|
Continental U.S. Power Transmission Grid
The electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three other regions include the Texas Interconnection, the Quebec Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection. Each region delivers power at a nominal frequency. The regions are not usually directly connected or synchronized to each other, but there exist some HVDC interconnectors. The Eastern and Western grids are connected via seven links that allow 1.32 GW to flow between them. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that increasing these interconnections would save energy costs. History In the United States in the 1920s, utilities formed joint operations to share peak load coverage and backup power. In 1934, with the passage of the Public Utility Holding Company Act, electric utilities were recognized as public goods of importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
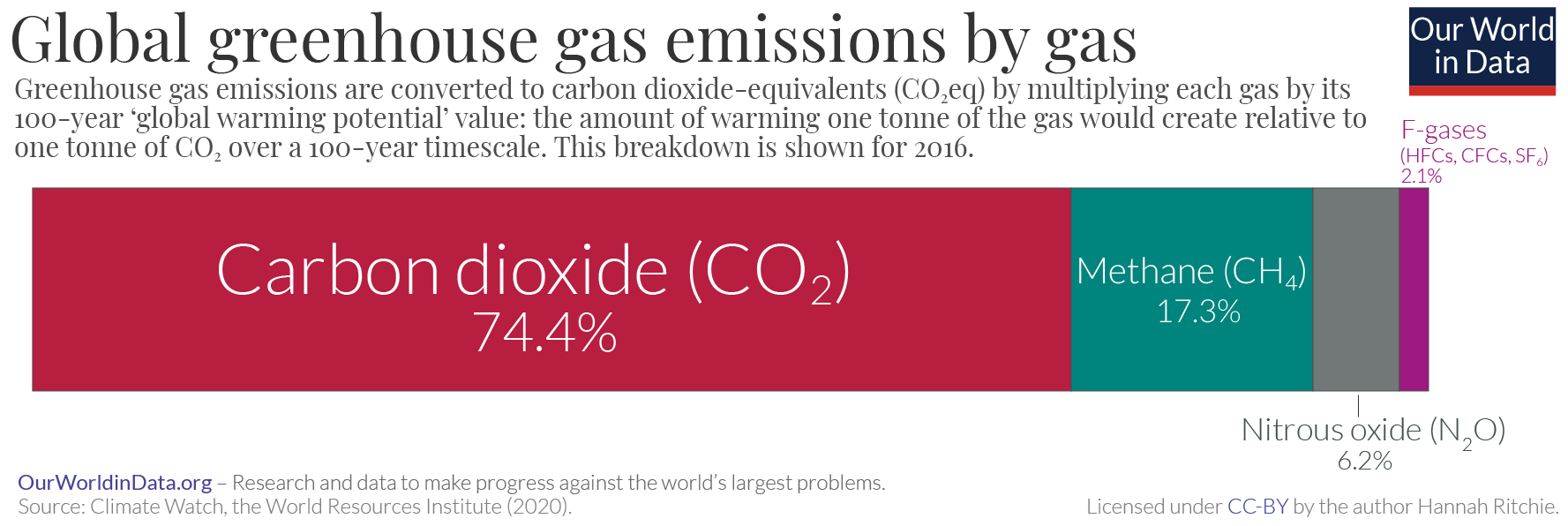
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Reliability Coordinating Council
The Florida Reliability Coordinating Council (FRCC) was (until 2019) one of the Regional Entities (REs) that were delegated authority to ensure reliability by North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) in North America and was formed on September 16, 1996. The area served by FRCC was previously served by SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC), RE functions of FRCC were transferred back to SERC in July 2019. NERC and the regional reliability councils were formed following the Northeast Blackout of 1965. FRCC's offices were located in Tampa, Florida. The FRCC is a not-for-profit company incorporated in the state of Florida. The FRCC’s mission was to ensure that the bulk power system in Peninsular Florida is reliable, adequate and secure. The FRCC served as a regional entity with delegated authority from the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) for the purpose of proposing and enforcing reliability standards within the FRCC Region. The FRCC footpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Electric Reliability Corporation
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) is a nonprofit corporation based in Atlanta, Georgia, and formed on March 28, 2006, as the successor to the North American Electric Reliability Council (also known as NERC). The original NERC was formed on June 1, 1968, by the electric utility industry to promote the reliability and adequacy of bulk power transmission in the electric utility systems of North America. NERC's mission states that it "is to assure the effective and efficient reduction of risks to the reliability and security of the grid". NERC oversees six regional reliability entities and encompasses all of the interconnected power systems of Canada and the contiguous United States, as well as a portion of the Mexican state of Baja California. NERC's major responsibilities include working with all stakeholders to develop standards for power system operation, monitoring and enforcing compliance with those standards, assessing resource adequacy, and prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Reliability Council Of Texas
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas, Inc. (ERCOT) is an American organization that operates Texas's electrical grid, the Texas Interconnection, which supplies power to more than 25 million Texas customers and represents 90 percent of the state's electric load. ERCOT is the first independent system operator (ISO) in the United States. ERCOT works with the Texas Reliability Entity (TRE), one of six regional entities within the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) that coordinate to improve reliability of the bulk power grid. As the ISO for the region, ERCOT dispatches power on an electric grid that connects more than 46,500 miles of transmission lines and more than 610 generation units. ERCOT also performs financial settlements for the competitive wholesale bulk-power market and administers retail switching for 7 million premises in competitive choice areas. According to an ERCOT report, the major sources of generating capacity in Texas in 2020 were natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Independent System Operator
New York energy law is the statutory, regulatory, and common law of the state of New York concerning the policy, conservation, taxation, and utilities involved in energy. Secondary sources have also influenced energy law in New York. The myriad legal issues concerning hydrofracking in New York has in the 2010s spawned a new body of legal authority with primary authorities such as case law, statutes, and zoning regulations, as well as secondary sources such as law review and newspaper articles, for this rapidly changing field of law. Energy Law (Consolidated Laws) The ''New York Consolidated Laws'' includes a statutory code called the "Energy Law". Under New York law, "energy" and "energy resources" are defined as: The N.Y. Energy Law became effective on July 26, 1976 as Chapter 17-A of the Consolidated Laws. The 1970s was a period of tremendous expansion of both federal and state laws concerning energy. This code is divided into these articles, which are ''not'' sequential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Independent System Operator
The California Independent System Operator (CAISO) is a non-profit Independent System Operator (ISO) serving California. It oversees the operation of California's bulk electric power system, transmission lines, and electricity market generated and transmitted by its member utilities. CAISO is one of the largest ISOs in the world, delivering 300 million megawatt-hours of electricity each year and managing about 80% of California's electric flow. History The California Legislature created CAISO in 1998 as part of the state restructuring of electricity markets. The legislature was responding to Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) recommendations following the passage of the federal Energy Policy Act of 1992, which removed barriers to competition in the wholesale generation of electricity business. FERC regulates CAISO because interstate transmission lines fall under the jurisdiction of federal commerce laws. Management CAISO's leadership consists of executive managem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Power Pool
Southwest Power Pool (SPP) manages the electric grid and wholesale power market for the central United States. As a regional transmission organization, the nonprofit corporation is mandated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to ensure reliable supplies of power, adequate transmission infrastructure and competitive wholesale electricity prices. Southwest Power Pool and its member companies coordinate the flow of electricity across approximately 60,000 miles of high-voltage transmission lines spanning 14 states. The company is headquartered in Little Rock, Arkansas. History SPP's story began in the early days of WWII, when America was ramping up production of weapons and military supplies. After entering the War, America needed to produce aluminum for aircraft manufacture. Alcoa and Reynolds Metals Company established themselves in Arkansas, which had the largest commercially exploitable bauxite deposit at that time. In 1941, government agency Defense Plant Corporation op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PJM Interconnection
PJM Interconnection LLC (PJM) is a regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States. It is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia. PJM is the largest power grid operator in the United States, serving 65 million customers from Chicago to New Jersey. PJM, headquartered in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania, was the world's largest competitive wholesale electricity market until the development of the European Integrated Energy Market in the 2000s. More than 1,000 companies are members of PJM, which serves 65 million people and has 185 gigawatts of generating capacity. With 1,436 electric power generators and 85,103 miles of transmission lines, PJM delivered 783 terawatt-hours of electricity in 2021. Started in 1927, the pool was renamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midcontinent Independent System Operator
The Midcontinent Independent System Operator, Inc., formerly named Midwest Independent Transmission System Operator, Inc. (MISO) is an Independent System Operator (ISO) and Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) established in 1998. It provides open-access transmission service and monitors the high-voltage transmission system in the Midwestern United States, in Manitoba, Canada, and in a southern U.S. region that includes much of Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana. MISO also operates one of the world's largest real-time energy markets. The 15 states covered by MISO are: Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Texas, and Wisconsin. Definition of ISOs and RTOs Both Independent System Operator (ISO)s and Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) are organizations formed with the approval of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) to coordinate, control and monitor the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO New England
ISO New England Inc. (ISO-NE) is an independent, non-profit regional transmission organization (RTO), headquartered in Holyoke, Massachusetts, serving Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. ISO-NE oversees the operation of New England's bulk electric power system and transmission lines, generated and transmitted by its member utilities, as well as Hydro-Québec, NB Power, the New York Power Authority and utilities in New York state, when the need arises. ISO-NE is responsible for reliably operating New England's 32,000 megawatt bulk electric power generation and transmission system. One of its major duties is to provide tariffs for the prices, terms, and conditions of the energy supply in New England. ISO New England ensures the day-to-day reliable operation of New England's bulk power generation and transmission system, oversees the administration of the region's wholesale electricity markets, and manages the regional planning processes. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Transmission Organization
A regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States is an electric power transmission system operator (TSO) that coordinates, controls, and monitors a multi-state electric grid. The transfer of electricity between states is considered interstate commerce, and electric grids spanning multiple states are therefore regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). The voluntary creation of RTOs was initiated by FERC in December 1999. The purpose of the RTO is to promote economic efficiency, reliability, and non-discriminatory practices while reducing government oversight. Definition A regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States is an electric power transmission system operator (TSO) that coordinates, controls, and monitors a multi-state electric grid. The transfer of electricity between states is considered interstate commerce, and electric grids spanning multiple states are therefore regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |