|
Creaser's Mud Turtle
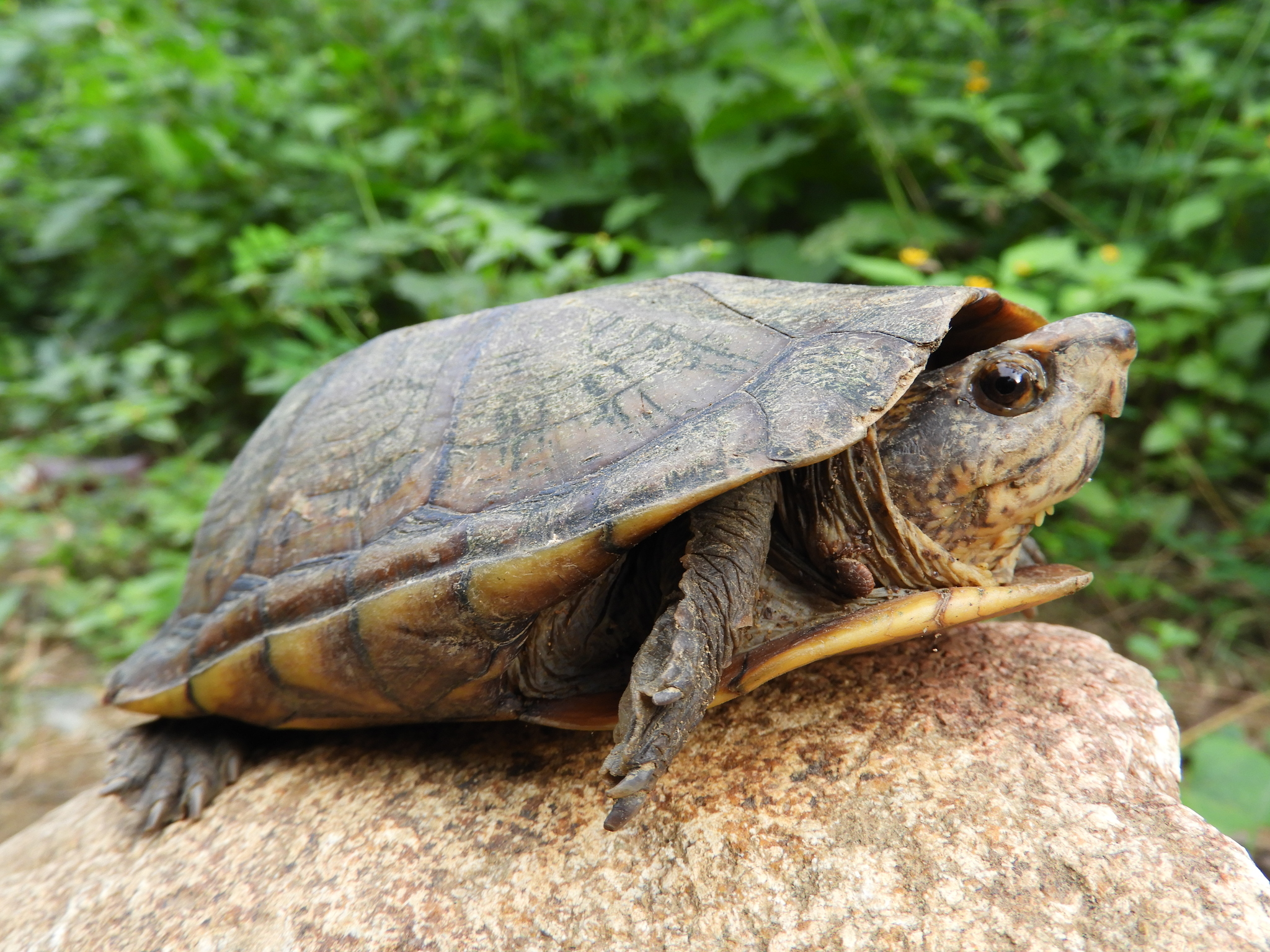
Creaser's mud turtle (''Kinosternon creaseri'') is a species of mud turtle in the Family (biology), family Kinosternidae. The species is Endemism, endemic to the Yucatán Peninsula in southeastern Mexico. The Specific name (zoology), specific name, ''creaseri'', is in honor of Americans, American Zoology, zoologist Edwin Phillip Creaser (1907–1981). Geographic range ''K. creaseri'' is found in the Mexican states of Campeche, Quintana Roo, and Yucatan. www.reptile-database.org. A 1988 study found that the densest population occurred in Quintana Roo, as the state had been subjected to less deforestation than Campeche or Yucatán. Habitat The preferred natural habitat of ''K. creaseri'' is small temporary pools of water in forests, shrubland, and freshwater wetlands, although they may occasionally be found in permanent pools of water as well. These temporary pools of water are generally devoid of fish. Description The species is of average size for the genus ''Kinosternon''. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucatán
Yucatán, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate municipalities, and its capital city is Mérida. Located on the northern part of the Yucatán Peninsula, it is bordered by the states of Campeche to the southwest and Quintana Roo to the southeast, with the Gulf of Mexico off its northern coast. Before the arrival of Spaniards, the peninsula was a very important region for the Maya civilization that reached the peak of its development here, where the Maya founded the cities of Chichen Itza, Izamal, Motul, Mayapan, Ek' Balam, and Ichkanzihóo (also called T'ho), now Mérida. After the Spanish conquest of Yucatán (early 16th to late 17th centuries), the Yucatán Peninsula became a single administrative and political entity, the Captaincy General of Yucatán. Following Mexican independence in 1821 the local Governor proclaimed indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviparity
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings known as hatchlings with little or no embryonic development within the mother. This is the reproductive method used by most animal species, as opposed to viviparous animals that develop the embryos internally and metabolically dependent on the maternal circulation, until the mother gives birth to live juveniles. Ovoviviparity is a special form of oviparity where the eggs are retained inside the mother (but still metabolically independent), and are carried internally until they hatch and eventually emerge outside as well-developed juveniles similar to viviparous animals. Modes of reproduction The traditional modes of reproduction include oviparity, taken to be the ancestral condition, traditionally where either unfertilised oocytes or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creaser's Mud Turtle (Kinosternon Creaseri)
Creaser's mud turtle (''Kinosternon creaseri'') is a species of mud turtle in the family Kinosternidae. The species is endemic to the Yucatán Peninsula in southeastern Mexico. The specific name, ''creaseri'', is in honor of American zoologist Edwin Phillip Creaser (1907–1981). Geographic range ''K. creaseri'' is found in the Mexican states of Campeche, Quintana Roo, and Yucatan. www.reptile-database.org. A 1988 study found that the densest population occurred in Quintana Roo, as the state had been subjected to less deforestation than Campeche or Yucatán. Habitat The preferred natural habitat of ''K. creaseri'' is small temporary pools of water in forests, shrubland, and freshwater wetlands, although they may occasionally be found in permanent pools of water as well. These temporary pools of water are generally devoid of fish. Description The species is of average size for the genus ''Kinosternon''. Males are slightly larger than females. The average carapace length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinosternon Creaseri 416914500
''Kinosternon'' is a genus of small aquatic turtles from the Americas known commonly as mud turtles. Geographic range They are found in the United States, Mexico, Central America, and South America. The greatest species richness is in Mexico, and only three species ('' K. dunni'', '' K. leucostomum'', and '' K. scorpioides'') are found in South America. Description They are very similar to the musk turtles, but generally smaller in size, and their carapaces are not as highly domed. Diet All mud turtles are carnivorous, consuming various aquatic invertebrates (especially molluscs and worms) , fish, and even carrion. Behavior Mud turtles live in the ground layer on the bed of bodies of slowly-flowing or still water. By burrowing deeply into mud, mud turtles are protected from danger. They occasionally like to bask in the sun. Species Extant * Central Chiapas mud turtle - ''K. abaxillare'' (Baur, 1925) * Tabasco mud turtle - ''K. acutum'' Gray, 1831 * Alamos mud turt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aestivation
Aestivation ( (summer); also spelled estivation in American English) is a state of animal dormancy, similar to hibernation, although taking place in the summer rather than the winter. Aestivation is characterized by inactivity and a lowered metabolic rate, that is entered in response to high temperatures and arid conditions. It takes place during times of heat and dryness, which are often the summer months. Invertebrate and vertebrate animals are known to enter this state to avoid damage from high temperatures and the risk of desiccation. Both terrestrial and aquatic animals undergo aestivation. Fossil records suggest that aestivation may have evolved several hundred million years ago. Physiology Organisms that aestivate appear to be in a fairly "light" state of dormancy, as their physiological state can be rapidly reversed, and the organism can quickly return to a normal state. A study done on '' Otala lactea'', a snail native to parts of Europe and Northern Africa, shows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastron
The turtle shell is a shield for the ventral and dorsal parts of turtles (the Order (biology), order Testudines), completely enclosing all the turtle's vital organs and in some cases even the head. It is constructed of modified bony elements such as the ribs, parts of the pelvis and other bones found in most reptiles. The bone of the shell consists of both skeletal and dermal bone, showing that the complete enclosure of the shell likely evolved by including dermal armor into the rib cage. The turtle's shell is an important study, not just because of the apparent protection it provides for the animal but also as an identification tool, in particular with fossils, as the shell is one of the likely parts of a turtle to survive fossilization. Hence understanding the shell structure in living species provides comparable material with fossils. The shell of the hawksbill turtle, among other species, has been used as a material for a wide range of small decorative and practical items sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabasco Mud Turtle
The Tabasco mud turtle (''Kinosternon acutum''), commonly known as pochitoque in Tabasco, Mexico, is a small turtle which belongs to the family Kinosternidae. It can be found in central Veracruz, Tabasco, northern Guatemala and Belize. This turtle lives in small streams, marshes and ponds. Its feeding habits are mainly carnivorous and it is a nocturnal animal. Although this turtle doesn't have a wide range it can be common at some sites. In Tabasco this turtle is an important part of its popular culture as well as being an ingredient in Tabasco's gastronomy in spite of its special protected status. File:Kinosternon acutum 61641628.jpg File:Kinosternon acutum 61641648.jpg File:Kinosternon acutum 61641541.jpg Pochitoque in Tabasco's culture In this south Mexican state this turtle has a significant importance. Since ancient time Chontales have used it as an ingredient in their traditional kitchen so next to other turtle species ( jicotea and mojina), pochitoque has a huge dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and taxon B are sister groups to each other. Taxa A and B, together with any other extant or extinct descendants of their most recent common ancestor (MRCA), form a monophyletic group, the clade AB. Clade AB and taxon C are also sister groups. Taxa A, B, and C, together with all other descendants of their MRCA form the clade ABC. The whole clade ABC is itself a subtree of a larger tree which offers yet more sister group relationships, both among the leaves and among larger, more deeply rooted clades. The tree structure shown connects through its root to the rest of the universal tree of life. In cladistic standards, taxa A, B, and C may represent specimens, species, genera, or any other taxonomic units. If A and B are at the same taxono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion Mud Turtle
The scorpion mud turtle or Tabasco mud turtle (''Kinosternon scorpioides'') is a species of mud turtle in the family Kinosternidae. It is found in Mexico, Central and South America. Description The scorpion mud turtle is a medium to large kinosternid (mud turtle) with a domed, oval upper shell 92–270 mm (3.6–10.6 in) long. Males regularly exceed 200 mm. The scorpion mud turtle is a highly aquatic, adaptable kinosternid that will live in almost any body of water. Subspecies Diet It is primarily omnicarnivorous, a glutton, and feeds on a wide variety of aquatic invertebrates (such as insects and their larvae, spiders, shrimp, crabs, snails and worms) and vertebrates (such as fish and frogs), as well as carrion and bird eggshells. It also feeds on plant material such as algae, fruits, flowers, Nut (fruit), nuts, seeds and aquatic plants. In captivity, poorly fed ''K. scorpioides'' can be cannibalistic, biting off the toes and limbs of conspecifics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinosternon
''Kinosternon'' is a genus of small aquatic turtles from the Americas known commonly as mud turtles. Geographic range They are found in the United States, Mexico, Central America, and South America. The greatest species richness is in Mexico, and only three species (''Dunn's mud turtle, K. dunni'', ''white-lipped mud turtle, K. leucostomum'', and ''scorpion mud turtle, K. scorpioides'') are found in South America. Description They are very similar to the Sternotherus, musk turtles, but generally smaller in size, and their carapaces are not as highly domed. Diet All mud turtles are carnivorous, consuming various aquatic invertebrates (especially molluscs and worms) , fish, and even carrion. Behavior Mud turtles live in the ground layer on the bed of bodies of slowly-flowing or still water. By burrowing deeply into mud, mud turtles are protected from danger. They occasionally like to bask in the sun. Species Extant *Central Chiapas mud turtle - ''K. abaxillare'' (Baur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |