|
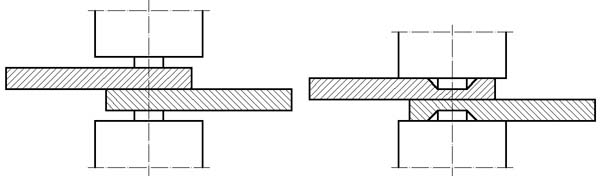
Cold Welding
Cold welding or contact welding is a solid-state welding process in which joining takes place without fusion or heating at the interface of the two parts to be welded. Unlike in fusion welding, no liquid or molten phase is present in the joint. Cold welding was first recognized as a general materials phenomenon in the 1940s. It was then discovered that two clean, flat surfaces of similar metal would strongly adhere if brought into contact while in a vacuum . Micro and nano-scale cold welding has shown potential in nanofabrication processes. Applications include wire stock and electrical connections (such as insulation-displacement connectors and wire wrap connections). In space Mechanical problems in early satellites were sometimes attributed to cold welding. In 2009 the European Space Agency published a peer reviewed paper detailing why cold welding is a significant issue that spacecraft designers need to carefully consider. The paper also cites a documented exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Diffusion
Surface diffusion is a general process involving the motion of adatoms, molecules, and atomic clusters ( adparticles) at solid material surfaces.Oura, Lifshits, Saranin, Zotov, and Katayama 2003, p. 325 The process can generally be thought of in terms of particles jumping between adjacent adsorption sites on a surface, as in figure 1. Just as in bulk diffusion, this motion is typically a thermally promoted process with rates increasing with increasing temperature. Many systems display diffusion behavior that deviates from the conventional model of nearest-neighbor jumps. Tunneling diffusion is a particularly interesting example of an unconventional mechanism wherein hydrogen has been shown to diffuse on clean metal surfaces via the quantum tunneling effect. Various analytical tools may be used to elucidate surface diffusion mechanisms and rates, the most important of which are field ion microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy.Oura, Lifshits, Saranin, Zotov, and Katayama 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
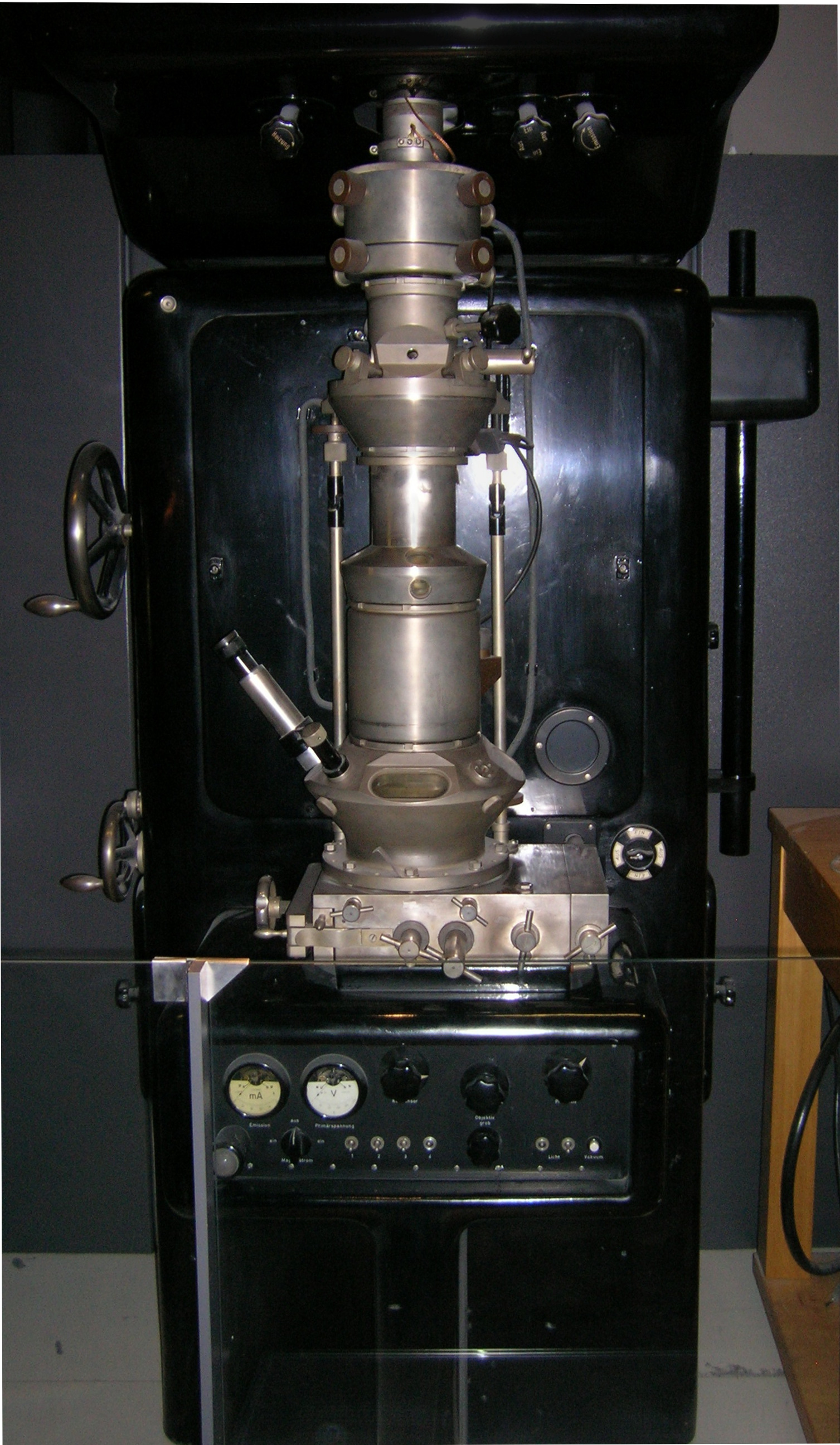
Transmission Electron Microscopy
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a detector such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device or a direct electron detector. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanowire
file:[email protected], upright=1.2, Crystalline 2×2-atom tin selenide nanowire grown inside a single-wall carbon nanotube (tube diameter ≈1 nm). A nanowire is a nanostructure in the form of a wire with the diameter of the order of a nanometre (10−9 m). More generally, nanowires can be defined as structures that have a thickness or diameter constrained to tens of nanometers or less and an unconstrained length. At these scales, quantum mechanical effects are important—which coined the term "quantum wires". Many different types of nanowires exist, including superconducting (e.g. Yttrium barium copper oxide, YBCO), metallic (e.g. nickel, Ni, platinum, Pt, gold, Au, silver, Ag), semiconducting (e.g. Silicon nanowire, silicon nanowires (SiNWs), indium phosphide, InP, gallium nitride, GaN) and insulating (e.g. Silicon dioxide, SiO2, Titanium dioxide, TiO2). Molecular nanowires are composed of repeating molecular units either organic (e.g. DNA) or inorganic (e.g. Mo6S9−''x'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or interface (matter), surfaces to cling to one another. (Cohesion (chemistry), Cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles and surfaces to cling to one another.) The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can be divided into several types. The intermolecular forces responsible for the function of various kinds of stickers and sticky tape fall into the categories of chemical adhesion, dispersive adhesion, and diffusive adhesion. In addition to the cumulative magnitudes of these intermolecular forces, there are also certain emergent mechanical effects. Surface energy Surface energy is conventionally defined as the work (physics), work that is required to build an area of a particular surface. Another way to view the surface energy is to relate it to the work required to cleave a bulk sample, creating two surfaces. If the new surfaces are identical, the surface energy γ of each surface is equal to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiction
Stiction (a portmanteau of the words '' static'' and ''friction'') is the force that needs to be overcome to enable relative motion of stationary objects in contact. Any solid objects pressing against each other (but not sliding) will require some threshold of force parallel to the surface of contact in order to overcome static adhesion. Stiction is a ''threshold'', not a continuous force. However, stiction might also be an illusion made by the rotation of kinetic friction. In situations where two surfaces with areas below the micrometer scale come into close proximity (as in an accelerometer), they may adhere together. At this scale, electrostatic and/or Van der Waals and hydrogen bonding forces become significant. The phenomenon of two such surfaces being adhered together in this manner is also called stiction. Stiction may be related to hydrogen bonding or residual contamination. Automobiles Stiction is also the same threshold at which a rolling object would begin to slide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fretting
Fretting refers to wear and sometimes corrosion damage of loaded surfaces in contact while they encounter small oscillatory movements tangential to the surface. Fretting is caused by adhesion of contact surface asperity (material science), asperities, which are subsequently broken again by the small movement. This breaking causes wear debris to be formed. If the debris and/or surface subsequently undergo chemical reaction, i.e., mainly oxidation, the mechanism is termed fretting corrosion. Fretting degrades the surface, leading to increased surface roughness and micropits, which reduces the fatigue strength of the components. The amplitude of the relative sliding motion is often in the order of micrometer (unit), micrometers to millimeters, but can be as low as 3 nanometers. Typically fretting is encountered in shrink fits, bearing seats, bolted parts, Spline (mechanical), splines, and dovetail connections. Materials Steel Fretting damage in steel can be identified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galling
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces. When a material galls, some of it is pulled with the contacting surface, especially if there is a large amount of force compressing the surfaces together. Galling is caused by a combination of friction and adhesion between the surfaces, followed by slipping and tearing of crystal structure beneath the surface. This will generally leave some material stuck or even friction welding, friction welded to the adjacent surface, whereas the galled material will appear worn, chipped, or even gouged and may have balled-up or torn lumps of material stuck to its surface. Galling is most commonly found in metal surfaces that are in sliding contact with each other. It is especially common where there is inadequate lubrication between the surfaces. However, certain metals will generally be more prone to galling, due to the atomic structure of their crystals. For example, aluminium will gall very easily, whereas annealed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Spacecraft
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany's Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Reviewed
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work ( peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review methods are used to maintain quality standards, improve performance, and provide credibility. In academia, scholarly peer review is often used to determine an academic paper's suitability for publication. Peer review can be categorized by the type and by the field or profession in which the activity occurs, e.g., medical peer review. It can also be used as a teaching tool to help students improve writing assignments. Henry Oldenburg (1619–1677) was a German-born British philosopher who is seen as the 'father' of modern scientific peer review. It developed over the following centuries with, for example, the journal ''Nature'' making it standard practice in 1973. The term "peer review" was first used in the early 1970s. A monument to peer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |