|
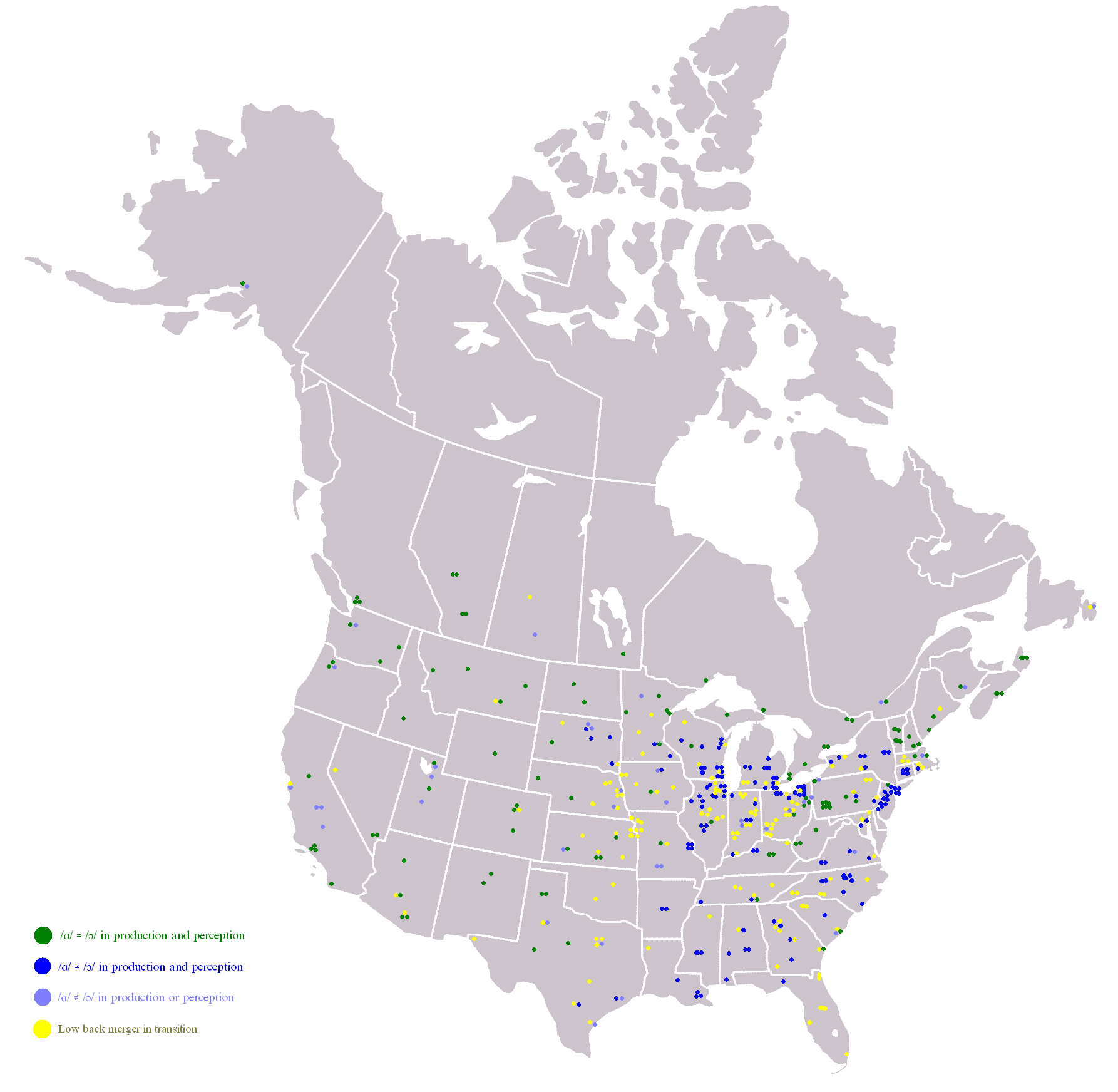
Cot–caught Merger
The ''cot''–''caught'' merger, also known as the merger or low back merger, is a sound change present in some dialects of English where speakers do not distinguish the vowel phonemes in words like ''cot'' versus ''caught''. ''Cot'' and ''caught'' (along with ''bot'' and ''bought'', ''pond'' and ''pawned'', etc.) is an example of a minimal pair that is lost as a result of this sound change. The phonemes involved in the ''cot''–''caught'' merger, the low back vowels, are typically represented in the International Phonetic Alphabet as and or, in most United States English, as and . The merger is typical of most Indian, Canadian, and Scottish English dialects as well as some Irish and U.S. English dialects. An additional vowel merger, the ''father''–''bother'' merger, which spread through North America in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, has resulted today in a three-way merger in which most Canadian and many U.S. accents have no vowel difference in words lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
In historical linguistics, a sound change is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (''phonological change''), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North–force Merger
In English, many vowel shifts affect only vowels followed by in rhotic dialects, or vowels that were historically followed by that has been elided in non-rhotic dialects. Most of them involve the merging of vowel distinctions, so fewer vowel phonemes occur before than in other positions of a word. Overview In rhotic dialects, is pronounced in most cases. In General American English (GA), is pronounced as an approximant or in most positions, but after some vowels, it is pronounced as ''r''-coloring. In Scottish English, is traditionally pronounced as a flap or trill , and there are no ''r''-colored vowels. In non-rhotic dialects like Received Pronunciation (RP), historic is elided at the end of a syllable, and if the preceding vowel is stressed, it undergoes compensatory lengthening or breaking (diphthongization). Thus, words that historically had often have long vowels or centering diphthongs ending in a schwa , or a diphthong followed by a schwa. * ''earth'': ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western American English
Western American English (also known as Western U.S. English) is a variety of American English that largely unites the entire Western United States as a single dialect region, including the states of California, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, and Montana. It also generally encompasses Washington, Oregon, and Idaho, some of whose speakers are classified under Pacific Northwest English. The West was the last area in the United States to be reached during the gradual westward expansion of settlement by English speakers and its history shows considerable mixing and leveling of the linguistic patterns of other regions. Therefore, since the settlement populations are relatively young when compared with other regions, the American West continues to be a dialect region in formation. According to the 2006 '' Atlas of North American English'', as a very broad generalization, Western U.S. accents are differentiated from Southern U.S. accents in maintaining as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England English
New England English is, collectively, the various distinct dialects and varieties of American English originating in the New England area. Most of eastern and central New England once spoke the " Yankee dialect", some of whose accent features still remain in Eastern New England today, such as "R-dropping" (though this and other features are now receding among younger speakers). Accordingly, one linguistic division of New England is into Eastern versus Western New England English, as defined in the 1939 '' Linguistic Atlas of New England'' and the 2006 '' Atlas of North American English'' (ANAE). The ANAE further argues for a division between Northern versus Southern New England English, especially on the basis of the cot–caught merger and fronting (applying twice, for example, in the phrase ''Park the car''). The ANAE also categorizes the strongest differentiated New England accents into four combinations of the above dichotomies, simply defined as follows: * Northeastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh English
Western Pennsylvania English, known more narrowly as Pittsburgh English or popularly as Pittsburghese, is a dialect of American English native primarily to the western half of Pennsylvania, centered on the city of Pittsburgh, but potentially appearing in some speakers as far north as Erie County, as far east as Harrisburg, as far south as Clarksburg, West Virginia, and as far west as Youngstown, Ohio. Commonly associated with the working class of Pittsburgh, users of the dialect are colloquially known as "Yinzers". Overview Scotch-Irish American, Scots-Irish, Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania Dutch, Polish people, Polish, Ukrainians, Ukrainian and Croats, Croatian immigrants to the area all provided certain loanwords to the dialect (see "Vocabulary" below). Many of the sounds and words found in the dialect are popularly thought to be unique to Pittsburgh, but that is a misconception since the dialect resides throughout the greater part of western Pennsylvania and the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American English
North American English (NAmE) encompasses the English language as spoken in both the United States and Canada. Because of their related histories and cultures, plus the similarities between the pronunciations (accents), vocabulary, and grammar of American English, U.S. English and Canadian English, linguists often group the two together. Canadians are generally tolerant of both British and American spellings, although certain words always take British spellings (e.g., ''cheque'') and others American spellings (e.g., ''tire'' rather than ''tyre''). Dialects of English spoken by United Empire Loyalists who fled the American Revolution (1775–1783) have had a large influence on Canadian English from its early roots. Some terms in North American English are used almost exclusively in Canada and the United States (for example, the terms ''diaper'' and ''gasoline'' are widely used instead of ''nappy'' and ''petrol''). Although many English speakers from outside North America regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulster English
Ulster English, also called Northern Hiberno-English or Northern Irish English, is the variety of English spoken mostly around the Irish province of Ulster and throughout Northern Ireland. The dialect has been influenced by the local Ulster dialect of the Scots language, brought over by Scottish settlers during the Plantation of Ulster and subsequent settlements throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. It also coexists alongside the Ulster dialect of the Irish (Gaelic) language, which also influenced the dialect. The two major divisions of Ulster English are ''Mid-Ulster English'', the most widespread variety, and ''Ulster Scots English'', spoken in much of northern County Antrim along a continuum with the Scots language. ''South Ulster English'' is a geographically transitional dialect between Mid-Ulster English and English spoken south of Ulster, in the Republic of Ireland. Phonology In general, Ulster English speakers' declarative sentences (with typical grammat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish English
Hiberno-English or Irish English (IrE), also formerly sometimes called Anglo-Irish, is the set of dialects of English native to the island of Ireland. In both the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland, English is the first language in everyday use and, alongside the Irish language, one of two official languages (with Ulster Scots, in Northern Ireland, being yet another local language). The writing standards of Irish English, such as its spelling, align with British English. But the diverse accents and some of the grammatical structures and vocabulary of Irish English are unique, including certain notably conservative phonological features and vocabulary: those that are no longer common in the dialects of England or North America. It shows significant influences from the Irish language and, in the north, the Scots language. Phonologists today often divide Irish English into four or five overarching dialects or accents: Ulster or Northern Irish accents, Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad And General Accents
The distinction between broad and general accents is a socio-economic-linguistic contrast made between different accents of the same language, typically spoken in a single geographical location and perceived by the language users themselves: *A broad accent (sometimes equated with a local or vernacular accent) is popularly perceived as very "strong" or "thick", highly recognizable to a particular population (typically within a particular region), and often linguistically conservative; almost always, it is the accent associated with the traditional speech of the local people or the working class (whether rural or urban) of a given region. *A general accent (sometimes equated with a standard accent) is perceived as geographically more widespread, not particularized to a certain population or location, sounding more "neutral" or "weak", and historico-linguistically innovative; it is typically associated with the middle class of a given region, a growing process of standardization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyme
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds (usually the exact same phonemes) in the final Stress (linguistics), stressed syllables and any following syllables of two or more words. Most often, this kind of rhyming (''perfect rhyming'') is consciously used for a musical or aesthetic effect in the final position of Line (poetry), lines within poems or songs. More broadly, a rhyme may also variously refer to other types of similar sounds near the ends of two or more words. Furthermore, the word ''rhyme'' has come to be sometimes used as a pars pro toto, shorthand term for any brief poem, such as a nursery rhyme or Balliol rhyme. Etymology The word derives from or , which might be derived from , a Germanic term meaning "series", or "sequence" attested in Old English (Old English: meaning "enumeration", series", or "numeral") and , ultimately cognate to , ( "number"). Alternatively, the Old French words may derive from , from (, rhythm). The spelling ''rhyme'' (from the original r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophone
A homophone () is a word that is pronounced the same as another word but differs in meaning or in spelling. The two words may be spelled the same, for example ''rose'' (flower) and ''rose'' (past tense of "rise"), or spelled differently, as in ''rain'', ''reign'', and ''rein''. The term ''homophone'' sometimes applies to units longer or shorter than words, for example a phrase, letter, or groups of letters which are pronounced the same as a counterpart. Any unit with this property is said to be ''homophonous'' (). Homophones that are spelled the same are both homographs and homonyms. For example, the word ''read'', in "He is well ''read''" and in "Yesterday, I ''read'' that book". Homophones that are spelled differently are also called heterographs, e.g. ''to'', ''too'', and ''two''. Wordplay and games Homophones are often used to create puns and to deceive the reader (as in crossword puzzles) or to suggest multiple meanings. The last usage is common in poetry and creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoneme
A phoneme () is any set of similar Phone (phonetics), speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible Phonetics, phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word from another. All languages contain phonemes (or the spatial-gestural equivalent in sign languages), and all spoken languages include both consonant and vowel phonemes; phonemes are primarily studied under the branch of linguistics known as phonology. Examples and notation The English words ''cell'' and ''set'' have the exact same sequence of sounds, except for being different in their final consonant sounds: thus, versus in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), a writing system that can be used to represent phonemes. Since and alone distinguish certain words from others, they are each examples of phonemes of the English language. Specifically they are consonant phonemes, along with , while is a vowel phoneme. The spelling of Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |