|
Culture Of Haiti
The culture of Haiti is a creolized blend of African, European and Taino elements due to the French colonization of Amerindian land (which was then renamed Saint-Domingue), in conjunction with the large diverse enslaved African population who had later freed themselves by a successful revolt. These attributions have largely influenced the art, cuisine, literature, music, religion as well as the languages of Haiti. Art Brilliant colors, naïve perspective, and sly humor characterize Haitian art. Big, delectable foods and lush landscapes are favorite subjects in this land. Going to market is the most social activity of country life, and figures prominently into the subject matter. Jungle animals, rituals, dances, and gods evoke the African past. Artists paint in fable as well. People are disguised as animals and animals are transformed into people. Symbols take on great meaning. For example, a rooster often represents Aristide and the red and blue colors of the flag of Hait ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual arts, visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, Composition (visual art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tropical Climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot temperatures and high humidity all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet (rainy/monsoon) season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates. There are three basic types of tropical climates within the tropical climate group: tropical rainforest climate (Af), tropical monsoon climate (Am) and Tropical savanna climate, tropical savanna or tropical wet and dry climate (Aw for dry winters, and As for dry summers), which are classified and distinguished by the precipitation levels of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Guardian Media Group, owned by the Scott Trust Limited. The trust was created in 1936 to "secure the financial and editorial independence of ''The Guardian'' in perpetuity and to safeguard the journalistic freedom and liberal values of ''The Guardian'' free from commercial or political interference". The trust was converted into a limited company in 2008, with a constitution written so as to maintain for ''The Guardian'' the same protections as were built into the structure of the Scott Trust by its creators. Profits are reinvested in its journalism rather than distributed to owners or shareholders. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. The editor-in-chief Katharine Viner succeeded Alan Rusbridger in 2015. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Open-air Treatment
Open-air treatment is the therapeutic use of fresh air and sunshine. In a hospital or sanitorium, this may be done by ensuring good ventilation in an airy, sunny room or by housing patients outdoors in tents or other open forms of accommodation. During the 20th century, such treatment was used for people with infectious respiratory diseases such as influenza or tuberculosis. In the 1960s, researchers into biological warfare found that microbes such as ''Escherichia coli'' were killed when exposed to outdoor air but that, when they were enclosed, they would remain viable for longer. They called this the open air factor but were unable to identify the exact mechanism or disinfecting agent. Open-air schools were established in several countries to provide a healthy environment for sickly children, emphasising fresh air, good food and exercise. In England, the first one opened at Bostall Heath and Woods, Bostall Wood in 1907 and, by the 1930s, there were over a hundred across ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Article 25
Article 25 is the UK’s leading international architectural NGO that builds high-quality hospitals, schools and homes in the places that need them mostRegistered charity number 1112621 Article 25 has designed and delivered over 100 projects for NGOs and governments worldwide, tackling challenges like earthquake risks, remote locations, extreme weather, and unreliable power supplies. Thanks to Article 25's work, more children are able to complete their education, healthcare is within reach of more communities, and people have safer homes that can withstand a changing climate. History Article 25 was established on 31 October 2005 by Maxwell Hutchinson as President, Dr Victoria Harris as founder-CEO and Jack Pringle as Chair. Following the Indian Ocean tsunami in 2004, the founders recognised the potential impact the built environment could have on saving lives and preventing natural hazards from turning into full-blown disasters. Originally named "Architects for Aid", the brief of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
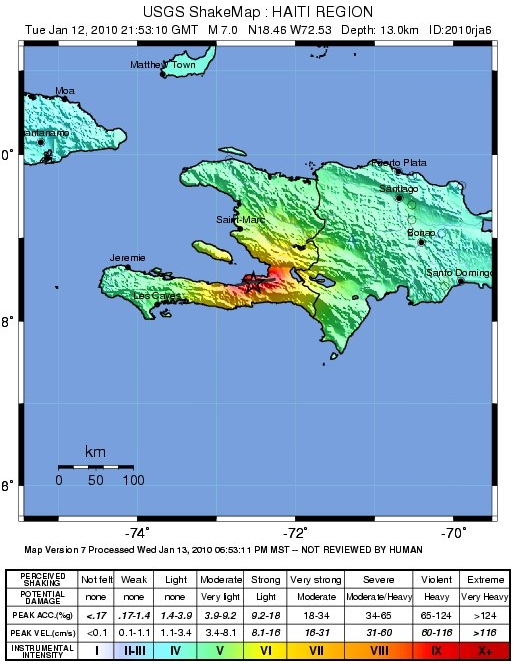
2010 Haiti Earthquake
The 2010 Haiti earthquake was a catastrophic Moment magnitude scale, magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake that struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest (department), Ouest department, approximately west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's capital. By 24 January, at least 52 aftershocks measuring 4.5 or greater had been recorded. An estimated three million people were affected by the quake. Death toll estimates range from 100,000 to about 160,000 to Haitian government figures from 220,000 to 316,000, although these latter figures are a matter of some dispute. The earthquake is the deadliest natural disaster of the 21st century for a single country. The government of Haiti estimated that 250,000 residential area, residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged. Haiti's history of External debt of Haiti, national debt, prejudicial trade policies by other countries, and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jacmel
Jacmel (; ) is a commune in southern Haiti founded by the Spanish in 1504 and repopulated by the French in 1698. It is the capital of the department of Sud-Est, 24 miles (39 km) southwest of Port-au-Prince across the Tiburon Peninsula, and has an estimated population of 40,000, while the commune of Jacmel had a population of 137,966 at the 2003 Census. The town's name is derived from its indigenous Taíno name of ''Yaquimel''. In 1925, Jacmel was dubbed as the "City of Light," becoming the first in the Caribbean to have electricity. The city is known for its well-preserved Gingerbread houses built in the early 19th century. The town has been tentatively accepted as a World Heritage Site. It sustained damage in the 2010 Haiti earthquake. Jacmel is home to the country's leading film school, the Ciné Institute. History The town was founded by the ''Compagnie de Saint-Domingue'' in 1698 as the capital of the southeastern part of the French colony Saint-Domingue. The area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Massif De La Hotte
The Massif de la Hotte () is a mountain range in southwestern Haiti, on the Tiburon Peninsula, Haiti, Tiburon Peninsula west of the Petit-Goâve-Jacmel fault. About 2.5 million years ago, Massif de la Hotte was separated from the Massif de la Selle by a deep, wide sea channel, and formed a separate island. This resulted in a hotbed of endemism in la Hotte's bird, plant, and reptile communities. The Massif de la Hotte is subdivided into the Oriental la Hotte in the East, the central la Hotte, and the Occidental la Hotte on the western tip of the Tiburon peninsula. The Occidental la Hotte is relatively remote and is one of the most biologically diverse and significant areas of all of Hispaniola. It also supports some of the last stands of Haiti's dense cloud forest on its peaks. Biodiversity and conservation Occidental la Hotte is the highest and biologically most diverse part of Massif de la Hotte. Rising to a peak level of approximately 7700 ft (2347 m) in Pic Macaya, Haiti's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site is nominated by its host country and determined by the UNESCO's World Heritage Committee to be a unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable, having a special cultural or physical significance, and to be under a sufficient system of legal protection. World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains or wilderness areas, and others. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humankind and serve as evidence of humanity's intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |