|
Constans (other)
Flavius Julius Constans ( 323 – 350), also called Constans I, was Roman emperor from 337 to 350. He held the imperial rank of ''caesar'' from 333, and was the youngest son of Constantine the Great. After his father's death, he was made ''augustus'' alongside his brothers in September 337. Constans was given the administration of the praetorian prefectures of Italy, Illyricum, and Africa. He defeated the Sarmatians in a campaign shortly afterwards. Quarrels over the sharing of power led to a civil war with his eldest brother and co-emperor Constantine II, who invaded Italy in 340 and was killed in battle by Constans's forces near Aquileia. Constans gained from him the praetorian prefecture of Gaul. Thereafter there were tensions with his remaining brother and co-''augustus'' Constantius II (), including over the exiled bishop Athanasius of Alexandria, who in turn eulogized Constans as "the most pious Augustus... of blessed and everlasting memory." In the following years he c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arrondissement (district or ward) and home to some of the most Western canon, canonical works of Art of Europe, Western art, including the ''Mona Lisa,'' ''Venus de Milo,'' and ''Winged Victory''. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II of France, Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basement of the museum. Due to urban expansion, the fortress eventually lost its defensive function, and in 1546 Francis I of France, Francis I converted it into the primary residence of the French kings. The building was redesigned and extended many times to form the present Louvre Palace. In 1682, Louis XIV chose the Palace of Versailles for his househ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine The Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acclamatio
In Ancient Roman and Byzantine tradition, acclamatio ( Koiné aktologia) was the public expression of approbation or disapprobation, pleasure or displeasure, etc., by loud acclamations. On many occasions, there appear to have been certain forms of acclamations always used by the Romans; as, for instance, at marriages, ', ', or '; at triumphs, '; at the conclusion of plays the last actor called out ' to the spectators; orators were usually praised by such expressions as ', ', ', etc. Under the Roman Empire, the name of ' was given to the praises and flatteries which the senate bestowed upon the emperor and his family. These , which are frequently quoted by the '' Scriptores Historiae Augustae'', were often of considerable length, and seem to have been chanted by the whole body of senators. Acclamations were also means of political expression and participation, especially in cities. While formulaic, they could play a powerful role in late antique governance. There were regular shou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Roman Army
In modern scholarship, the Later Roman Empire, "late" period of the Roman army begins with the accession of the Emperor Diocletian in AD 284, and ends in 480 with the death of Julius Nepos, being roughly coterminous with the Dominate. During the period 395–476, the army of the Roman Empire's Western Roman Empire, western half progressively disintegrated, while its counterpart in the Byzantine Empire, East, known as the East Roman army (or the early Byzantine army) remained largely intact in size and structure until the reign of Justinian I (r. AD 527–565). The Imperial Roman army of the Principate (30 BC – 284 AD) underwent a significant transformation as a result of the Crisis of the Third Century, chaotic 3rd century. Unlike the army of the Principate, the army of the 4th century was heavily dependent on conscription and its soldiers were paid much less than in the 2nd century. Barbarians from outside the empire probably supplied a much larger proportion of the late army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovians And Herculians
The Jovians () and Herculians (Latin: ''Herculiani'') were the senior palatine imperial guard units under the rule of Roman Emperor Diocletian (r. 284–305). They continued in existence thereafter as senior units in the field armies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. History The name originated in the equation of the two co-emperors Diocletian and Maximian with the Roman gods Jove and Hercules. The old-established Praetorian Guard was based at the ''Castra Praetoria'' in Rome, and had frequently proved disloyal, making and deposing emperors and even on one occasion in 193 putting the Imperial throne up for auction to the highest bidder (cf: Didius Julianus). Thus Diocletian, who ruled from Nicomedia, promoted two faithful legions from the Illyricum ( Legio V ''Iovia'' and VI ''Herculia''), the area he was also descended from, to be the personal protectors of the Roman Emperors.Gibbon, Edward. ''The Decline And Fall Of The Roman Empire'' Vol 1 Chapter XIII New Bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuel II Palaiologos
Manuel II Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 27 June 1350 – 21 July 1425) was Byzantine emperor from 1391 to 1425. Shortly before his death he was tonsured a monk and received the name Matthaios (). Manuel was a vassal of the Ottoman Empire, which sometimes threatened to capture his territory outright. Accordingly he continued his father's practice of soliciting Western European aid against the Ottomans, and personally visited several foreign courts to plead his cause. These efforts failed, although an Ottoman civil war and Byzantine victories against Latin neighbors helped Manuel's government survive and slightly expand its influence. His wife Helena Dragaš saw to it that their sons, John VIII and Constantine XI, became emperors. He is commemorated by the Greek Orthodox Church on 21 July. Life Manuel II Palaiologos was the second son of Emperor John V Palaiologos and his wife Helena Kantakouzene. Granted the title of '' despotēs'' by his father, the future Manuel II tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which was the most northerly province of the Roman Empire in continental Europe. These Frankish tribes lived for centuries under varying degrees of Roman hegemony and influence, but after the collapse of Roman institutions in western Europe they took control of a large empire including areas which had been ruled by Rome, and what it meant to be a Frank began to evolve. Once they were deeply established in Gaul, the Franks became a multilingual, Catholic Christian people, who subsequently came to rule over several other post-Roman kingdoms both inside and outside the old empire. In a broader sense much of the population of western Europe could eventually described as Franks in some contexts. The term "Frank" itself first appeared in the third cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athanasius Of Alexandria
Athanasius I of Alexandria ( – 2 May 373), also called Athanasius the Great, Athanasius the Confessor, or, among Coptic Christians, Athanasius the Apostolic, was a Christian theologian and the 20th patriarch of Alexandria (as Athanasius I). His intermittent episcopacy spanned 45 years ( – 2 May 373), of which over 17 encompassed five exiles, when he was replaced on the order of four different Roman emperors. Athanasius was a Church Father, the chief proponent of Trinitarianism against Arianism, and a noted Egyptian Christian leader of the fourth century. Conflict with Arius and Arianism, as well as with successive Roman emperors, shaped Athanasius' career. In 325, at age 27, Athanasius began his leading role against the Arians as a deacon and assistant to Bishop Alexander of Alexandria during the First Council of Nicaea. Roman Emperor Constantine the Great had convened the council in May–August 325 to address the Arian position that the Son of God, Jesus of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefecture Of Gaul
The Praetorian Prefecture of Gaul () was one of four large praetorian prefecture, prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided in the 4th century. History The prefecture was established after the death of Constantine I in 337, when the empire was split up among his sons and Constantine II (emperor), Constantine II received the rule of the western provinces, with a praetorian prefect as his chief aide. The prefecture comprised not only Roman Gaul, Gaul, but also of Roman Britain, Hispania, Spain, and Mauretania Tingitana in Africa (Roman province), Africa Proconsulare. Its territory overlapped considerably with what was once controlled by the short-lived Gallic Empire in the 260s. After the permanent partition of the Empire in 395 into West and East spheres of control, the prefecture of Gaul continued to belong to the Western Roman Empire. ''Augusta Treverorum'' (present-day Trier in Germany) served as the prefecture's seat until 407 (or, according to other estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river Natiso (modern Natisone), the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times. Today, the city is small (about 3,500 inhabitants), but it was large and prominent in classical antiquity as one of the world's largest cities with a population of 100,000 in the second century AD and is one of the main archaeological sites of northern Italy. In late antiquity the city was the first city in the Italian Peninsula to be sacked by Attila the Hun. It is currently a (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, Friuli-Venezia Giulia. History Classical Antiquity Roman Republic Aquileia was founded as a colony by the Romans in 180/181 BC along the Natiso River, on land south of the Julian Alps but about north of the lagoons. The colony served as a strategic frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4th century CE. The earliest known reference to the Sarmatians occurs in the Avesta, where they appear as ''Sairima-'', which in later Iranian sources becomes ''*Sarm'' and Salm (Shahnameh), ''Salm''. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BCE, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BCE. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BCE, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black Sea, Black and Caspian Sea, Caspian seas and the Caucasus to the south. In the first century CE, the Sarmatians beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
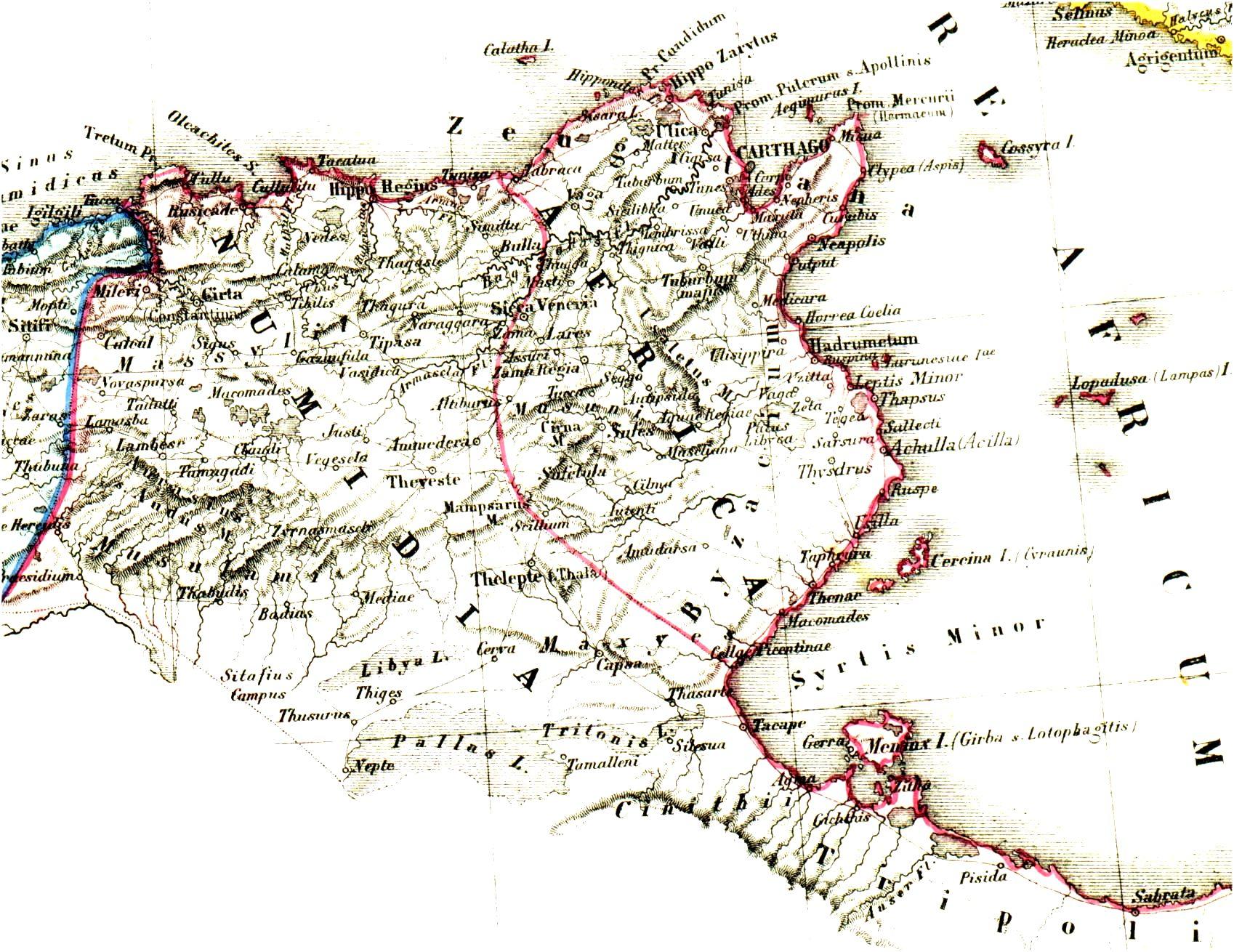
Praetorian Prefecture Of Africa
The Praetorian Prefecture of Africa () was an administrative division of the Byzantine Empire in the Maghreb. With its seat at Carthage, it was established after the reconquest of northwestern Africa from the Vandals in 533–534 by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. It continued to exist until 591, when it was replaced by the Exarchate of Africa. History Establishment In 533, the Eastern Roman army under Belisarius defeated and destroyed the Vandal Kingdom that had existed in the former Roman territories of Northern Africa. Immediately after the victory, in April 534, the emperor Justinian published a law concerning the administrative organization of the recovered territories. The old provinces of the Roman Diocese of Africa had been mostly preserved by the Vandals, but large parts, including almost all of Mauretania Tingitana, much of Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis and large parts of the interior of Numidia and Byzacena, had been lost to the inland Berbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |