|
Clausius–duhem Inequality
The Clausius–Duhem inequality is a way of expressing the second law of thermodynamics that is used in continuum mechanics. This inequality is particularly useful in determining whether the constitutive relation of a material is thermodynamically allowable.. This inequality is a statement concerning the irreversibility of natural processes, especially when energy dissipation is involved. It was named after the German physicist Rudolf Clausius and French physicist Pierre Duhem. Clausius–Duhem inequality in terms of the specific entropy The Clausius–Duhem inequality can be expressed in integral form as : \frac\left(\int_\Omega \rho \eta \, dV\right) \ge \int_ \rho \eta \left(u_n - \mathbf\cdot\mathbf\right) dA - \int_ \frac~ dA + \int_\Omega \frac~dV. In this equation t is the time, \Omega represents a body and the integral, integration is over the volume of the body, \partial \Omega represents the surface of the body, \rho is the mass density of the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
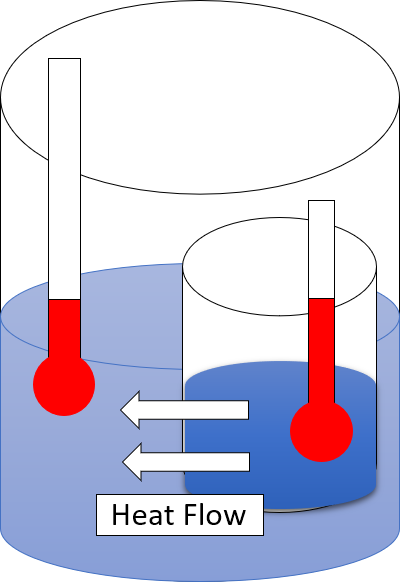
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on Universal (metaphysics), universal empirical observation concerning heat and Energy transformation, energy interconversions. A simple statement of the law is that heat always flows spontaneously from hotter to colder regions of matter (or 'downhill' in terms of the temperature gradient). Another statement is: "Not all heat can be converted into Work (thermodynamics), work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It predicts whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. For example, the first law allows the process of a cup falling off a table and breaking on the floor, as well as allowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Vector
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. A '' vector quantity'' is a vector-valued physical quantity, including units of measurement and possibly a support, formulated as a '' directed line segment''. A vector is frequently depicted graphically as an arrow connecting an ''initial point'' ''A'' with a ''terminal point'' ''B'', and denoted by \stackrel \longrightarrow. A vector is what is needed to "carry" the point ''A'' to the point ''B''; the Latin word means 'carrier'. It was first used by 18th century astronomers investigating planetary revolution around the Sun. The magnitude of the vector is the distance between the two points, and the direction refers to the direction of displacement from ''A'' to ''B''. Many algebraic operations on real numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy Production
Entropy production (or generation) is the amount of entropy which is produced during heat process to evaluate the efficiency of the process. Short history Entropy is produced in irreversible processes. The importance of avoiding irreversible processes (hence reducing the entropy production) was recognized as early as 1824 by Carnot. In 1865 Rudolf Clausius expanded his previous work from 1854 on the concept of "unkompensierte Verwandlungen" (uncompensated transformations), which, in our modern nomenclature, would be called the entropy production. In the same article in which he introduced the name entropy, Clausius gives the expression for the entropy production for a cyclical process in a closed system, which he denotes by ''N'', in equation (71) which reads :N=S-S_0-\int\frac. Here ''S'' is the entropy in the final state and ''S0'' the entropy in the initial state; ''S0-S'' is the entropy difference for the backwards part of the process. The integral is to be taken from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissipation
In thermodynamics, dissipation is the result of an irreversible process that affects a thermodynamic system. In a dissipative process, energy ( internal, bulk flow kinetic, or system potential) transforms from an initial form to a final form, where the capacity of the final form to do thermodynamic work is less than that of the initial form. For example, transfer of energy as heat is dissipative because it is a transfer of energy other than by thermodynamic work or by transfer of matter, and spreads previously concentrated energy. Following the second law of thermodynamics, in conduction and radiation from one body to another, the entropy varies with temperature (reduces the capacity of the combination of the two bodies to do work), but never decreases in an isolated system. In mechanical engineering, dissipation is the irreversible conversion of mechanical energy into thermal energy with an associated increase in entropy. Processes with defined local temperature produce ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate System
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane (geometry), plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point (geometry), point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the positive and negative numbers, signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called ''coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the ''Origin (mathematics), origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes direction (geometry), directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum (from Latin '' pellere'' "push, drive") is: \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is dimensionally equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame of reference, it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be Conservation law, ''conserved'' over time. In the case of a Closed system#In thermodynamics, closed system, the principle says that the total amount of energy within the system can only be changed through energy entering or leaving the system. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is Energy conversion, converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, the conservation of energy was distinct from the conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of f. If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point p, the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from p, and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function f(\mathbf) may be defined by: df=\nabla f \cdot d\mathbf where df is the total infinitesimal change in f for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes Force, forces present during Deformation (physics), deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to Tension (physics), ''tensile'' stress and may undergo Elongation (materials science), elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to Compression (physics), ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has Dimension (physics), dimension of force per area, with SI Units, SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while Strain (mechanics), ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation (mechanics), deformation of the material. For example, when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Energy
The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is the energy of the system as a state function, measured as the quantity of energy necessary to bring the system from its standard internal state to its present internal state of interest, accounting for the gains and losses of energy due to changes in its internal state, including such quantities as magnetization. It excludes the kinetic energy of motion of the system as a whole and the potential energy of position of the system as a whole, with respect to its surroundings and external force fields. It includes the thermal energy, ''i.e.'', the constituent particles' kinetic energies of motion relative to the motion of the system as a whole. Without a thermodynamic process, the internal energy of an isolated system cannot change, as expressed in the law of conservation of energy, a foundation of the first law of thermodynamics. The notion has been introduced to describe the systems characterized by temperature variations, te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Mass
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter the mass of the system must remain constant over time. The law implies that mass can neither be created nor destroyed, although it may be rearranged in space, or the entities associated with it may be changed in form. For example, in chemical reactions, the mass of the chemical components before the reaction is equal to the mass of the components after the reaction. Thus, during any chemical reaction and low-energy thermodynamic processes in an isolated system, the total mass of the reactants, or starting materials, must be equal to the mass of the products. The concept of mass conservation is widely used in many fields such as chemistry, mechanics, and fluid dynamics. Historically, mass conservation in chemical reactions was primarily demonstrated in the 17th century and finally confirmed by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material Time Derivative
In continuum mechanics, the material derivative describes the time rate of change of some physical quantity (like heat or momentum) of a material element that is subjected to a space-and-time-dependent macroscopic velocity field. The material derivative can serve as a link between Eulerian and Lagrangian descriptions of continuum deformation. For example, in fluid dynamics, the velocity field is the flow velocity, and the quantity of interest might be the temperature of the fluid. In this case, the material derivative then describes the temperature change of a certain fluid parcel with time, as it flows along its pathline (trajectory). Other names There are many other names for the material derivative, including: *advective derivative *convective derivative *derivative following the motion *hydrodynamic derivative *Lagrangian derivative *particle derivative *substantial derivative *substantive derivative *Stokes derivative *total derivative, although the material derivative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |