|
Deoxyribonucleases
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells includes breaking down extracellular DNA (ecDNA) excreted by apoptosis, necrosis, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) of cells to help reduce inflammatory responses that otherwise are elicited. A wide variety of deoxyribonucleases are known and fall into one of two families ( DNase I or DNase II), which differ in their substrate specificities, chemical mechanisms, and biological functions. Laboratory applications of DNase include purifying proteins when extracted from prokaryotic organisms. Additionally, DNase has been applied as a treatment for diseases that are caused by ecDNA in the blood plasma. Assays of DNase are emerging in the research field as well. Types The two main types of DNase found in animals are known as deoxyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exodeoxyribonuclease
Exodeoxyribonucleases are both exonucleases and deoxyribonucleases. They catalyze digestion of the ends of linear DNA. They are a type of esterase. They are classified EC 3.1.11. See also * Deoxyribonuclease Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells ... External links * EC 3.1 Deoxyribonucleases {{3.1-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNase MOA
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolytic cleavage of phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells includes breaking down extracellular DNA (ecDNA) excreted by apoptosis, necrosis, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) of cells to help reduce inflammatory responses that otherwise are elicited. A wide variety of deoxyribonucleases are known and fall into one of two families ( DNase I or DNase II), which differ in their substrate specificities, chemical mechanisms, and biological functions. Laboratory applications of DNase include purifying proteins when extracted from prokaryotic organisms. Additionally, DNase has been applied as a treatment for diseases that are caused by ecDNA in the blood plasma. Assays of DNase are emerging in the research field as well. Types The two main types of DNase found in animals are known as deoxyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
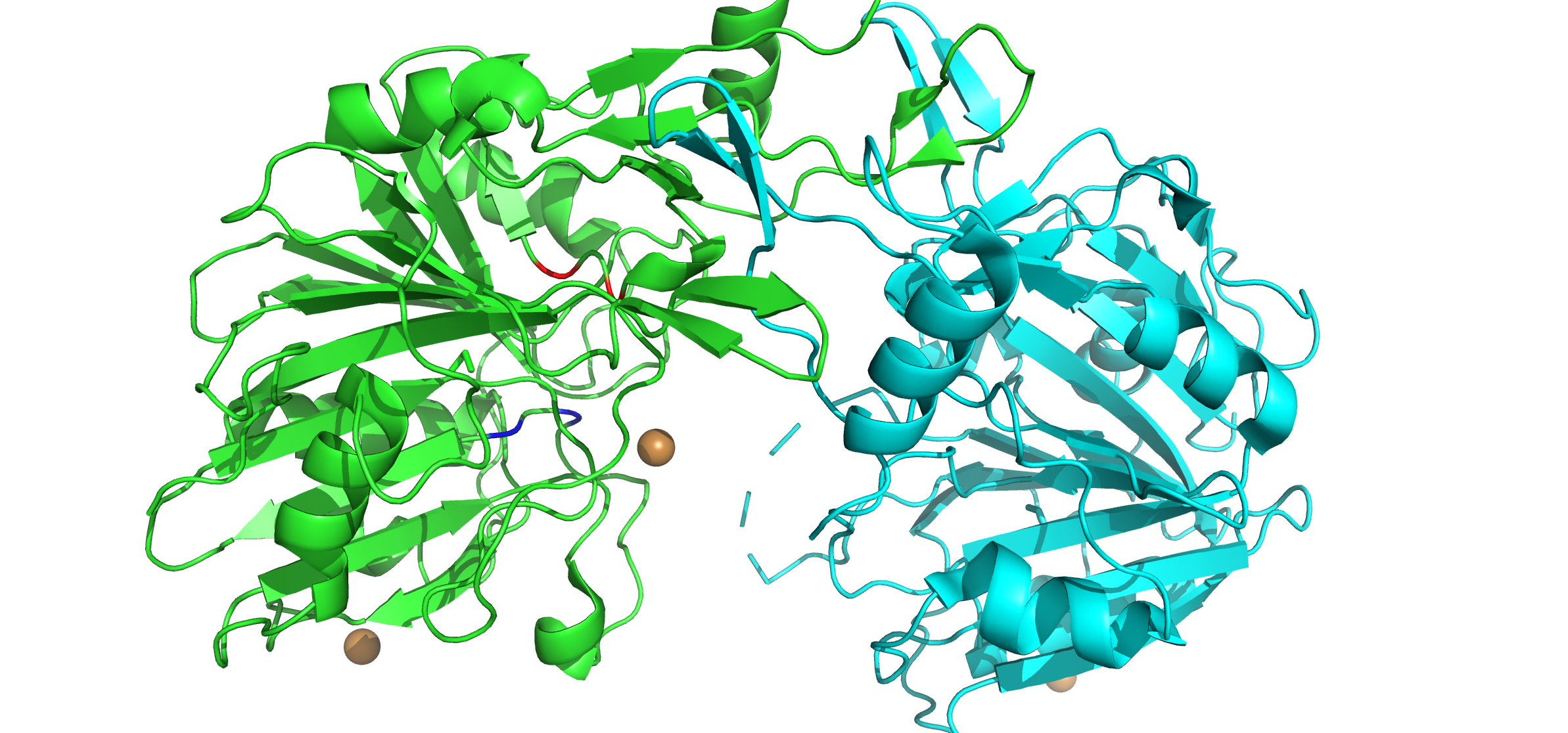
DNase 1 Image 1
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase, for short) refers to a group of glycoprotein endonucleases which are enzymes that catalyze the Hydrolysis, hydrolytic cleavage of Phosphodiester bonds, phosphodiester linkages in the DNA backbone, thus degrading DNA. The role of the DNase enzyme in cells includes breaking down extracellular DNA (ecDNA) excreted by apoptosis, necrosis, and neutrophil extracellular traps (NET) of cells to help reduce inflammatory responses that otherwise are elicited. A wide variety of deoxyribonucleases are known and fall into one of two families (Deoxyribonuclease I, DNase I or Deoxyribonuclease II, DNase II), which differ in their Substrate (biochemistry), substrate specificities, chemical mechanisms, and biological functions. Laboratory applications of DNase include Protein purification, purifying proteins when extracted from Prokaryote, prokaryotic organisms. Additionally, DNase has been applied as a treatment for diseases that are caused by ecDNA in the blood plasma. Ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endodeoxyribonuclease
In biochemistry, an endodeoxyribonuclease is a class of enzyme which is a type of deoxyribonuclease (a DNA cleaver), itself a type of endonuclease (a nucleotide cleaver). They catalyze cleavage of the phosphodiester bonds in DNA. They are classified with EC numbers 3.1.21 through 3.1.25. Examples include: * DNA restriction enzymes * micrococcal nuclease See also * Ribonuclease Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within th ... * UvrABC endonuclease External links * EC 3.1 Deoxyribonucleases {{hydrolase-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease. In both archaea and eukaryotes, one of the main routes of RNA degradation is performed by the multi-protein exosome complex, which consists largely of 3′ to 5′ exoribonucleases. Significance to polymerase RNA polymerase II is known to be in effect during transcriptional termination; it works with a 5' exonuclease (human gene Xrn2) to degrade the newly formed transcr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNASE1L3
Deoxyribonuclease gamma (also termed DNase γ, deoxyribonuclease 1L3, DNASE1L3, of deoxyribonuclease I like 3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNASE1L3'' (also termed the ''deoxyribonuclease 1L3'' or ''deoxyribonuclease 1 like 3'') gene. This gene's is located on chromosome 3's " p arm", i.e., short arm, between region 1, band 4, sub-band 3 and region 2, band 1, sub-band 1 (this location's is abbreviation as 3p14.3-p21.1) Function DNASE1L3 belongs to the family of deoxyribonuclease enzymes that are responsible for degrading DNA. Specifically, DNASE1L3 plays a key role in the breakdown of extracellular DNA, particularly DNA released from dying cells due to apoptosis or necrosis. This function is important for maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing the accumulation of DNA debris, which could otherwise trigger widespread inflammatory autoimmune responses. Clinical significance Role in autoimmune response Humans with inactivating mutations in both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |