|
Château De Meudon
Château de Meudon (), also known as the Royal Castle of Meudon or Imperial Palace of Meudon, is a French castle in Meudon, Hauts-de-Seine. At the edge of a wooded plateau, the castle offers views of Paris and the Seine, as well as of the Chalais, Charente, Chalais valley. Located between Paris and Palace of Versailles, Versailles, in the heart of a hunting reserve, the castle has an ideal topography for large gardens. It had many successive owners from the Renaissance until the fall of the Second French Empire. It should not be confused with the Château de Bellevue, also located in Meudon. Famous past residents include: Anne de Pisseleu d'Heilly, Duchess of Étampes; the Cardinal of Lorraine, Abel Servien; François Michel Le Tellier, Marquis of Louvois and Louis, Grand Dauphin, also known as ''Monseigneur'', who linked the Chaville Castle to Meudon Castle. The Château-Vieux (Old Castle) burned down in 1795 and was rebuilt as the Château-Neuf (New Castle), which in turn burn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meudon
Meudon () is a French Communes of France, commune located in the Hauts-de-Seine Departments of France, department in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, on the left bank of the Seine. It is located from the Kilometre Zero, center of Paris. The city is known for many historic monuments. Geography The town of Meudon is built on the hills and valleys of the Seine. The forest of Meudon lies for the most part to the west of the town. The north-west part of Meudon, overlooking the Seine, is known as ''Bellevue'' ("beautiful view"). The neighboring communes are: Sèvres (North-west), Boulogne-Billancourt (North); Issy-les-Moulineaux (northeast), Clamart (east and southeast), Vélizy (south and southwest) and Chaville (west). The town includes several districts: Meudon-sur-Seine, Val Fleury, Meudon-Centre, Bellevue and Meudon-la-Forêt. History At Meudon, the argile plastique clay was extensively mined in the 19th century. The first fossil of the European diatryma ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
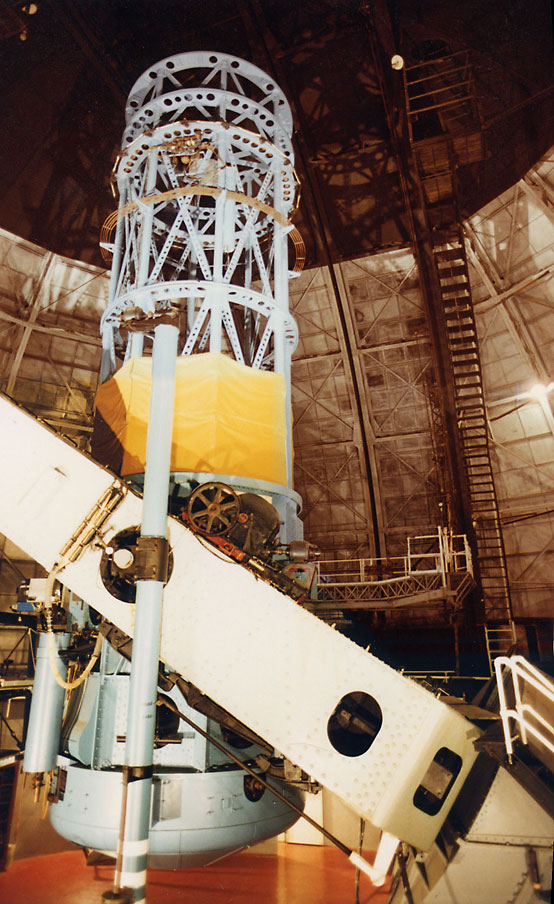
Astronomical Telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors. The first known practical telescopes were refracting telescopes with glass lenses and were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 17th century. They were used for both terrestrial applications and astronomy. The reflecting telescope, which uses mirrors to collect and focus light, was invented within a few decades of the first refracting telescope. In the 20th century, many new types of telescopes were invented, including radio telescopes in the 1930s and infrared telescopes in the 1960s. Etymology Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy () was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by the Crown lands of France, French crown in 1477, and later by members of the House of Habsburg, including Holy Roman Emperors and kings of Spain, who claimed Burgundy proper and ruled the Burgundian Netherlands. The Duchy of Burgundy was a small portion of the traditional lands of the Burgundians west of the river Saône which, in 843, was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of the West Franks. Under the Ancien Régime, the duke of Burgundy was the premier lay Peerage of France, peer of the Kingdom of France. Beginning with Robert II of France (), the title was held by the Capetians, the French royal family. In 1032 King Henry I of France granted the duchy to his younger brother, Robert I, Duke of Burgundy, Robert, who founded the House of Burgundy. When the senior line of the House of Burgundy became extinct in 1361, the title was inherited by King Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles VII Of France
Charles VII (22 February 1403 – 22 July 1461), called the Victorious () or the Well-Served (), was King of France from 1422 to his death in 1461. His reign saw the end of the Hundred Years' War and a ''de facto'' end of the English claims to the French throne. During the Hundred Years' War, Charles VII inherited the throne of France under desperate circumstances. Forces of the Kingdom of England and the duke of Burgundy occupied Guyenne and northern France, including Paris, the capital and most populous city, and Reims, the city in which French kings were traditionally crowned. In addition, his father, Charles VI, had disinherited him in 1420 and recognized Henry V of England and his heirs as the legitimate successors to the French crown. At the same time, a civil war raged in France between the Armagnacs (supporters of the House of Valois) and the Burgundian party (supporters of the House of Valois-Burgundy, which was allied to the English). With his court removed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupbearer
A cup-bearer was historically an officer of high rank in royal courts, whose duty was to pour and serve the drinks at the royal table. On account of the constant fear of plots and intrigues (such as poisoning), a person had to be regarded as thoroughly trustworthy to hold the position. He would guard against poison in the king's cup, and was sometimes required to swallow some of the drink before serving it. His confidential relations with the king often gave him a position of great influence. A9 Egyptian hieroglyph for a cup-bearer The cup-bearer as an honorific role, for example as the Egyptian hieroglyph for "cup-bearer", was used as late as 196 BC in the Rosetta Stone for the Kanephoros cup-bearer Areia, daughter of Diogenes; each Ptolemaic Decree starting with the Decree of Canopus honored a cup-bearer. A much older role was the appointment of Sargon of Akkad as cup-bearer in the 23rd century BC. In the Bible Cup-bearers are mentioned several times in the Bible. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamberlain (office)
A chamberlain (Medieval Latin: ''cambellanus'' or ''cambrerius'', with charge of treasury ''camerarius'') is a senior royal official in charge of managing a royal household. Historically, the chamberlain superintends the arrangement of domestic affairs and was often also charged with receiving and paying out money kept in the royal chamber. The position was usually awarded as an honour to a high-ranking member of the nobility (nobleman) or the clergy, often a favourite, royal favourite. Roman emperors appointed this officer under the title of ''cubicularius''. The Camerlengo of the Holy Roman Church, Chamberlain of the Holy Roman Church enjoys very extensive powers, having the revenues of the papal household under his charge. As a sign of their dignity, chamberlains bore a key, which in the seventeenth century was often silvered, and actually fitted the door-locks of chamber rooms. Since the eighteenth century, it has turned into a merely symbolic, albeit splendid, Order of prece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Faye
La Faye is a commune in the Charente department in southwestern France. Population See also *Communes of the Charente department The following is a list of the 359 communes of the Charente department of France on 1 January 2025. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Communes of Charente {{Confolens-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vue De Paris Depuis Meudon Langlacé Musée Art Et D'histoire De Meudon
Vue or VUE may refer to: Places * Vue, Loire-Atlantique, a commune in France * The Vue, a skyscraper in Charlotte, North Carolina Arts, entertainment and media * Vue (band), a rock and roll band from San Francisco, California * Vue International, a cinema company in the United Kingdom * ''Vue Weekly'', an alternative newspaper in Edmonton, Canada * PlayStation Vue, a former American streaming service from Sony Television stations * KVUE, the ABC TV affiliate for Austin, Texas, US * WVUE (Wilmington, Delaware), a defunct TV station in Wilmington, Delaware, US * WVUE-DT, the Fox TV affiliate for New Orleans, Louisiana, US Brands and enterprises * Pearson VUE, an electronic testing company * Saturn Vue, a sport utility vehicle * Vue International, a multinational cinema holding company based in the UK * Vue Pack, single-serve coffee system by Keurig * Vue.ai, A Madstreetden brand based in the USA Science and technology * Villitis of unknown etiology, a placental injury Software * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip IV Of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. Jure uxoris, By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre and Count of Champagne as Philip I from 1284 to 1305. Although Philip was known to be handsome, hence the epithet ''le Bel'', his rigid, autocratic, imposing, and inflexible personality gained him (from friend and foe alike) other nicknames, such as the Iron King (). His fierce opponent Bernard Saisset, Roman Catholic Diocese of Pamiers, bishop of Pamiers, said of him: "He is neither man nor beast. He is a statue." Philip, seeking to reduce the wealth and power of the nobility and clergy, relied instead on skilful civil servants, such as Guillaume de Nogaret and Enguerrand de Marigny, to govern Kingdom of France, the kingdom. The king, who sought an uncontested monarchy, compelled his vassals by wars and restricted their feudal privileges, paving the way for the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Panetier Of France
The Grand Panetier of France (roughly "Great Breadmaster", sometimes rendered as Panter) was one of the Great Officers of the Crown of France, a member of the Maison du Roi ("King's Household"), one of the Great Offices of the Maison du Roi, and functional chief of the "(grande) paneterie" (the root of the English word pantry) or bread department. French history Originally the paneterie (known since the 11th century) one of the two sections of the ''gobelet du roi'' ('King's drinking-cup) with a staff of 12 sommeliers, four aides, one ''garde-vaiselle'' (for the dirty dishes), two porte(u)rs and a ''lavandier'' (laundryman), helping him to wash, prepare and gather again all the royal table utensils, as well as the bread. In time some of these duties were transferred to other sections, so his function at the King's table became ceremonial. Under the Sun King his was one of the seven sections of the ''bouche du Roi'' or king's table. He did gain several privileges, including juris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronymic
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic. Patronymics are used, by custom or official policy, in many countries worldwide, although elsewhere their use has been replaced by or transformed into patronymic surnames. Examples of such transformations include common English surnames such as Johnson (surname), Johnson (son of John). Origins of terms The usual noun and adjective in English is ''patronymic'', but as a noun this exists in free variation alongside ''patronym''. The first part of the word ''patronym'' comes from Greek language, Greek πατήρ ''patēr'' 'father' (Genitive case, GEN πατρός ''patros'' whence the combining form πατρο- ''patro''-); the second part comes from Greek ὄνυμα ''onyma'', a variant form of ὄνομα ''onoma'' 'name'. In the form ''patronymic'', this stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerostat
An aerostat (, via French) or lighter-than-air aircraft is an aircraft that relies on buoyancy to maintain flight. Aerostats include unpowered balloons (free-flying or tethered) and powered airships. The relative density of an aerostat as a whole is lower than that of the surrounding atmospheric air (hence the name "lighter-than-air"). Its main component is one or more gas capsules made of lightweight skins, containing a lifting gas (hot air, or any gas with lower density than air, typically hydrogen or helium) that displaces a large volume of air to generate enough buoyancy to overcome its own weight. Payload (passengers and cargo) can then be carried on attached components such as a basket, a gondola, a cabin or various hardpoints. With airships, which need to be able to fly against wind, the lifting gas capsules are often protected by a more rigid outer envelope or an airframe, with other gasbags such as ballonets to help modulate buoyancy. Aerostats are so named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |