|
Comăna De Sus
Comăna (; ) is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of four villages: Comăna de Jos (the commune center), Comăna de Sus (''Felsőkomána''), Crihalma (''Königsberg''; ''Királyhalma'') and Ticușu Nou (''Rumänisch Tekes''; ''Felsőtyúkos''). Comăna is traversed north to south by the Olt River. It borders the following communes: Părău to the south, Măieruș to the east, Hoghiz to the north, and Ticușu to the west. History Comăna de Jos was an important administrative center of the eastern part of Țara Făgărașului, at a time when – who was born here in 1502 – ruled over Transylvania. Villages falling within the jurisdiction of this center were: Comăna de Sus, Veneția de Jos, Veneția de Jos, Crihalma, Ticușu Nou, Cuciulata, and Lupșa. In the current area of Comăna de Jos, human settlements were discovered that attest to the existence of people in the following places: *A Bronze Age settlement from the 2nd to the 1st century B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commune In Romania
A commune (''comună'' in Romanian language, Romanian) is the lowest level of administrative subdivision in Romania. There are 2,686 communes in Romania. The commune is the rural subdivision of a Counties of Romania, county. Urban areas, such as towns and cities within a county, are given the status of ''Cities in Romania, city'' or ''Municipality in Romania, municipality''. In principle, a commune can contain any size population, but in practice, when a commune becomes relatively urbanised and exceeds approximately 10,000 residents, it is usually granted city status. Although cities are on the same administrative level as communes, their local governments are structured in a way that gives them more power. Some urban or semi-urban areas of fewer than 10,000 inhabitants have also been given city status. Each commune is administered by a mayor (''primar'' in Romanian). A commune is made up of one or more villages which do not themselves have an administrative function. Communes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
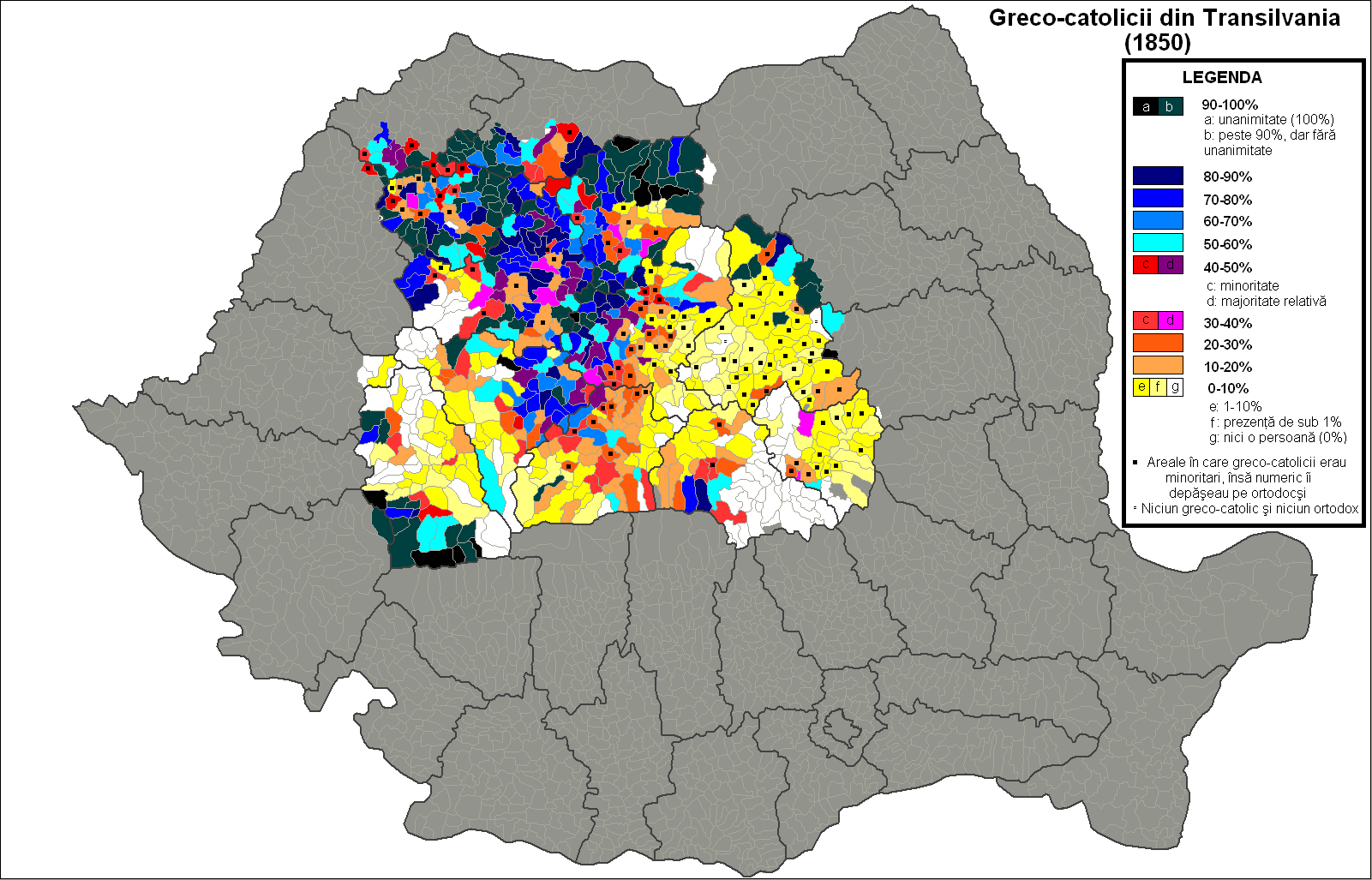
Romanian Greek Catholic Church
The Romanian Greek Catholic Church or Romanian Church United with Rome is a '' sui iuris'' Eastern Catholic Church, in full union with the Catholic Church. It has the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church and it uses the Byzantine liturgical rite in the Romanian language. It is part of the Major Archiepiscopal Churches of the Catholic Church that are not distinguished with a patriarchal title. Cardinal Lucian Mureșan, Archbishop of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, has served as the head of the Romanian Greek-Catholic Church since 1994. On December 16, 2005, as the ''Romanian Church United with Rome'', the Greek-Catholic church was elevated to the rank of a Major Archiepiscopal Church by Pope Benedict XVI, with Lucian Mureșan becoming its first major archbishop. Mureşan was made a cardinal, at the consistory of February 18, 2012. Besides the Archeparchy of Făgăraș and Alba Iulia, there are five more Greek-Catholic eparchies in Romania ( Eparchy of Oradea Mare, Eparchy of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Transylvania
The Prince of Transylvania (, , , Fallenbüchl 1988, p. 77.) was the head of state of the Principality of Transylvania from the late-16th century until the mid-18th century. John Sigismund Zápolya was the first to adopt the title in 1570, but its use only became stable from 1576. Origins The integration of Transylvania into the newly established Kingdom of Hungary began around 1003. The province became subject to intensive colonization, leading to the arrival and settlement of colonists of diverse origin, including the Hungarian-speaking Székelys and the Ethnic Germans. The territory of Transylvania was divided for administrative reasons within territorial units known as "counties" and "seats". The seven Transylvanian counties ( Doboka, Fehér, Hunyad, Kolozs, Küküllő, Szolnok, and Torda County) were institutions primarily run by local noblemen. However, their heads or '' ispáns''Makkai 1994, p. 207. were subject to the authority of a higher official, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Făgăraș Citadel
Făgăraș Citadel ( , , ) is a History, historic Ancient monument, monument in Făgăraș, Brașov County, Romania. History The construction of the fortress started in 1310, on the site of a wooden fortification with earth Rampart (fortification), ramparts from the 12th century. Archeological research shows that the old fortification was violently destroyed around the middle of the 13th century, presumably in connection with the Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongol invasion of 1241. Located halfway between Brașov and Sibiu and close to Wallachia, the Făgăraș Citadel provided a defensive position against possible incursions into south-eastern Transylvania. In 1526, consolidated the citadel, doubling the thickness of the walls. In 1541, the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans attacked the fortress and captured Mailat, who died in captivity at Yedikule Fortress in Istanbul. Gáspár Bekes, owner of the citadel between 1567 and 1573, constructed the moat around the fortress, the excavated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary ethnic groups, second largest ethno-linguistic community. At around 46 million worldwide, Ukrainians are the second largest Slavs, Slavic ethnic group after Russians. Ukrainians have been Endonym and exonym, given various names by foreign rulers, which have included Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Habsburg monarchy, the Austrian Empire, and then Austria-Hungary. The East Slavic population inhabiting the territories of modern-day Ukraine were known as Ruthenians, referring to the territory of Ruthenia; the Ukrainians living under the Russian Empire were known as Little Russians, named after the territory of Little Russia. The ethnonym Ukrainian, which was associated with the Cossack Hetmanate, was adopted following the Ukrainian natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roma In Romania
Romani people in Romania, locally and pejoratively referred to as the (), constitute the second largest ethnic minority in the country (the first being Hungarians). According to the 2021 census, their number was 569,477 people and 3.4% of the total population. The size of the total population of people with Romani ancestry in Romania is even more, with different estimates varying from 4.6 percent to over 10 percent of the population, because many people of Romani descent do not declare themselves Roma. For example, in 2007 the Council of Europe estimated that approximately 1.85 million Roma lived in Romania, based on an average between the lowest estimate (1.2 to 2.2 million people) and the highest estimate (1.8 to 2.5 million people) available at the time. This figure is equivalent to 8.32% of the population. On the other hand, less than half are native speakers of the Romani language. Origins History, genetics and linguistics all indicate the Roma originate from northern Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War II, defines a German as a German nationality law, German citizen. During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent, and history.. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity." Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary, though not exclusive, criterion of German identity. Estimates on the total number of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
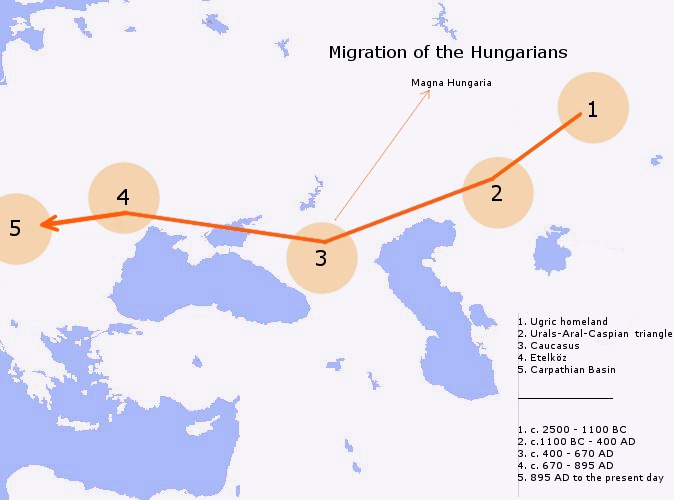
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, common culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, they speak the Romanian language and live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2021 Romanian census found that 89.3% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians. In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova, the majority of Moldovans were counted as ethnic Romanians as well.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson (author), David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Romanian Census
The 2021 Romanian census () was a census held in Romania between 1 February and 31 July 2022, with the reference day for the census data set at 1 December 2021. The census was supposed to be done in 2021, but it was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic in Romania in order to avoid census takers from getting infected when coming into contact with ill or quarantined people. It was the first census held in Romania in which data was collected online, something that had support among Romanian youth. The census was divided into three phases: one in which personal data of the Romanian population was collected from various sites; another in which the population was to complete more precise data such as religion, in which town halls would help the natives of rural areas to answer the census; and a third one in which census takers would go to the homes and households of those who did not register their data online. Data for this census was planned not to be collected on paper, but inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Romanian Census
The 2011 Romanian census was a census held in Romania between 20 and 31 October 2011. It was performed by some 120,000 census takers in around 101,000 statistic sectors throughout the country established by the National Institute of Statistics (INS) of Romania. Preparations started already in 2009, and it was announced that the process would not end until 2014. Anyone who did not answer questions in the census questionnaire would be fined between 1,500 and 4,500 Romanian lei, although 4 of the 100 questions related to the respondent's ethnicity, mother language, religion, and possible disabilities were not mandatory. Preliminary results were released once on 2 February 2012 and again on 20 August 2012. The final definitive result of the census came out on 4 July 2013, showing that, among other things, Romania had lost 1,559,300 people since the 2002 census, consequently having 20,121,641 inhabitants. Some people like sociologist Vasile Ghețău, director of the Center of Demog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inocențiu Micu-Klein
Ioan Inocențiu Micu-Klein, also known by his lay name Ioan Micu (1692 – 22 September 1768), was a Bishop of Fogaras and Primate of the Romanian Greek Catholic Church from 1730 to his resignation in 1751. He played an instrumental role in the establishment of national rights for Romanians in Transylvania (part of the Habsburg monarchy at the time of his life). Life He was born as ''Ioan Micu'' (''Inocențiu'' being his clergy name, and ''Klein'' the German translation of his surname, sometimes rendered back into Romanian transcription as ''Clain'') in Cók, Szeben County (nowadays Sadu, Sibiu County, Romania), in 1692 from a lower-class family. He studied by the Jesuits in Kolozsvár (today Cluj-Napoca, Romania) and trained in theology in Nagyszombat (today Trnava, Slovakia). On 18 November 1728, following the death of previous bishop Ioan Giurgiu Patachi, the electoral synod convened and Micu resulted the more voted, even if he was young and he had not yet terminated hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |