|
Coniothyrium Lignorum
''Coniothyrium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Coniothyriaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Czech mycologist August Carl Joseph Corda in 1840. It was formerly placed in the Phaeosphaeriaceae family until 1983 when the family was established. The genus are diverse geographically, and have a cosmopolitan distribution across the world. The etymology of ''Coniothyrium'' is derived from New Latin, from ''coni-'' (from conus) and ''thyr-'' (from Greek ''thyreos'' meaning oblong shield, from ''thyra'' meaning door) and ''-ium'' (ending for a genus). ''Coniothyrium palmarum'' is the type species of the genus ''Coniothyrium''. It is characterised by ostiolate pycnidial (asexual fruiting body) conidiomata, annellidic conidiogenous cells, the absence of conidiophores, and brown, thick-walled, 0- or 1-septate, verrucose conidia. ''Coniothyrium'' is similar morphologically to some species in the genus '' Microsphaeropsis''. However, ''Microsphaeropsis'' is characterised by the produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
August Carl Joseph Corda
August Carl Joseph Corda (15 November 1809 – 1849) was a physician, botanist, and mycologist from Bohemia. This botanist is denoted by the List of botanists by author abbreviation, author abbreviation Corda when Author citation (botany), citing a botanical name. Early life and education Corda was born in Reichenberg (now Liberec), Bohemia on November 15, 1809. Corda's father was a textile seller. Both of Corda's parents died suddenly only a few weeks following his birth, and Corda was raised by his grandmother, attending the Normale School in Reichenberg. Corda's grandmother died in 1819 and Corda was sent to live with an "unacquainted family" for two years during which time he did not receive schooling. Two years later, Corda was transferred to the care of an uncle in Prague where he attended the "Lyceum of New Prague". As a result of family difficulties, Corda left the Lyceum in 1824 to attend Czech Technical University in Prague, polytechnical school. There, he studied physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyabean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed. Soy is a key source of food, useful both for its protein and oil content. Soybean oil is widely used in cooking, as well as in industry. Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include edamame, as well as soy milk, from which tofu and tofu skin are made. Fermented soy foods include soy sauce, fermented bean paste, nattō, and tempeh. Fat-free (defatted) soybean meal is a significant and cheap source of protein for animal feeds and many packaged meals. For example, soybean products, such as textured vegetable protein (TVP), are ingredients in many meat and dairy substitutes. Soy based foods are traditionally associated with East Asian cuisines, and still constitute a major part of East Asian diets, but processed soy products are increasingly used in Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GBIF
The Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) is an international organisation that focuses on making scientific data on biodiversity available via the Internet using web services. The data are provided by many institutions from around the world; GBIF's information architecture makes these data accessible and searchable through a single portal. Data available through the GBIF portal are primarily distribution data on plants, animals, fungi, and microbes for the world, and scientific names data. The mission of the GBIF is to facilitate free and open access to biodiversity data worldwide to underpin sustainable development. Priorities, with an emphasis on promoting participation and working through partners, include mobilising biodiversity data, developing protocols and standards to ensure scientific integrity and interoperability, building an informatics architecture to allow the interlinking of diverse data types from disparate sources, promoting capacity building and cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Fungorum
''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (Binomial nomenclature, scientific names) in the fungus Kingdom (biology), kingdom. As of 2015, the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research New Zealand Limited, Landcare Research and the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. It is somewhat comparable to the International Plant Names Index (IPNI), in which the Royal Botanic Gardens is also involved. A difference is that where IPNI does not indicate Correct name (botany), correct names, the ''Index Fungorum'' does indicate the status of a name. In the returns from the search page, a currently correct name is indicated in green, while others are in blue (a few, aberrant usages of names are indicated in red). All names are linked to pages giving the correct name, with lists of Synonym (taxonomy), synonyms. ''Index Fungorum'' is one of three nomenclatural repositories recognized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
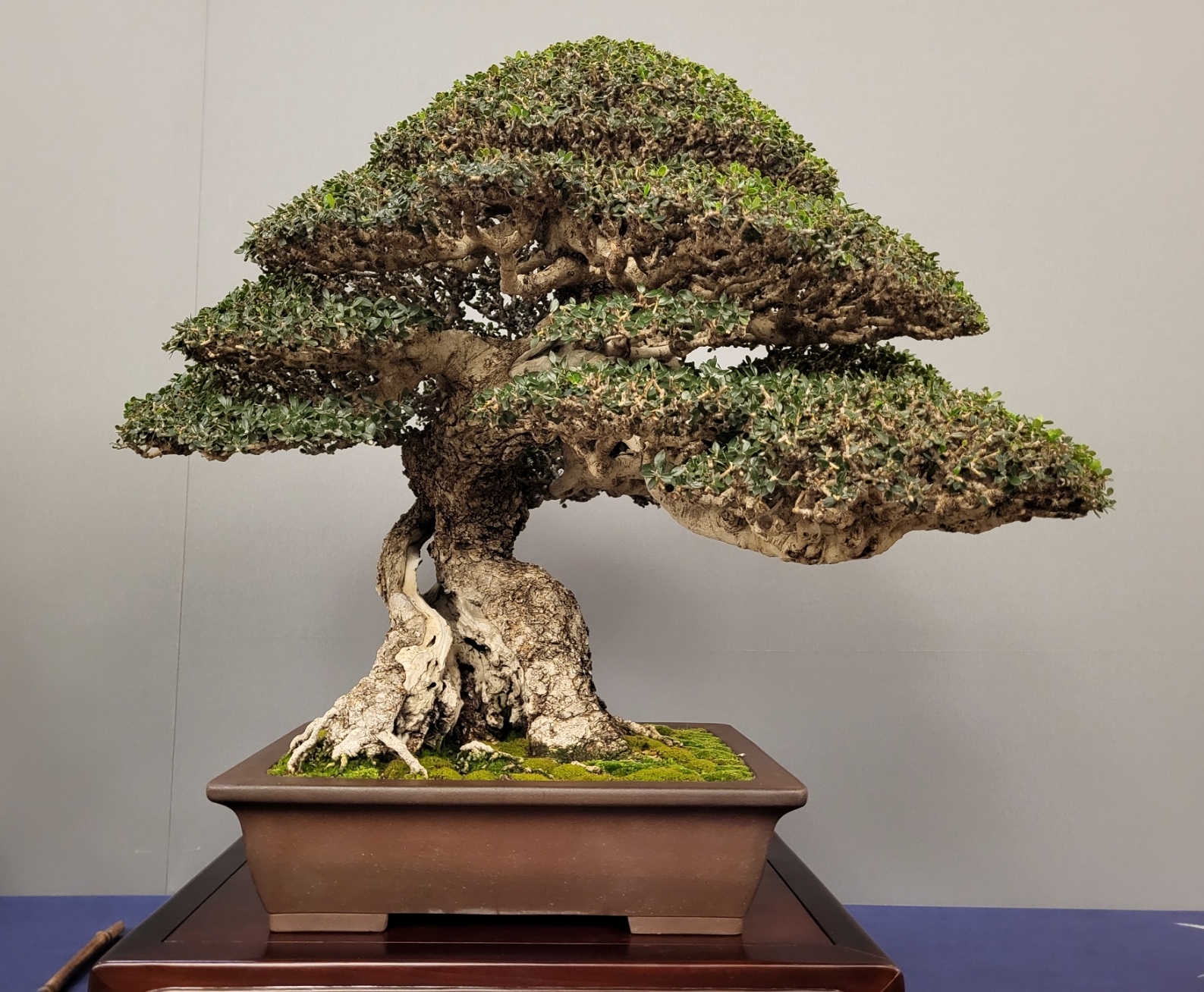
Olea Europaea
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of subtropical evergreen tree in the family Oleaceae. Originating in Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean Basin, with wild subspecies in Africa and western Asia; modern cultivars are traced primarily to the Near East, Aegean Sea, and Strait of Gibraltar. The olive is the type species for its genus, '' Olea'', and lends its name to the Oleaceae plant family, which includes species such as lilac, jasmine, forsythia, and ash. The olive fruit is classed botanically as a drupe, similar to the cherry or peach. The term oil—now used to describe any viscous water-insoluble liquid—was virtually synonymous with olive oil, the liquid fat made from olives. The olive has deep historical, economic, and cultural significance in the Mediterranean; Georges Duhamel remarked that the "Mediterranean ends where the olive tree no longer grows". Among the oldest fruit trees domesticated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prunus
''Prunus'' is a genus of flowering plant, flowering trees and shrubs from the family (biology), family Rosaceae. The genus includes plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots and almonds (collectively Drupe, stonefruit). The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, being native to the temperate regions of North America, the neotropics of South America, and temperate and tropical regions of Eurasia and Africa, There are about 340 accepted species . Many members of the genus are widely cultivated for their sweet, fleshy fruit and for decorative purposes of their flowers. ''Prunus'' fruit are drupes, or stone fruits. The fleshy Fruit anatomy, mesocarp surrounding the Fruit anatomy, endocarp is edible while the endocarp itself forms a hard, inedible shell called the pyrena ("stone" or "pit"). This shell encloses the seed (or "kernel"), which is edible in some species (such as sweet almonds), but poisonous in many others (such as apricot kernels). Besides being eaten off the hand, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis Vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. , there were between List of grape varieties, 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of ''Vitis vinifera'' grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production. The wild grape is often classified as ''Vitis vinifera'' ''sylvestris'' (in some classifications considered ''Vitis sylvestris''), with ''Vitis vinifera'' ''vinifera'' restricted to cultivated forms. Domesticated vines have hermaphrodite#Plants, hermaphrodite flowers, but ''sylvestris'' is plant sexuality, dioecious (male and female flowers on separate plants) and pollination is required for fruit to develop. Grapes can be eaten fresh or dried to produce raisins, Sultana (grape)#Raisins, sultanas, and Zante currant, currants. Grape leaves are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
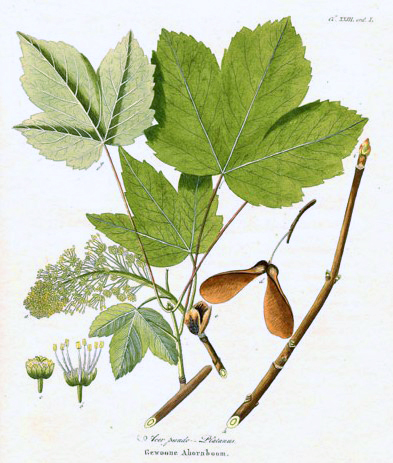
Acer Pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of maple native to Central Europe and Western Asia. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. Although native to an area ranging from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus, and southward to the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia, the sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now Naturalisation (biology), naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded Crown (botany), crown. The Bark (botany), bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long Petiole (botany), leafstalks and are large and List of botanical terms#palmate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphne Mucronata
''Daphne mucronata'' is a shrub, of the family Thymelaeaceae. It is native to western Asia, ranging from eastern Turkey to the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and the western Himalayas. Description The shrub is evergreen, and grows to 2.5 m tall. Its slender branches are pale green. It is often found near river banks at around 800–3000 m elevation. The leaves contain poisonous properties that are not potent towards goats and the bark can be used to heal bone diseases and for washing hair. The fruits it bears are edible and can be used as a dye. Plant pathogen fungal species '' Coniothyrium ferrarisianum'' has been isolated from leaves of ''Daphne mucronata'' in Iran. Subspecies Three subspecies are accepted: * ''Daphne mucronata'' subsp. ''linearifolia'' (Hart) Halda – Syria to Saudi Arabia * ''Daphne mucronata'' subsp. ''mucronata'' – southwestern Turkey, Transcaucasus, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and the western Hima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coniothyrium Ferrarisianum
''Coniothyrium'' is a genus of fungi in the family Coniothyriaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Czech mycologist August Carl Joseph Corda in 1840. It was formerly placed in the Phaeosphaeriaceae family until 1983 when the family was established. The genus are diverse geographically, and have a cosmopolitan distribution across the world. The etymology of ''Coniothyrium'' is derived from New Latin, from ''coni-'' (from conus) and ''thyr-'' (from Greek ''thyreos'' meaning oblong shield, from ''thyra'' meaning door) and ''-ium'' (ending for a genus). ''Coniothyrium palmarum'' is the type species of the genus ''Coniothyrium''. It is characterised by ostiolate pycnidial (asexual fruiting body) conidiomata, annellidic conidiogenous cells, the absence of conidiophores, and brown, thick-walled, 0- or 1-septate, verrucose conidia. ''Coniothyrium'' is similar morphologically to some species in the genus '' Microsphaeropsis''. However, ''Microsphaeropsis'' is characterised by the produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monographella Maydis
''Monographella'' is a genus of fungi in the family Amphisphaeriaceae. The anamorph In mycology, the terms teleomorph, anamorph, and holomorph apply to portions of the life cycles of fungi in the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota: *Teleomorph: the sexual reproductive stage (morph), typically a fruiting body. *Anamorph: an ase ... is '' Microdochium''. References External links Index Fungorum Xylariales Sordariomycetes genera {{Xylariales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllachora Maydis
''Phyllachora maydis'' is a plant pathogen causing ascomycete diseases in maize/corn, and is more commonly referred to as ''tar spot''. Identified by the distinctive development of stroma, this pathogen in itself is of little economic importance in the production of corn. However, the accompanying fungal infection of ''Monographella maydis,'' identified by "fish-eye" lesions, was claimed to cause significant foliar damage and subsequently yield reduction. there is insufficient information about this pathogen and its management. Symptoms and signs This pathogen is an obligate parasite solely of the species ''Zea mays''. The first symptoms are yellowing spots on both upper and lower leaf surfaces. Within the spot develops the characteristic black stromata over the ascomata, along with chlorosis of surrounding tissue. The chlorotic rings may be elliptical, circular, or may conjoin to form striping up to long. Some of the chlorotic tissue around the ascomata may become necrotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |