|
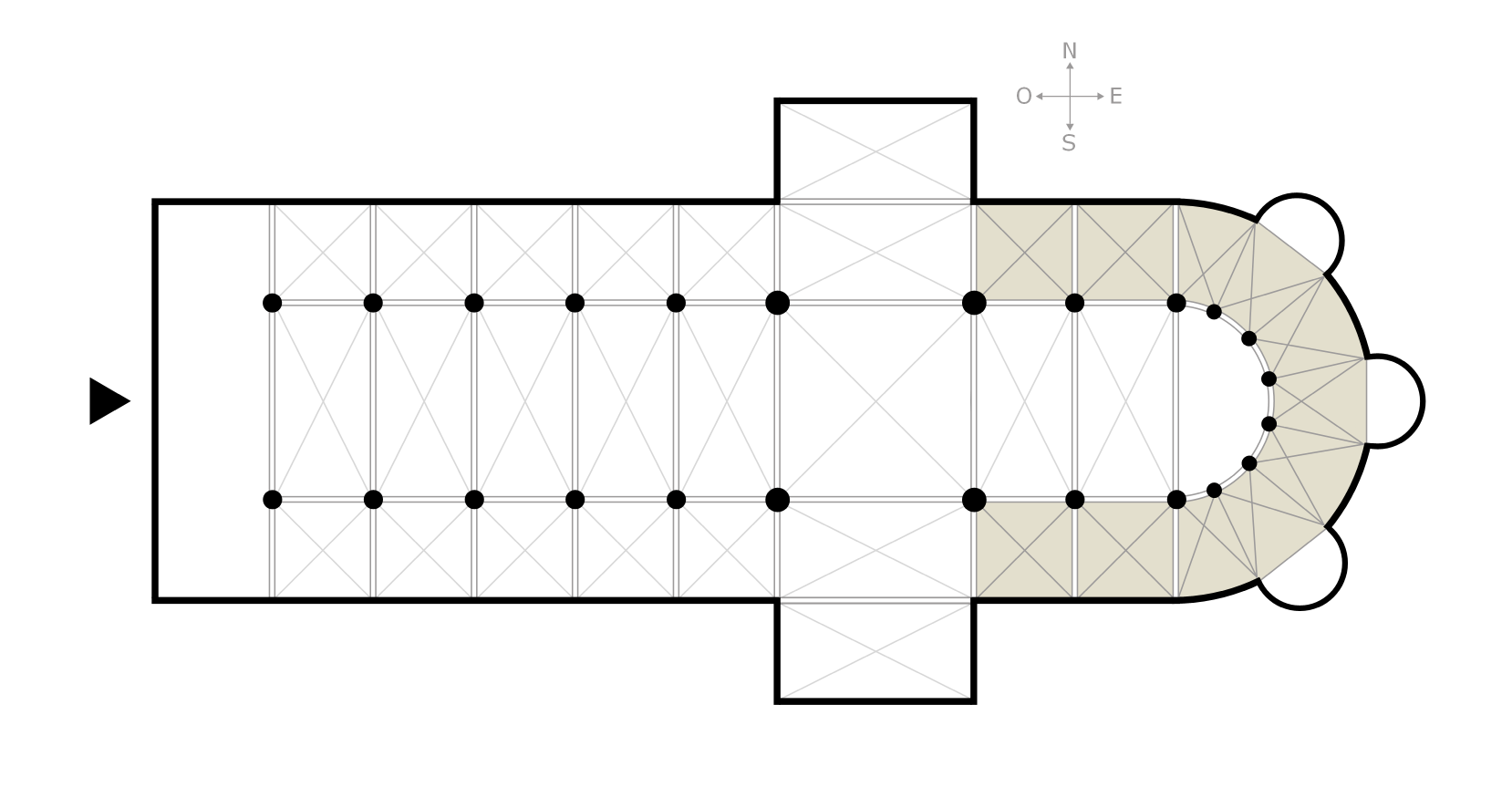
Church Of Saint-Éloi, Dunkirk
The Church of Saint-Éloi (), nicknamed the Cathedral of the Sands, is a Catholic Church, Roman Catholic church in Dunkirk, France. It was listed as a Monument historique, Historic Monument in 1916,, whereas the belfry of Dunkerque, belfry of the original church across the street was listed in 1840. The belfry is also part of the World Heritage Site, World Heritage-listed Belfries of Belgium and France. History The original church of the mid-15th century had the shape of a Latin cross. It was consecrated around 1443. It is said to have been erected by prime contractors from Ghent on the site of St. John's Hospice. In 1558, the French troops led by Paul de Thermes, Maréchal de Thermes invaded the city and burnt the church. Only the tower survived. The re-construction of the church started in 1559 under the supervision of prime contractor Jean de Renneville and ended in 1567. The sanctuary was enlarged to the east, the main nave was elevated and the side aisles were re-built with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunkirk
Dunkirk ( ; ; ; Picard language, Picard: ''Dunkèke''; ; or ) is a major port city in the Departments of France, department of Nord (French department), Nord in northern France. It lies from the Belgium, Belgian border. It has the third-largest French harbour. The population of the commune in 2019 was 86,279. Etymology and language use The name of Dunkirk derives from West Flemish 'dune' or 'dun (fortification), dun' and 'church', thus 'church in the dunes'. A smaller town 25 km (15 miles) farther up the Flemish coast originally shared the same name, but was later renamed Oostduinkerke(n) in order to avoid confusion. Until the middle of the 20th century, French Flemish (the local variety of Dutch language, Dutch) was commonly spoken. History Middle Ages A fishing village arose late in the tenth century, in the originally flooded coastal area of the English Channel south of the Western Scheldt, when the area was held by the County of Flanders, Counts of Flanders, va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul De Thermes
Paul de La Barthe de Thermes or de Termes (1482–1562), also Paul de Terme or Maréchal de Thermes, was a French army Marshal ("Maréchal"). Reign of Henri II Rough Wooing In June 1549, de Thermes was sent to Scotland to help in the war against England now called the Rough Wooing. He was instructed to continue the fortification of border strongholds, and came with massive reinforcements, munitions and money. De Thermes began the construction of an artillery fort at Luffness near Aberlady to prevent English supplies reaching Haddington. The Scottish leader Regent Arran came to stay at Carberry Tower and Seton Palace to see the works commence. De Thermes was helped at the site by a Scottish pursuivant Alexander Ross. Gilbert Kennedy, 3rd Earl of Cassilis was lieutenant of the Scottish force there. There was a scare that English soldiers would over-run the building site on 23 June. Men were summoned from as far away as Perth and Strathearn. On 25 June the lairds of East and West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Texel (1694)
The Battle of Texel was a sea battle fought during the Nine Years' War on 29 June 1694, when a force of eight French ships, under Jean Bart, recaptured a French convoy, which had earlier that month been taken by the Dutch, and captured three ships of the escorting force (consisting of eight ships) under Hidde Sjoerds de Vries. De Vries was captured by the French, but shortly after died of wounds.Haws/Hurst p.335 Context In 1692 and 1693 there were massive harvest failures in France, leading to acute famine and epidemics. From 1693 to 1694 over 2 million people died. Therefore, France needed to import large quantities of grain from neutral countries like Poland-Lithuania, Sweden and Denmark-Norway. On 29 May 1694 Jean Bart was instructed to sail to Norway, to escort a huge fleet of 120 ships full of grain to France. The convoy didn't wait for the arrival of Bart's squadron and left under the protection of 3 neutral warships (2 Danish and one Swedish). Battle The convoy was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Bart
Jean Bart (; ; 21 October 1650 – 27 April 1702) was a Flemish naval commander and privateer. Early life Jean Bart was born in Dunkirk in 1650 to a seafaring family, the son of Jean-Cornil Bart (c. 1619–1668) who has been described variously as a fisherman or corsair commander sailing for the Dutch Republic. His grandfather, Cornil Weus( fr), was a vice-admiral and fought the Dutch on behalf of Spain at the beginning of the Eighty Years' War. His great-grandfather, Michel Jacobsen, distinguished himself in the service of the Spanish crown, bringing back the Invincible Armada after its failed attempt to invade England in 1588, and was appointed vice-admiral by Philip IV of Spain. His great-uncle, Jan Jacobsen, also in the service of Spain, blew himself up with his ship in 1622 rather than surrender. He almost certainly spoke Dutch, at that time the native language in the region, and his birth name was ''Jan Baert''. Naval career When he was young, Bart served in the Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaudin
Pierre Gaudin (1908–1973), son of Jean Gaudin (1879–1954) and grandson of Félix Gaudin (1851–1930) was a glass painter and mosaic artist. His studio executed mosaic designs and stained-glass Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ... windows for the Basilica of St. Thérèse, Lisieux. Monuments et Musées, Lisieux (French). Accessed 2011-08-20. Gaudin had a daughter, Sylvie Gaudin and Catherine Aboulian Notes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
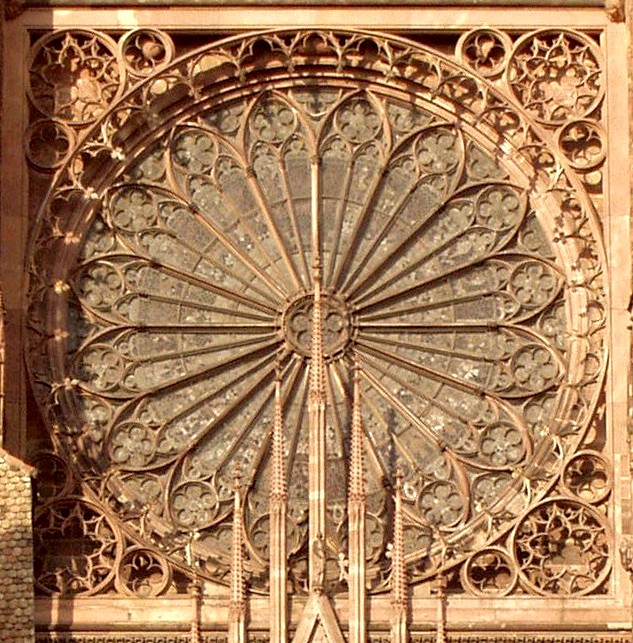
Rose Window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' was not used before the 17th century and comes from the English flower name rose. The name "wheel window" is often applied to a window divided by simple spokes radiating from a central boss or opening, while the term "rose window" is reserved for those windows, sometimes of a highly complex design, which can be seen to bear similarity to a multi-petalled rose. Rose windows are also called "Catherine windows" after Saint Catherine of Alexandria, who was sentenced to be executed on a spiked breaking wheel. A circular window without tracery such as are found in many Italian churches, is referred to as an ocular window or Oculus (architecture), oculus. Rose windows are particularly characteristic of Gothic architecture and may be seen in all th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apse Chapel
An apse chapel, apsidal chapel, or chevet is a chapel in traditional Christian church architecture, which radiates tangentially from one of the bays or divisions of the apse. It is reached generally by a semicircular passageway, or ambulatory, exteriorly to the walls or piers of the apse. Features In plan, the normal type of the tangential chapel is semicircular; some, however, are pentagonal, and some composed of a small circle, serving as choir, and part of a large circle, as nave; some are oblong with eastern apses. In England, sometimes an ambulatory connects the north and south aisles of the choir and from the ambulatory projects an eastern chapel or chapels. The eastern chevet of Westminster Abbey, surrounded by five apsidal chapels, is the only complete example of this feature in England. The common source of the ambulatory and radiating chapels seems to have been the church of St. Martin of Tours, where originally there was a choir of two bays, and an apse of five bays, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulatory
The ambulatory ( 'walking place') is the covered passage around a cloister or the processional way around the east end of a cathedral or large church and behind the high altar. The first ambulatory was in France in the 11th century but by the 13th century ambulatories had been introduced in England and many English cathedrals were extended to provide an ambulatory. The same feature is often found in Indian architecture and Buddhist architecture generally, especially in older periods. Ritual circumambulation or parikrama around a stupa or cult image is important in Buddhism and Hinduism. Often the whole building was circumambulated, often many times. The Buddhist chaitya hall always allowed a path for this, and the Durga temple, Aihole (7th or 8th century) is a famous Hindu example. The term is also used to describe a garden feature in the grounds of a country house. A typical example is the one shown, which stands in the grounds of Horton Court in Gloucestershire, England. File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incendiary Device
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires. They may destroy structures or sensitive equipment using fire, and sometimes operate as anti-personnel weapon, anti-personnel weaponry. Incendiaries utilize materials such as napalm, thermite, magnesium, magnesium powder, chlorine trifluoride, or white phosphorus munitions, white phosphorus. Though colloquially often called "bombs", they are not explosives but in fact operate to slow the process of chemical reactions and use Combustion, ignition rather than detonation to start or maintain the reaction. Napalm, for example, is petroleum especially thickened with certain chemicals into a gel to slow, but not stop, combustion, releasing energy over a longer time than an explosive device. In the case of napalm, the gel adheres to surfaces and resists suppression. Pre-modern history A range of early thermal weapons were utilized by Ancient history, ancient, Middle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Church At St
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Reason
A Temple of Reason () was, during the French Revolution, a state atheist temple for a new belief system created to replace Christianity: the Cult of Reason, which was based on the ideals of reason, virtue, and liberty. This "religion" was supposed to be universal and to spread the ideas of the revolution, summarized in its "" motto, which was also inscribed on the Temples. Services The symbols of Christianity were covered up, and the symbols of the Cult of Reason replaced them. In the Churches of Reason, there were specially created services meant to replace the Christian liturgy. For instance, at the Notre-Dame Cathedral in Paris, on 10 November 1793, a special ritual was held for the "Feast of Reason": the nave had an improvised mountain on which stood a Greek temple dedicated to Philosophy and decorated with busts of philosophers. At the base of the mountain was located an altar dedicated to Reason, and in front of it was a torch of Truth. The ceremony included the crowd payi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |