|
Château De Domfront
The Château de Domfront is a ruined castle in the town of Domfront, in the Orne département of France. The Château de Domfront has been protected as a ''monument historique'' by the French Ministry of Culture since 1875. The ruins include the keep, the enceinte, ramparts, towers, casemates and the former Sainte-Catherine et Saint-Symphorien chapels. The castle ruins have been repaired since 1984 by the '. The ruins stand in a public park and are open to the public free of charge. History In 1051, the castle at Domfront, belonging to Guillaume II Talvas, lord of Bellême, and occupied by the forces of Geoffrey of Anjou, was besieged by William the Conqueror, duke of Normandy.David C. Douglas, William the Conqueror (1967) In 1092, the people of Domfront revolted against Robert II de Bellême, Earl of Shrewsbury, transferring their allegiance to the third son of William the Conqueror, Henri Beauclerc, who became Duke of Normandy (1106) and King of England (1100). In 116 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Of Bellême, 3rd Earl Of Shrewsbury
Robert de Bellême ( – after 1130), seigneur de Bellême (or Belèsme), seigneur de Montgomery, viscount of the Hiémois, 3rd Earl of Shrewsbury and Count of Ponthieu, was an Anglo-Norman nobleman, and one of the most prominent figures in the competition for the succession to England and Normandy between the sons of William the Conqueror. He was a member of the powerful House of Bellême. Robert became notorious for his alleged cruelty. Referring to his activities in the rebellion against Henry I of 1110–1112, the chronicler Orderic Vitalis, in Book XI of his ''Historia Ecclesiastica'', calls Robert "grasping and cruel, an implacable persecutor of the Church of God and the poor ... unequalled for his iniquity in the whole Christian era", as well as "the tyrant who had disturbed the land and was preparing to add still worse crimes to his many offences of plundering and burning". The stories of his brutality may have inspired the legend of Robert the Devil. Early life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert III Of Artois
Robert III of Artois (1287 – between 6 October & 20 November 1342) was a French nobleman of the House of Artois. He was the Lord of Conches-en-Ouche, of Château de Domfront, Domfront, and of Mehun-sur-Yèvre, and in 1309 he received as appanage the county of Beaumont-le-Roger in restitution for the County of Artois, which he claimed. He was also briefly Earl of Richmond in 1341 after the death of John III, Duke of Brittany. Life Early years Robert was the son of Philip of Artois, Lord of Conches-en-Ouche, and Blanche of Brittany, daughter of John II, Duke of Brittany. Both were male descendants of the Capetian dynasty. His father died on 11 September 1298 from wounds received at the Battle of Furnes on 20 August 1297 against the Flemings, Flemish. His father's early death was an indirect cause of the dispute over the succession to the County of Artois. After the death of his grandfather Robert II, Count of Artois, at the Battle of Courtrai (1302), Battle of Courtrai in 130 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
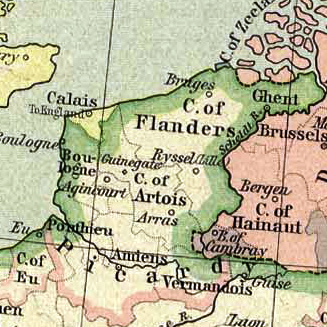
Artois
Artois ( , ; ; Picard: ''Artoé;'' English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities include Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht''), Saint-Omer, Lens, and Béthune. It is the eponym for the term ''Artesian''. Location Artois occupies the interior of the Pas-de-Calais ''département'',"Artois" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th ed., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 607. the western part of which constitutes the former Boulonnais. Artois roughly corresponds to the arrondissements of Arras, Béthune, Saint Omer, and Lens, and the eastern part of the arrondissement of Montreuil. It occupies the western end of the coalfield which stretches eastward through the neighbouring Nord ''département'' and across central Belgium. History Originally a feudal county itself, Artois was annexed by the county of Flanders. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Artois
The count of Artois (, ) was the ruler over the County of Artois from the 9th century until the abolition of the countship by the French revolutionaries in 1790. House of Artois *Odalric () *Altmar () *Adelelm (?–932) *''Conquered by Arnulf I, Count of Flanders and directly under Flanders, 932–1180'' * Philip I, Count of Flanders (1168–1180), gave Artois as dowry to Isabelle of Hainaut, niece of Philip of Flanders, for her marriage to Philip II of France House of Capet * Isabella (1180–1190) * Louis VIII of France (1190–1223), her son Merged into royal domain. Capetian House of Artois * Robert I (1237–1250), his second surviving son * Robert II (1250–1302), his son * Matilda (1302–1329), his daughter, married to Otto IV, Count of Burgundy **contested by Robert III (1302–1329) House of Burgundy * Joan I (1329–1330), her daughter * Joan II (1330–1347), her daughter ** married to Odo (1330–1347) * Philip I, Duke of Burgundy (1347–1361 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert II Of Artois
Robert II (September 1250 – 11 July 1302) was the Count of Artois, the posthumous son and heir of Robert I and Matilda of Brabant. He was a nephew of two kings; Louis IX of France and Charles I of Sicily. A capable military commander and administrator, Robert was involved in a number of conflicts involving the French Capetian dynasty, including the War of the Sicilian Vespers and the Franco-Flemish War. He died during the latter conflict while leading a French army at the Battle of the Golden Spurs. Life A close confidant of the Capetian royal family and experienced soldier, Robert served as a military commander and administrator under the rule of uncle, Philip III of France and Philip's son, Philip IV. During the former Philip's early reign, he dispatched Robert and a French army to Iberia to suppress a rebellion in the Kingdom of Navarre. In 1285, he was named as regent of the Angevin Kingdom of Naples while the kingdom was engaged in the War of the Sicilian Vespers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IX Of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), also known as Saint Louis, was King of France from 1226 until his death in 1270. He is widely recognized as the most distinguished of the Direct Capetians. Following the death of his father, Louis VIII, he was Coronation of the French monarch, crowned in Reims at the age of 12. His mother, Blanche of Castile, effectively ruled the kingdom as regent until he came of age, and continued to serve as his trusted adviser until her death. During his formative years, Blanche successfully confronted rebellious vassals and championed the Capetian cause in the Albigensian Crusade, which had been ongoing for the past two decades. As an adult, Louis IX grappled with persistent conflicts involving some of the most influential nobles in his kingdom, including Hugh X of Lusignan and Peter I of Brittany. Concurrently, England's Henry III of England, Henry III sought to reclaim the Angevin Empire, Angevin continental holdings, only to be decisively def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Lands Of France
The crown lands, crown estate, royal domain or (in French) ''domaine royal'' (from demesne) of France were the lands, fiefs and rights directly possessed by the kings of France. While the term eventually came to refer to a territorial unit, the royal domain originally referred to the network of "castles, villages and estates, forests, towns, religious houses and bishoprics, and the rights of justice, tolls and taxes" effectively held by the king or under his domination. In terms of territory, before the reign of Henry IV, the ''domaine royal'' did not encompass the entirety of the territory of the kingdom of France and for much of the Middle Ages significant portions of the kingdom were the direct possessions of other feudal lords. In the tenth and eleventh centuries, the first Capetians—while being the kings of France—were among the least powerful of the great feudal lords of France in terms of territory possessed. Patiently, through the use of feudal law (and, in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Hurepel
Philip I of Boulogne (Philip Hurepel) (1200–1235) was a French prince, Counts of Clermont-en-Beauvaisis, Count of Clermont-en-Beauvaisis in his own right, and Count of Boulogne, Count of Mortain, Mortain, Count of Aumale, Aumale, and Dammartin-en-Goële ''jure uxoris''. Philip was born in September 1200, the son of Philip II of France and his controversial third wife Agnes of Merania. Illegitimacy shadowed his birth and career, but he was legitimated by Pope Innocent III. He was associated with founding the Tour du Guet in Calais. He is the first recorded person to bear a Capetian Armorial#Cadet Branches of the direct Capetians, differenced version of the Fleur-de-lis, arms of France. Marriage Philip was married in c. 1223 to Matilda II, Countess of Boulogne. Philip, by Jure uxoris, right of his wife, became Count of Boulogne, Mortain, Aumale, and Dammartin-en-Goële. He revolted against his sister-in-law Blanche of Castile when his elder half-brother Louis VIII of France, Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Boulogne
Count of Boulogne was a historical title in the Kingdom of France. The city of Boulogne-sur-Mer became the centre of the County of Boulogne during the ninth century. Little is known of the early counts, but the first holder of the title is recorded in the 11th century. Eustace II of Boulogne accompanied William I of England (the Conqueror) during the Norman Conquest in 1066 and fought on his side at the Battle of Hastings. His son, Eustace III, was a major participant in the First Crusade with his younger brothers: Geoffrey and Baldwin (who later became King of Jerusalem). After Baldwin's death the throne was offered to Eustace, who was reluctant and declined; the throne was then offered to Geoffrey. Afonso III of Portugal, Afonso (also King of Portugal) from Dammartin became Count of Boulogne from 1235 to 1253. Count Renaud of Boulogne obtained the title by abducting and marrying Countess Ida in 1190 and later gained title to Dammartin and Aumale. An early friend of King Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaud De Dammartin
Renaud de Dammartin (Reginald of Boulogne) (c. 1165 – 1227) was Count of Boulogne from 1190, Count of Dammartin from 1200 to 1214 and Count of Aumale from 1204 to 1214. He was the eldest son of Alberic III of Dammartin and Mathilde of Clermont. Brought up at the French court, he was a childhood friend of Philip Augustus. At his father's insistence he fought for the Plantagenets. Received back into Philip's favour, he married Marie de Châtillon, daughter of Guy II de Châtillon and Adèle of Dreux, a royal cousin. In 1191, Dammartin's father, Alberic, kidnapped and had Dammartin marry Ida, Countess of Boulogne. The County of Boulogne thereby became vassal to the French king, rather than the count of Flanders. While this marriage made Dammartin a power, it also made enemies in the House of Dreux, Dreux family and that of the count of Guînes, who had been betrothed to Ida. In 1203, Dammartin and his wife gave a merchant's charter to Boulogne-sur-Mer, Boulogne. This was prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of England
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empire and contributing to the subsequent growth in power of the French Capetian dynasty during the 13th century. The First Barons' War, baronial revolt at the end of John's reign led to the sealing of Magna Carta, a document considered a foundational milestone in English and later British constitution of the United Kingdom, constitutional history. John was the youngest son of King Henry II of England and Duchess Eleanor of Aquitaine. He was nicknamed John Lackland () because, as a younger son, he was not expected to inherit significant lands. He became Henry's favourite child following the failed revolt of 1173–1174 by his brothers Henry the Young King, Richard I of England, Richard, and Geoffrey II, Duke of Brittany, Geoffrey against their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |