|
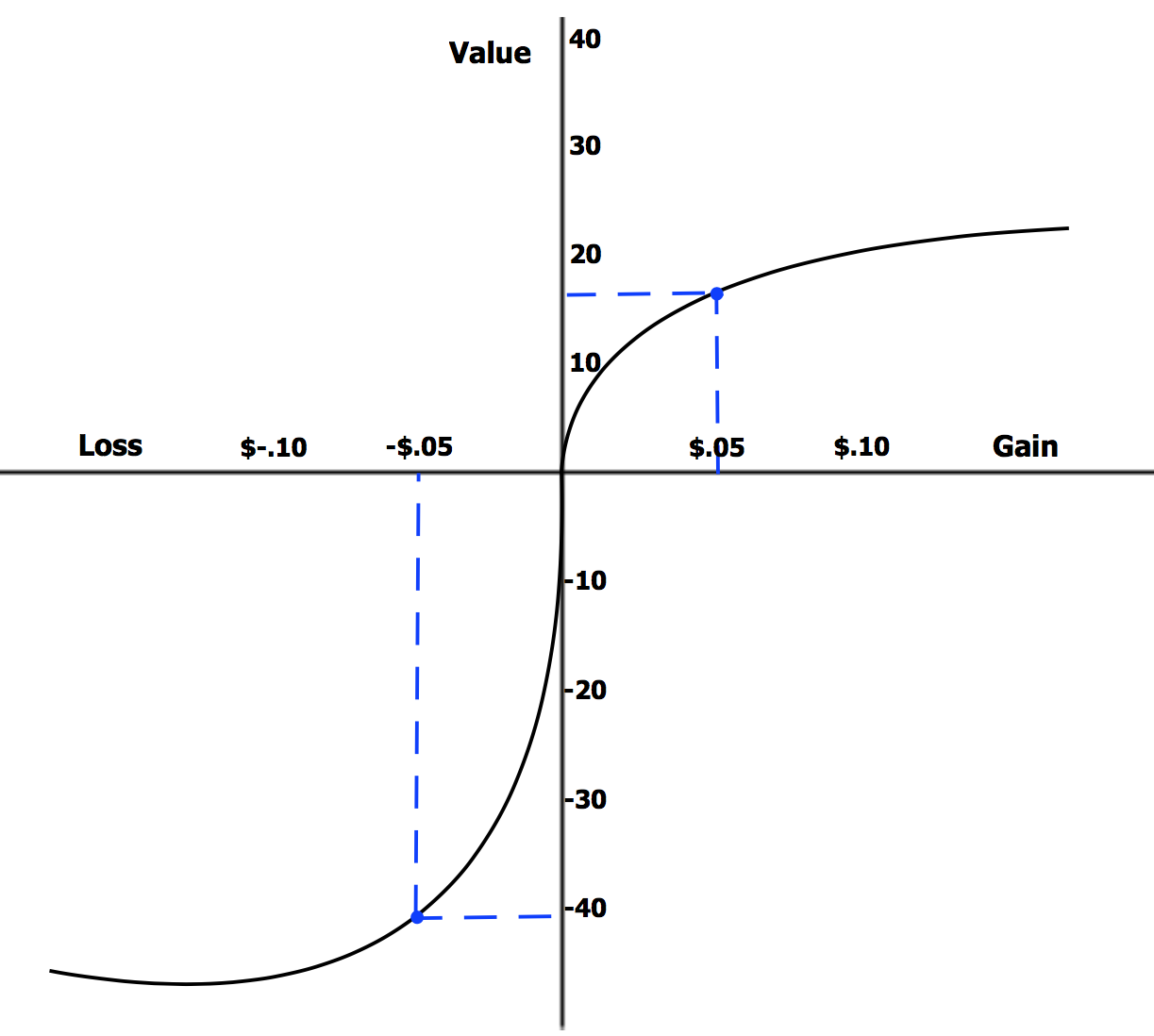
Cumulative Prospect Theory
In behavioral economics, cumulative prospect theory (CPT) is a model for descriptive decisions under risk and uncertainty which was introduced by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman in 1992 (Tversky, Kahneman, 1992). It is a further development and variant of prospect theory. The difference between this version and the original version of prospect theory is that weighting is applied to the cumulative probability distribution function, as in rank-dependent expected utility theory but not applied to the probabilities of individual outcomes. In 2002, Daniel Kahneman received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to behavioral economics, in particular the development of CPT. Outline of the model The main observation of CPT (and its predecessor prospect theory) is that people tend to think of possible outcomes usually relative to a certain reference point (often the status quo) rather than to the final status, a phenomenon which is called framin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman (3283955327) (cropped)
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kahne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Framing (social Sciences)
In the social sciences, framing comprises a set of concepts and theoretical perspectives on how individuals, groups, and societies organize, perceive, and communicate about reality. Framing can manifest in cognition, thought or interpersonal communication. ''Frames in thought'' consist of the mental representations, interpretations, and simplifications of reality. ''Frames in communication'' consist of the communication of frames between different actors. Framing is a key component of sociology, the study of social interaction among humans. Framing is an integral part of conveying and processing data daily. Successful framing techniques can be used to reduce the ambiguity of intangible topics by contextualizing the information in such a way that recipients can connect to what they already know. Framing is mistaken in the world outside of communication as bias, or arguments around Nature versus nurture, nature vs nurture. While biases and how a person is raised might add to stere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance Theories
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and discipline of money, currency, assets and liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due to its wide scope, a broad range of subfields exists within finance. Asset-, money-, risk- and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis assesses the viability, stability, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endowment Effect
In psychology and behavioral economics, the endowment effect, also known as divestiture aversion, is the finding that people are more likely to retain an object they own than acquire that same object when they do not own it. The endowment theory can be defined as "an application of prospect theory positing that loss aversion associated with ownership explains observed exchange asymmetries." This is typically illustrated in two ways. In a valuation paradigm, people's maximum willingness to pay (WTP) to acquire an object is typically lower than the least amount they are willing to accept (WTA) to give up that same object when they own it—even when there is no cause for attachment, or even if the item was only obtained minutes ago. In an exchange paradigm, people given a good are reluctant to trade it for another good of similar value. For example, participants first given a pen of equal expected value to that of a coffee mug were generally unwilling to trade, whilst participants f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertemporal Consumption
Economic theories of intertemporal consumption seek to explain people's preferences in relation to consumption (economics), consumption and saving over the course of their lives. The earliest work on the subject was by Irving Fisher and Roy Harrod, who described 'hump saving', hypothesizing that savings would be highest in the middle years of a person's life as they saved for retirement. In the 1950s, more well-defined models were built on discounted utility theory and approached the question of inter-temporal consumption as a lifetime income optimization problem. Solving this problem mathematically, assuming that individuals are rational and have access to complete markets, Franco Modigliani, Modigliani & Brumberg (1954), Albert K. Ando, Albert Ando, and Milton Friedman (1957) developed what became known as the life-cycle model. See for details. The life-cycle model of consumption suggests that consumption is based on average Natural borrowing limit, lifetime income instead of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Status Quo Bias
A status quo bias or default bias is a cognitive bias which results from a preference for the maintenance of one's existing state of affairs. The current baseline (or status quo) is taken as a reference point, and any change from that baseline is perceived as a loss or gain. Corresponding to different alternatives, this current baseline or default option is perceived and evaluated by individuals as a positive. Status quo bias should be distinguished from a rational preference for the status quo, as for when the current state of affairs is more beneficial to the available alternatives, or when imperfect information is a significant problem. A large body of evidence, however, shows that status quo bias frequently affects human decision-making. Status quo bias should also be distinguished from psychological inertia, which refers to a lack of intervention in the current course of affairs. The bias intersects with other non-rational cognitive processes such as loss aversion, in which l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asset Allocation Puzzle
In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned or controlled by a business or an economic entity. It is anything (tangible or intangible) that can be used to produce positive economic value. Assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash (although cash itself is also considered an asset). The balance sheet of a firm records the monetaryThere are different methods of assessing the monetary value of the assets recorded on the Balance Sheet. In some cases, the ''Historical Cost'' is used; such that the value of the asset when it was bought in the past is used as the monetary value. In other instances, the present fair market value of the asset is used to determine the value shown on the balance sheet. value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business. ''Total assets'' can also be called the ''balance sheet total''. Assets can be grouped into two major classes: tangible assets and inta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Premium Puzzle
The equity premium puzzle refers to the inability of an important class of economic models to explain the average equity risk premium (ERP) provided by a diversified portfolio of equities over that of government bonds, which has been observed for more than 100 years. There is a significant disparity between returns produced by stocks compared to returns produced by government treasury bills. The equity premium puzzle addresses the difficulty in understanding and explaining this disparity. This disparity is calculated using the equity risk premium: The equity risk premium is equal to the difference between equity returns and returns from government bonds. It is equal to around 5% to 8% in the United States. The risk premium represents the compensation awarded to the equity holder for taking on a higher risk by investing in equities rather than government bonds. However, the 5% to 8% premium is considered to be an implausibly high difference and the equity premium puzzle refers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Dominance
Stochastic dominance is a Partially ordered set, partial order between random variables. It is a form of stochastic ordering. The concept arises in decision theory and decision analysis in situations where one gamble (a probability distribution over possible outcomes, also known as prospects) can be ranked as superior to another gamble for a broad class of decision-makers. It is based on shared preference (economics), preferences regarding sets of possible outcomes and their associated probabilities. Only limited knowledge of preferences is required for determining dominance. Risk aversion is a factor only in second order stochastic dominance. Stochastic dominance does not give a total order, but rather only a partial order: for some pairs of gambles, neither one stochastically dominates the other, since different members of the broad class of decision-makers will differ regarding which gamble is preferable without them generally being considered to be equally attractive. Through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utility Function
In economics, utility is a measure of a certain person's satisfaction from a certain state of the world. Over time, the term has been used with at least two meanings. * In a Normative economics, normative context, utility refers to a goal or objective that we wish to maximize, i.e., an objective function. This kind of utility bears a closer resemblance to the original Utilitarianism, utilitarian concept, developed by moral philosophers such as Jeremy Bentham and John Stuart Mill. * In a Positive economics, descriptive context, the term refers to an ''apparent'' objective function; such a function is Revealed preference, revealed by a person's behavior, and specifically by their preferences over Lottery (decision theory), lotteries, which can be any quantified choice. The relationship between these two kinds of utility functions has been a source of controversy among both Economics, economists and Ethics, ethicists, with most maintaining that the two are distinct but generally re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Utility Hypothesis
The expected utility hypothesis is a foundational assumption in mathematical economics concerning decision making under uncertainty. It postulates that rational agents maximize utility, meaning the subjective desirability of their actions. Rational choice theory, a cornerstone of microeconomics, builds this postulate to model aggregate social behaviour. The expected utility hypothesis states an agent chooses between risky prospects by comparing expected utility values (i.e., the weighted sum of adding the respective utility values of payoffs multiplied by their probabilities). The summarised formula for expected utility is U(p)=\sum u(x_k)p_k where p_k is the probability that outcome indexed by k with payoff x_k is realized, and function ''u'' expresses the utility of each respective payoff. Graphically the curvature of the u function captures the agent's risk attitude. For example, imagine you’re offered a choice between receiving $50 for sure, or flipping a coin to win $100 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Aversion
In cognitive science and behavioral economics, loss aversion refers to a cognitive bias in which the same situation is perceived as worse if it is framed as a loss, rather than a gain. It should not be confused with risk aversion, which describes the rational behavior of valuing an uncertain outcome at less than its expected value. When defined in terms of the pseudo-utility function as in cumulative prospect theory (CPT), the left-hand of the function increases much more steeply than gains, thus being more "painful" than the satisfaction from a comparable gain. Empirically, losses tend to be treated as if they were twice as large as an equivalent gain. Loss aversion was first proposed by Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman as an important component of prospect theory. History In 1979, Daniel Kahneman and his associate Amos Tversky originally coined the term "loss aversion" in their initial proposal of prospect theory as an alternative descriptive model of decision makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |