|
Control Unit (other)
A control unit (CU) is a central, sometimes distributed but clearly distinguishable, part of a mechanism that controls its operation, for example in a computer or a motor vehicle. Control unit may refer to: *Control unit, a component of a computer's central processing unit *Control unit, a special area of a prison that is used to keep prisoners in solitary confinement (also called a "segregation unit") *Another name for a Controller * Multipoint control unit, a device commonly used to bridge videoconferencing connections *Packet control unit, performs some of the processing tasks of a base station subsystem *Premises control unit, the "brain" of a burglar alarm *Telecommunication control unit, a device attached to a computer multiplexer channel which supports multiple terminals *Camera control unit, typically part of a live television broadcast "chain" *Electronic control unit, an embedded system that controls electrical systems in a motor vehicle ** Engine control unit, an electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Unit
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. A CU typically uses a binary decoder to convert coded instructions into timing and control signals that direct the operation of the other units (memory, arithmetic logic unit and input and output devices, etc.). Most computer resources are managed by the CU. It directs the flow of data between the CPU and the other devices. John von Neumann included the control unit as part of the von Neumann architecture. In modern computer designs, the control unit is typically an internal part of the CPU with its overall role and operation unchanged since its introduction. Multicycle control units The simplest computers use a multicycle microarchitecture. These were the earliest designs. They are still popular in the very smallest computers, such as the embedded systems that operate machinery. In a multicycle computer, the control unit often steps through the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which inmates (or prisoners) are confined against their will and usually denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Prisons are most commonly used within a criminal justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those pleading or being found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment. In simplest terms, a prison can also be described as a building in which people are legally held as a punishment for a crime they have committed. Prisons can also be used as a tool of political repression by authoritarian regimes. Their perceived opponents may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Controller (computing) (other)
In computer hardware, a controller may refer to: * Memory controller, a unit that manages access to memory * Game controller, a device by which the user controls the operation of the computer * Host controller * Network controller * Graphics controller or video display controller * SCSI host bus adapter * Network interface controller (NIC) * Parallel port controller * Microcontroller unit (MCU) * Keyboard controller * Programmable Interrupt Controller * Northbridge (computing) * Southbridge (computing) * Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) communications controller chip * Peripheral DMA controller * Floppy disk controller * Disk array controller, also known as a RAID controller, a type of storage controller * Flash controller, or SSD controller, which manages flash memory * Terminal Access Controller * IBM 2821 Control Unit, used to attach card readers, punches and line printers to IBM System/360 and IBM System/370 computers * IBM 270x and IBM 37xx, used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Station Subsystem
The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network. Base transceiver station The base transceiver station, or BTS, contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving radio signals ( transceivers), antennas, and equipment for encrypting and decrypting communications with the base station controller (BSC). Typically a BTS for anything other than a picocell will have several transceivers (TRXs) which allow it to serve several different frequencies and different sectors of the cell (in the case of sectorised base stations). A BTS is controlled by a parent BSC via the "base station control function" (BCF). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burglar Alarm
A security alarm is a system designed to detect intrusion, such as unauthorized entry, into a building or other areas such as a home or school. Security alarms used in residential, commercial, industrial, and military properties protect against burglary (theft) or property damage, as well as personal protection against intruders. Security alerts in neighborhoods show a connection with diminished robbery. Car alarms likewise help protect vehicles and their contents. Prisons also use security systems for the control of inmates. Some alarm systems serve a single purpose of burglary protection; combination systems provide fire and intrusion protection. Intrusion-alarm systems are combined with closed-circuit television surveillance (CCTV) systems to record intruders' activities and interface to access control systems for electrically locked doors. There are many types of security systems. Homeowners typically have small, self-contained noisemakers. These devices can also be comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunication Control Unit
A telecommunication control unit (TCU), line control unit, or terminal control unit (although terminal control unit may also refer to a terminal ''cluster controller'') is a Front-end processor for mainframes and some minicomputers which supports attachment of one or more telecommunication lines. TCUs free processors from handling the data coming in and out of RS-232 ports. The TCU can support multiple terminals, sometimes hundreds. Many of these TCUs can support RS-232 when it is required, although there are other serial interfaces as well. The advent of ubiquitous TCP/IP has reduced the need for telecommunications control units. See also * Terminal access controller * IBM 270x * IBM 3705 Communications Controller * IBM 3720 * IBM 3745 The IBM 3745 is the latest and last of a 37xx family of communications controllers for the IBM mainframe environment. As of mid-2009 there were an estimated 7,000+ of the larger 3745 models still in active production status, down from 20,000 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera Control Unit
The camera control unit (CCU) is typically part of a live television broadcast chain. It is responsible for powering the professional video camera, handling signals sent over the camera cable to and from the camera, and can be used to control various camera parameters remotely. History Before cameras became self-contained units, broadcast cameras required vast racks of control units just to generate a usable picture. In outside broadcast production, these racks took up an entire section of the OB truck and were operated by a small team of skilled engineers. These vision engineers had two roles. Firstly, they set up the CCUs at the start of a production and ensured that the picture created was of broadcast quality. This process included a lengthy alignment process in which the vision engineer would work with the camera operator, to adjust the settings on both the actual camera and the CCU in tandem. During production, it was the vision engineers job to operate the CCUs and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
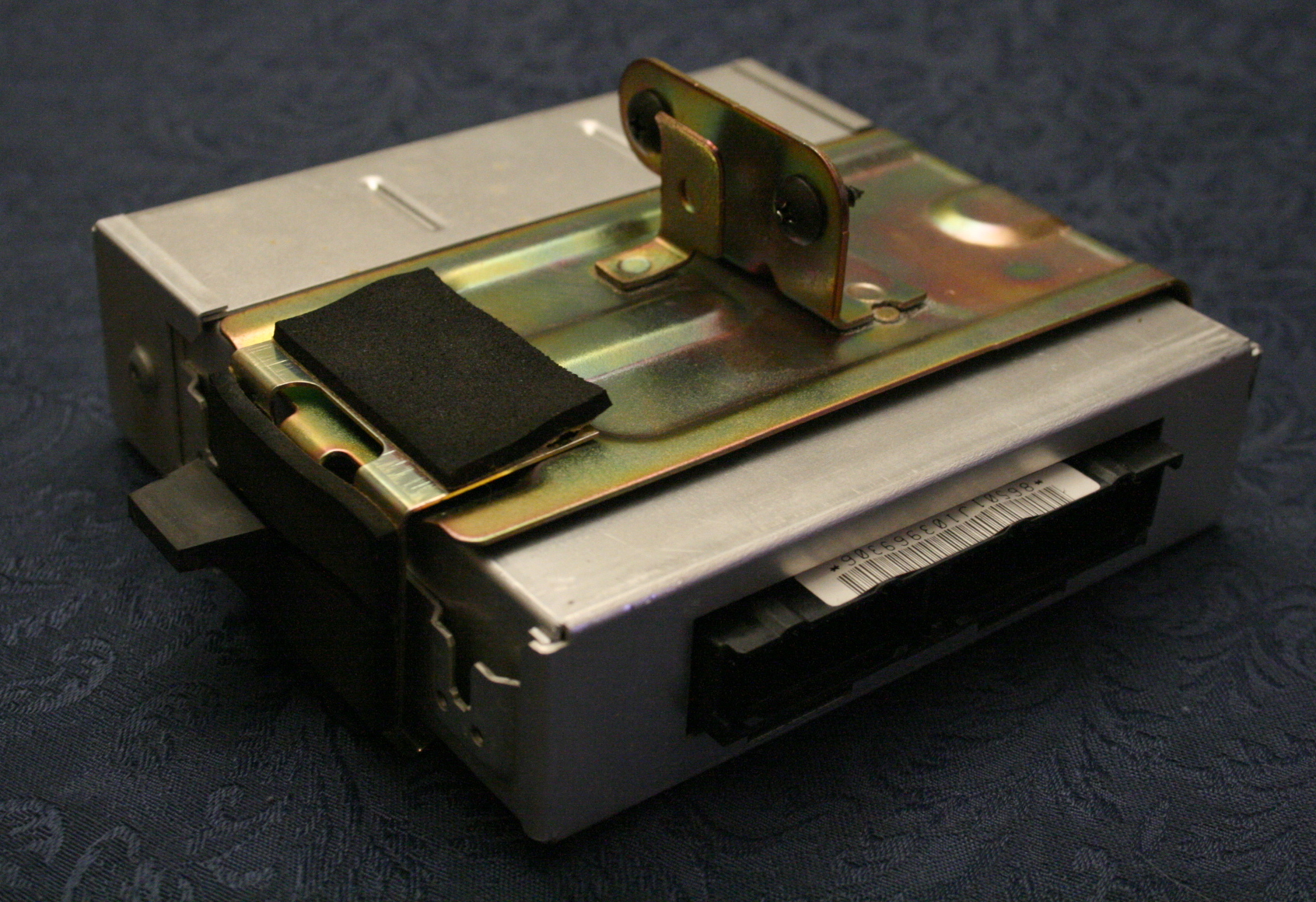
Electronic Control Unit
An electronic control unit (ECU), also known as an electronic control module (ECM), is an embedded system in automotive electronics that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a car or other motor vehicle. Modern vehicles have many ECUs, and these can include some or all of the following: engine control module (ECM), powertrain control module (PCM), transmission control module (TCM), brake control module (BCM or EBCM), central control module (CCM), central timing module (CTM), general electronic module (GEM), body control module (BCM), and suspension control module (SCM). These ECUs together are sometimes referred to collectively as the car's computer though technically they are all separate computers, not a single one. Sometimes an assembly incorporates several individual control modules (a PCM often controls both the engine and the transmission). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Control Unit
An engine control unit (ECU), also commonly called an engine control module (ECM), is a type of electronic control unit that controls a series of actuators on an internal combustion engine to ensure optimal engine performance. It does this by reading values from a multitude of sensors within the engine bay, interpreting the data using multidimensional performance maps (called lookup tables), and adjusting the engine actuators. Before ECUs, air–fuel mixture, ignition timing, and idle speed were mechanically set and dynamically controlled by mechanical and pneumatic means. If the ECU has control over the fuel lines, then it is referred to as an electronic engine management system (EEMS). The fuel injection system has the major role of controlling the engine's fuel supply. The whole mechanism of the EEMS is controlled by a stack of sensors and actuators. Workings Control of air–fuel ratio Most modern engines use some type of fuel injection to deliver fuel to the cylind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Control Unit
A fuel control unit is a control system for gas turbine engines. Fundamentals of turbine engine control Gas turbine engines are primarily controlled by the amount of fuel supplied to the combustion chambers. With this in mind we can say that, the very simplest fuel control for a turbine engine is a fuel valve operated by the pilot. Many pre-production models of early turbojet engines featured just that, but it was soon found that this kind of control was difficult and dangerous in actual use. Closing the valve too quickly while trying to reduce power output could cause a ''lean die-out'', where the airflow through the engine blows the flame out of the combustion chamber and extinguishes it. Adding fuel too quickly to increase power can damage the turbines due to excessive heat, or the sudden rise in combustion chamber pressure may cause a compressor stall. Another danger of too much fuel is a ''rich blow-out'', where soaking the fire with fuel displaces the oxygen and lowers the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |