|
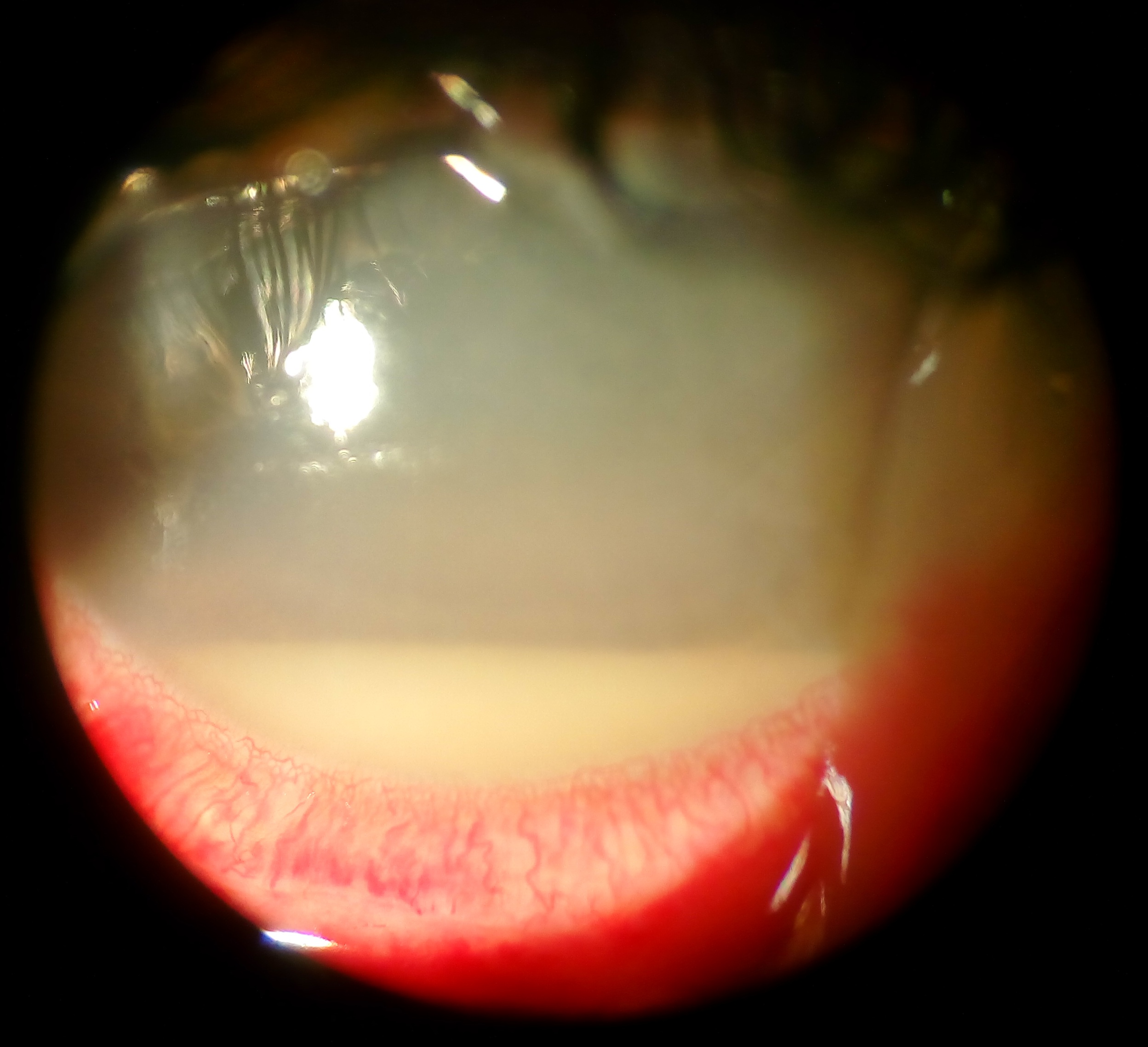
Corneal Ulcer
Corneal ulcer, often resulting from keratitis is an inflammatory or, more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and in farming. In developing countries, children afflicted by vitamin A deficiency are at high risk for corneal ulcer and may become blind in both eyes persisting throughout life. In ophthalmology, a corneal ulcer usually refers to having an infection, while the term corneal abrasion refers more to a scratch injury. Types Superficial and deep corneal ulcers Corneal ulcers are a common human eye disease. They are caused by trauma, particularly with vegetable matter, as well as chemical injury, contact lenses and infections. Other eye conditions can cause corneal ulcers, such as entropion, distichiasis, corneal dystrophy, and keratoconjunctivitis sicca (dry eye). Many micro-organisms cause infective corneal ulce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Keratitis
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired eyesight, photophobia (light sensitivity), red eye and a 'gritty' sensation. Diagnosis of infectious keratitis is usually made clinically based on the signs and symptoms as well as eye examination, but corneal scrapings may be obtained and evaluated using microbiological culture or other testing to identify the causative pathogen. Classification (by chronicity) Acute * Acute epithelial keratitis * Nummular keratitis * Interstitial keratitis * Disciform keratitis Chronic * Neurotrophic keratitis * Mucous plaque keratitis Classification (infective) Viral The most common causes of viral keratitis include herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV), which cause herpes simplex keratitis and herpes zoster keratitis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterococci
''Enterococcus'' is a large genus of lactic acid bacteria of the phylum Bacillota. Enterococci are Gram-positive cocci that often occur in pairs (diplococci) or short chains, and are difficult to distinguish from streptococci on physical characteristics alone. Two species are common commensal organisms in the intestines of humans: '' E. faecalis'' (90–95%) and '' E. faecium'' (5–10%). Rare clusters of infections occur with other species, including '' E. durans'' , ''E. casseliflavus'', '' E. gallinarum'', and ''E. raffinosus''. Physiology and classification Enterococci are facultative anaerobic organisms, i.e., they are capable of cellular respiration in both oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environments. Though they are not capable of forming spores, enterococci are tolerant of a wide range of environmental conditions: extreme temperature (10–45 °C), pH (4.6–9.9), and high sodium chloride concentrations. ''E. faecium'' and ''E. faecalis'' can be differentiated bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * '' Aviadenovirus'' * '' Barthadenovirus'' * '' Ichtadenovirus'' * ''Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * '' Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Zoster
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster or zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area. Other common symptoms are fever, headache, and tiredness. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks, but some people develop ongoing nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with poor immune function the rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox has resolved, the virus can remain dormant (inactive) in human n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
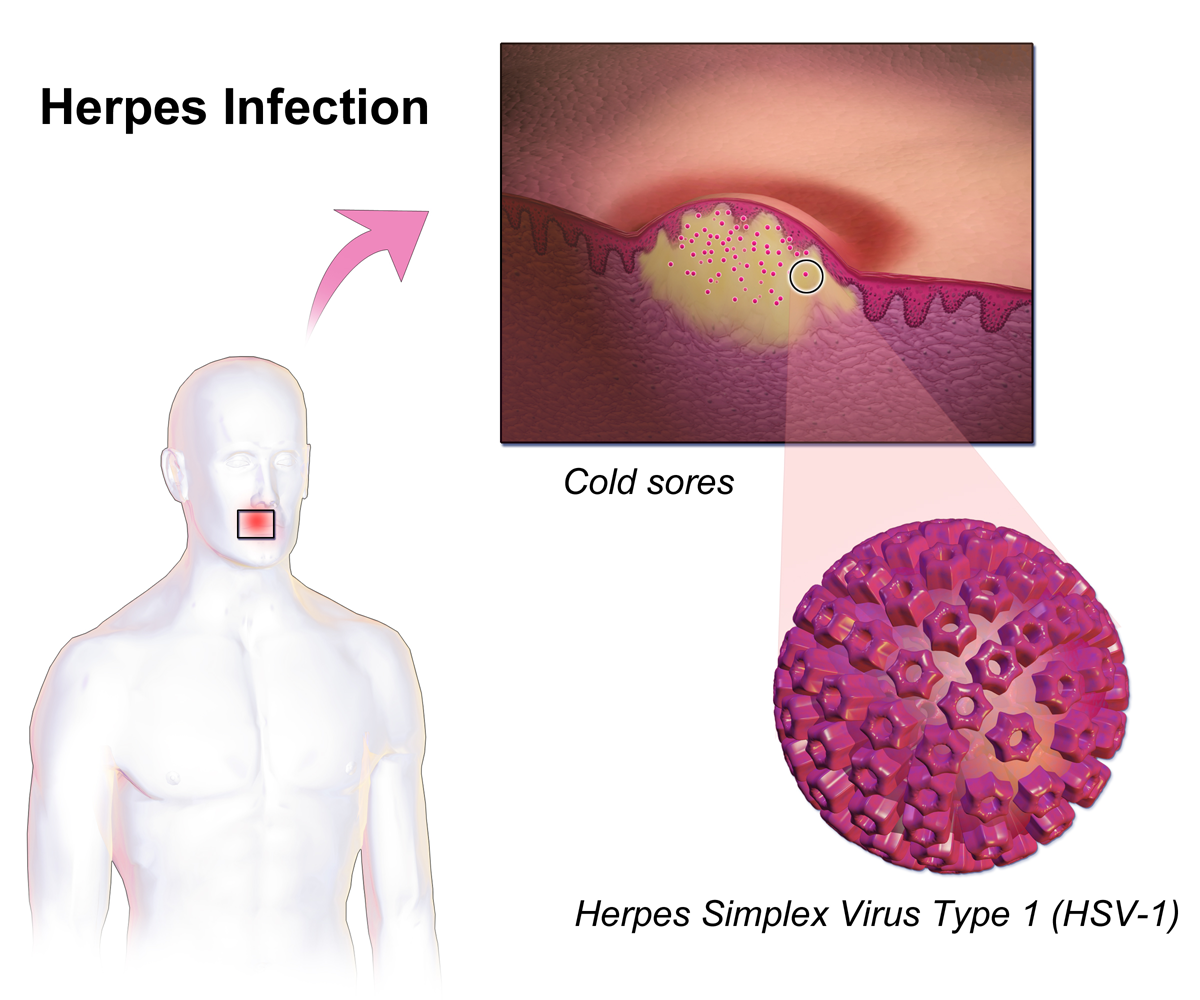
Herpes Simplex
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral disease, viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are Cold sore, oral herpes and genital herpes, though Herpes simplex#Types of herpes, other forms also exist. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups, often called cold sores or fever blisters, or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypopyon
Hypopyon is a medical condition involving Inflammation#Cellular component, inflammatory cells in the anterior chamber of the human eye, eye. It is an exudate rich in white blood cells, seen in the anterior chamber, usually accompanied by redness of the conjunctiva and the underlying episclera. It is a sign of inflammation of the anterior uvea and iris (anatomy), iris, i.e. iritis, which is a form of uveitis, anterior uveitis. The exudate settles at the dependent aspect of the eye due to gravity. It can be sterile (in bacterial corneal ulcer) or not sterile (fungal corneal ulcer). Differential diagnosis Hypopyon can be present in a corneal ulcer. It can occur as a result of Behçet's disease, endophthalmitis, panuveitis/panophthalmitis, or adverse reactions to some drugs (such as rifabutin). Hypopyon is also known as ''sterile pus'' because it occurs due to the release of toxins and not by the actual invasion of pathogens. The toxins secreted by the pathogens mediate the outpouri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
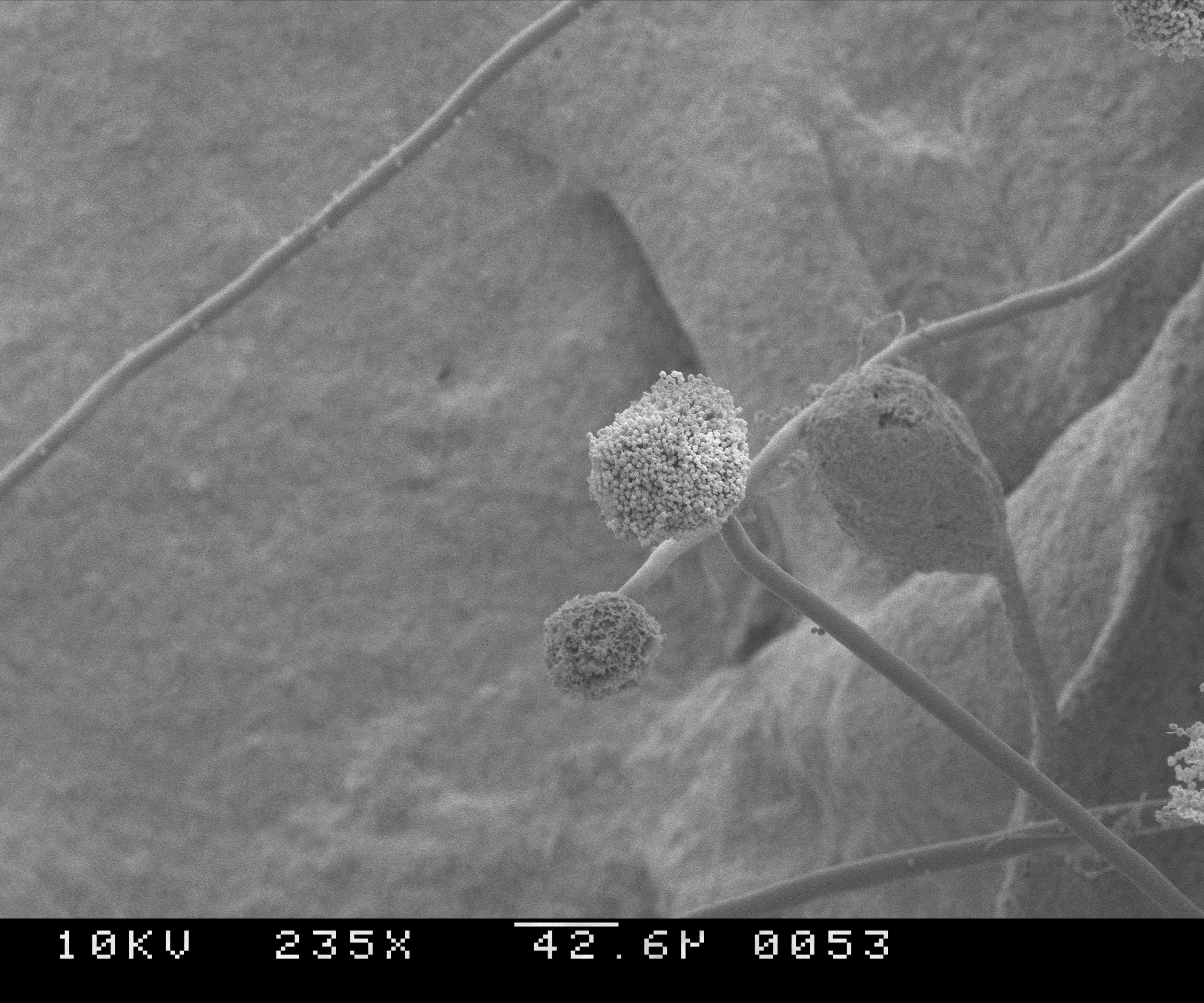
Mucor
''Mucor'' is a microbial genus of approximately 40 species of molds and dimorphic fungi in the family Mucoraceae. The genus includes both pathogenic and avirulent species, and some members of it can be utilized in biotechnical applications. These fungi are commonly found in soil, digestive systems, plant surfaces, some cheeses like Tomme de Savoie, rotten vegetable matter and iron oxide residue in the biosorption process. Description Colonies of this fungal genus are typically yellow, beige or grey. They are characterized by rapid growth and sporulation in high aw environments, and they reproduce both sexually and asexually. ''Mucor'' spores or sporangiospores can be simple or branched and form apical, globular sporangia that are supported and elevated by a column-shaped columella. ''Mucor'' species can be differentiated from molds of the genera ''Absidia'', '' Rhizomucor'', and ''Rhizopus'' by the shape and insertion of the columella, and the lack of stolons and rhizoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizopus
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some ''Rhizopus'' species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species. ''Rhizopus'' species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, spores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, a zygosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candida (genus)
''Candida'' is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeasts. The genus ''Candida'' encompasses about 200 species. Many species are harmless Commensalism, commensals or endosymbionts of hosts including humans. When Mucous membrane, mucosal barriers are disrupted or the immune system is compromised, however, they can invade and cause disease, known as an opportunistic infection. Candida is located on most mucosal surfaces and mainly the gastrointestinal tract, along with the skin. ''Candida albicans'' is one of the most commonly isolated species and can cause infections (candidiasis or thrush) in humans and other animals. In yeast in winemaking, winemaking, some species of ''Candida'' can potentially wine fault, spoil wines. Many species are found in gut flora, including ''C. albicans'' in mammalian hosts, whereas others live as endosymbionts in insects. Systemic disease, Systemic infections of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusarium
''Fusarium'' (; ) is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these ''Fusarium'' species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless (some existing on the skin as commensal members of the skin flora), some ''Fusarium'' species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals. The name of ''Fusarium'' comes from Latin ''fusus'', meaning a spindle. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the genus is complex. A number of different schemes have been used, and up to 1,000 species have been identified at times, with approaches varying between wide and narrow concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus
'''' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an '' aspergillum'' (holy water sprinkler), from Latin ''spargere'' (to sprinkle), and named the genus accordingly. Aspergillum is an asexual spore-forming structure common to all ''Aspergillus'' species; around one-third of species are also known to have a sexual stage. While some species of ''Aspergillus'' are known to cause fungal infections, others are of commercial importance. Taxonomy Species In March 2010, ''Aspergillus'' covered 837 species of fungi. Notable species placed in Aspergillus include: * '' Aspergillus flavus'' is a notable plant pathogen impacting crop yields and a common cause of aspergillosis. * '' Aspergillus fumigatus'' is the most common cause of aspergillosis in individuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Trachomatis
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' () is a Gram-negative, Anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium responsible for Chlamydia infection, chlamydia and trachoma. ''C. trachomatis'' exists in two forms, an extracellular infectious elementary body (EB) and an intracellular non-infectious reticulate body (RB). The EB attaches to host cells and enter the cell using Effector (biology), effector proteins, where it transforms into the metabolically active RB. Inside the cell, RBs rapidly replicate before transitioning back to EBs, which are then released to infect new host cells. The earliest description of ''C. trachomatis'' was in 1907 by Stanislaus von Prowazek and Ludwig Halberstädter as a protozoan. It was later thought to be a virus due to its small size and inability to grow in laboratories. It was not until 1966 when it was discovered as a bacterium by Electron microscope, electron microscopy after its internal structures were visually observed. There are currently 18 Serotype, serovars of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |