|
Conditional Logistic Regression
Conditional logistic regression is an extension of logistic regression that allows one to account for stratification and matching. Its main field of application is observational studies and in particular epidemiology. It was devised in 1978 by Norman Breslow, Nicholas Day, Katherine Halvorsen, Ross L. Prentice and C. Sabai. It is the most flexible and general procedure for matched data. Background Observational studies use stratification or matching as a way to control for confounding. Logistic regression can account for stratification by having a different constant term for each stratum. Let us denote Y_\in\ the label (e.g. case status) of the \ellth observation of the ith stratum and X_\in\mathbb^p the values of the corresponding predictors. We then take the likelihood of one observation to be : \mathbb(Y_=1, X_)=\frac where \alpha_i is the constant term for the ith stratum. The parameters in this model can be estimated using maximum likelihood estimation. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Regression
In statistics, a logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the logit, log-odds of an event as a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent variables. In regression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) estimation theory, estimates the parameters of a logistic model (the coefficients in the linear or non linear combinations). In binary logistic regression there is a single binary variable, binary dependent variable, coded by an indicator variable, where the two values are labeled "0" and "1", while the independent variables can each be a binary variable (two classes, coded by an indicator variable) or a continuous variable (any real value). The corresponding probability of the value labeled "1" can vary between 0 (certainly the value "0") and 1 (certainly the value "1"), hence the labeling; the function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, hence the name. The unit of measurement for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confounding
In causal inference, a confounder is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Confounding is a causal concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlations or associations.Pearl, J., (2009). Simpson's Paradox, Confounding, and Collapsibility In ''Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference'' (2nd ed.). New York : Cambridge University Press. The existence of confounders is an important quantitative explanation why correlation does not imply causation. Some notations are explicitly designed to identify the existence, possible existence, or non-existence of confounders in causal relationships between elements of a system. Confounders are threats to internal validity. Example Let's assume that a trucking company owns a fleet of trucks made by two different manufacturers. Trucks made by one manufacturer are called "A Trucks" and trucks made by the other manufacturer are called "B Trucks." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paired Difference Test
A paired difference test, better known as a paired comparison, is a type of location test that is used when comparing two sets of paired sample, paired measurements to assess whether their expected value, population means differ. A paired difference test is designed for situations where there is dependence between pairs of measurements (in which case a test designed for comparing two independent samples would not be appropriate). That applies in a within-subjects study design, i.e., in a study where the same set of subjects undergo both of the conditions being compared. Specific methods for carrying out paired difference tests include the paired-samples t-test, the paired Z-test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and others. Use in reducing variance Paired difference tests for reducing variance are a specific type of blocking (statistics), blocking. To illustrate the idea, suppose we are assessing the performance of a drug for treating high cholesterol. Under the design of our stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
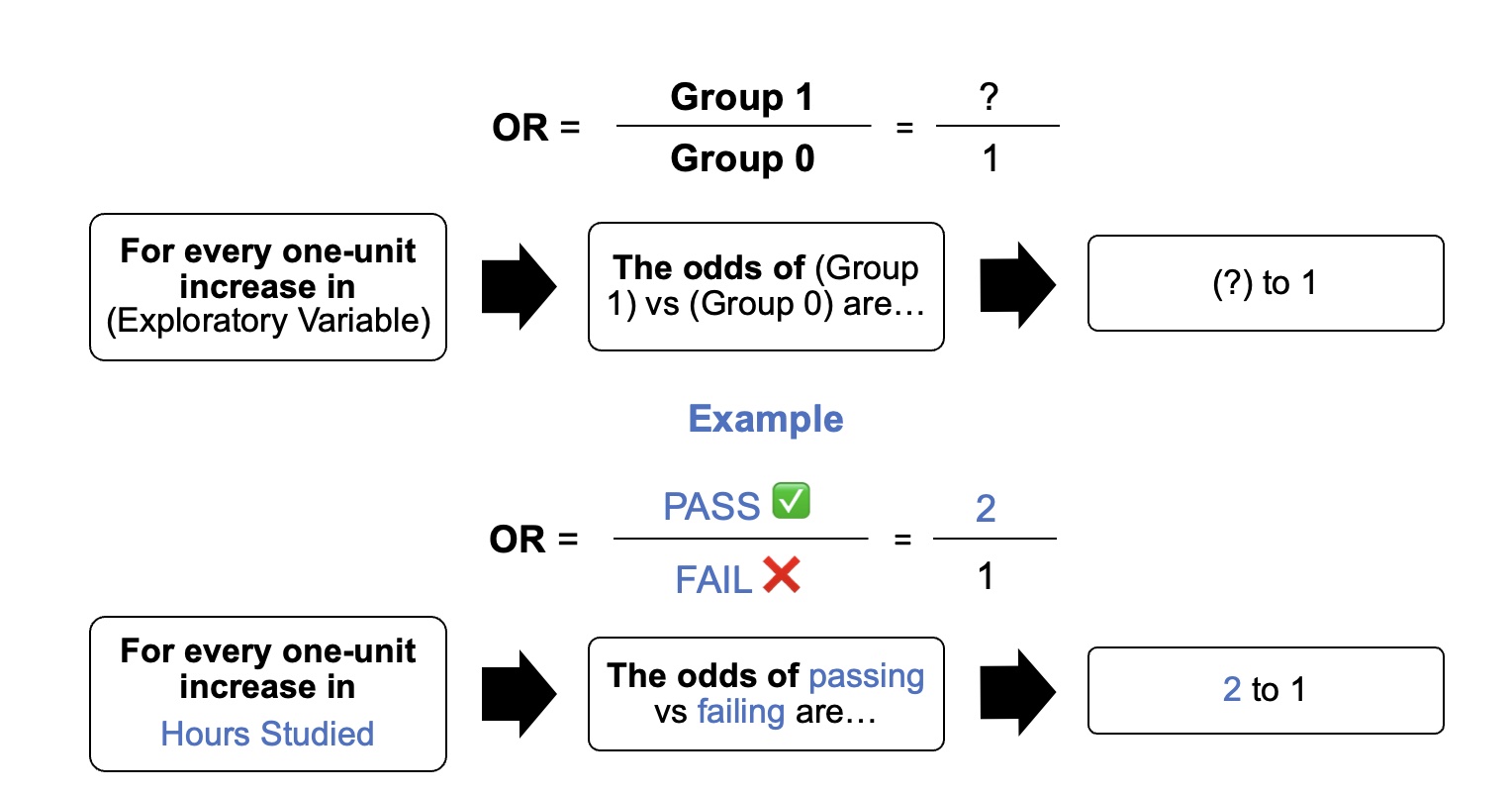
Odds Ratio
An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B. The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of event A taking place in the presence of B, and the odds of A in the absence of B. Due to symmetry, odds ratio reciprocally calculates the ratio of the odds of B occurring in the presence of A, and the odds of B in the absence of A. Two events are independent if and only if the OR equals 1, i.e., the odds of one event are the same in either the presence or absence of the other event. If the OR is greater than 1, then A and B are associated (correlated) in the sense that, compared to the absence of B, the presence of B raises the odds of A, and symmetrically the presence of A raises the odds of B. Conversely, if the OR is less than 1, then A and B are negatively correlated, and the presence of one event reduces the odds of the other event occurring. Note that the odds ratio is symmetric in the two events, and no causa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimation theory, estimating the Statistical parameter, parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by Mathematical optimization, maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the Realization (probability), observed data is most probable. The point estimate, point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is Differentiable function, differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logistic Regression
In statistics, a logistic model (or logit model) is a statistical model that models the logit, log-odds of an event as a linear function (calculus), linear combination of one or more independent variables. In regression analysis, logistic regression (or logit regression) estimation theory, estimates the parameters of a logistic model (the coefficients in the linear or non linear combinations). In binary logistic regression there is a single binary variable, binary dependent variable, coded by an indicator variable, where the two values are labeled "0" and "1", while the independent variables can each be a binary variable (two classes, coded by an indicator variable) or a continuous variable (any real value). The corresponding probability of the value labeled "1" can vary between 0 (certainly the value "0") and 1 (certainly the value "1"), hence the labeling; the function that converts log-odds to probability is the logistic function, hence the name. The unit of measurement for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ross L
Ross may refer to: People and fictional characters * Ross (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name Ross, as well as the meaning * Clan Ross, a Highland Scottish clan Places Antarctica * Ross Sea * Ross Ice Shelf * Ross Dependency * Ross Island Ireland *"Ross", a common nickname for County Roscommon * Ross, County Mayo, a townland bordering Moyne Townland * Ross, County Westmeath, a townland in Noughaval civil parish * Diocese of Ross (Ireland), West Cork United Kingdom * Ross, Northumberland, England, a village * Ross, Scottish Borders, a hamlet * Ross-on-Wye, England * Ross, Scotland, a region of Scotland and former earldom * County of Ross, Scotland * Diocese of Ross (Scotland) United States * Ross, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Ross, California, a town * Ross, Indiana, an unincorporated community * Ross, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Ross, Minnesota, an unincorporated community * Ross, North Dakota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratification (clinical Trials)
Stratification may refer to: Mathematics * Stratification (mathematics), any consistent assignment of numbers to predicate symbols * Stratified sampling , Data stratification in statistics Earth sciences * Stable and unstable stratification * Stratification, or stratum, the layering of rocks * Stratification (archeology), the formation of layers (strata) in which objects are found * Stratification (water), the formation of water layers based on temperature (and salinity, in oceans) ** Ocean stratification ** Lake stratification * Atmospheric stratification, the dividing of the Earth's atmosphere into strata * Inversion (meteorology) Social sciences * Social stratification, the dividing of a society into levels based on power or socioeconomic status Biology * Stratification (seeds), where seeds are treated to simulate winter conditions so that germination may occur * Stratification (clinical trials), partitioning of subjects by a factors other than the intervention * Stratificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katherine Halvorsen
Katherine Taylor Halvorsen is an American statistician and statistics educator whose research topics have included statistical significance for contingency tables, and the conditional logistic regression method for analysis of multiple risk factors in case–control studies. She was co-author of four editions of ''Mathematics Education in the United States'', a quadrennial review publication of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics, and serves on the Mathematical Sciences Academic Advisory Committee of the College Board. Education and career Halvorsen is a graduate of the University of Michigan. After earning master's degrees from Boston University and in 1978, the University of Washington, she completed her Ph.D. in biostatistics in 1984 at the Harvard School of Public Health, with the dissertation ''Estimating Population Parameters Using Information from Several Independent Sources'' supervised by Frederick Mosteller. She is a professor emerita of mathematics and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Day (statistician)
Nicholas Edward Day, CBE, FRS (born 24 September 1939) is a retired statistician and cancer epidemiologist. Education He was educated at Gresham's School and the University of Oxford, from 1958-1962, where he gained a B.A. in Mathematics and a Diploma in Statistics, and the University of Aberdeen from 1962-1966, where he obtained a Doctorate of Philosophy. Career Day worked at the International Agency for Research on Cancer in Lyon from 1969 to 1986, where he rose to become head of the Unit of Biostatistics and Field Studies. He was director of the Medical Research Council Biostatistics Unit from 1986 to 1989, and continued as honorary director until 1999. From 1997 until his retirement in 2004 he was co-director of the Strangeways Research Laboratory in Cambridge. He was also professor of public health at the University of Cambridge from 1989 to 1999, and professor of epidemiology from 1999 until 2004. Day was made a Commander of the Order of the British Empire in the 2001 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |