each cyclase shows structural similarities and is derived from the common precursor of ''syn''-copalyl diphosphate. References Diterpenes Cyclopentanes {{alkanederivativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stemarene
Stemarene is a diterpene hydrocarbon can be produced biosynthetically through enzyme An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ... extracts from rice. References Diterpenes Cyclopentanes {{alkanederivative-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labdane
Labdane is a natural bicyclic diterpene. It forms the structural core for a wide variety of natural products collectively known as ''labdanes'' or ''labdane diterpenes''. The labdanes were so named because the first members of the class were originally obtained from labdanum, a resin derived from the gum rockrose. A variety of biological activities have been determined for labdane diterpenes including antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, and anti-inflammatory activities. Natural labdanes in tree resin are believed to be the precursors of amber, which polymerise under great pressure. Example labdane derivatives * Forskolin * Galanolactone * Isocupressic acid - is an abortifacient component of ''Cupressus macrocarpa''. * Medigenin *Sclareol Sclareol is a fragrant chemical compound found in '' Salvia sclarea'', from which it derives its name. It is classified as a bicyclic diterpene alcohol. It is an amber colored solid with a sweet, balsamic scent. In an experime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclarene
Sclarene is a diterpene present in the foliage of '' Podocarpus hallii''. References Diterpenes Decalins Polyenes Vinylidene compounds {{organic-compound-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cembrene A
Cembrene A, or sometimes neocembrene, is a natural monocyclic diterpene isolated from corals of the genus ''Nephthea''. It is a colorless oil with a faint wax-like odor. Cembrene A is a trail pheromone for termites; however, the chemical structure of cembrene is central to a very wide variety of other natural products found both in plants and in animals.''Terpenes: Flavors, Fragrances, Pharmaca, Pheromones'', Eberhard Breitmaier, page 7. ''Pinus leucodermis'' tree bark and wood essential oils contain a high percentage of cembrene. Cembrenes are biosynthesized by macrocyclization of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of diterpenes and diterpenoids. It is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls. It is also a precursor to geranylgeranylated proteins, whic .... References {{reflist Diterpenes Alkene derivatives Insect ecology Insect pheromones Cycloalkenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abietane
Abietane is an organic compound with the formula C20H36. It is a tricyclic, saturated hydrocarbon with an elaborate stereochemistry. It is a colorless solid. It is of little biochemical interest except as a reference structure of the abietanes. Abietanes Abietanes are a large family of diterpenoids. Individual members of these diterpenoids are also colorless hydrophobic organic compounds. They are usually encountered as mixtures. Most prominent of the abietanes is abietic acid, the major constituent of rosin. Other abietanes are carnosic acid and ferruginol. Some abietanes are of interest in biogeochemistry as markers indicating the source organisms. Abietanes are tricyclic 20-carbon Diterpene, diterpenoids characterized by three fused six-membered rings and alkyl groups at carbons 4, 10, and 13. In higher plants, abietanes and other diterpenoids are synthesized from four five-carbon isoprene units. Abietanes are generally nonpolar, volatile, and less dense than water. The pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |