|
Church Of Our Lady, Bruges
The Church of Our Lady () is a Roman Catholic church in Bruges, Belgium, dating mainly from the 13th, 14th and 15th centuries. Its tower remains the tallest structure in the city and the third tallest brickwork tower in the world (after St. Mary's Church in Lübeck and St. Martin's Church in Landshut, both in Germany). The church demonstrates the Gothic style in the prominent Flying buttresses on the exterior which were constructed in the 1270s and 80s. The nave contains cross-vaults and black and white tiled flooring. The interior demonstrates the heavily ornamented Baroque style in the side aisles and chancel. One of the chapels in the church was created in 1482 for a wealthy man named Lodewijk van Gruuthuse, as his personal worship area. Burials In the choir space behind the high altar are the tombs of Charles the Bold, last Valois Duke of Burgundy, and that of his daughter, the duchess Mary. The gilded bronze effigies of both father and daughter repose at full length o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruges
Bruges ( , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the province of West Flanders, in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is in the northwest of the country, and is the sixth most populous city in the country. The area of the whole city amounts to more than 14,099 hectares (140.99 km2; 54.44 sq. miles), including 1,075 hectares off the coast, at Zeebrugge (from , meaning 'Bruges by the Sea'). The historic city center is a prominent World Heritage Site of UNESCO. It is oval and about 430 hectares in size. The city's total population is 117,073 (1 January 2008),Statistics Belgium; ''Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008'' (excel-file) Population of all municipalities in Belgium, as of 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 19 October 2008. of who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Style
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from the early 17th century until the 1750s. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep color, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to the rest of Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, Poland and Russia. By the 1730s, it had evolved into an even more flamboyant style, called ''rocaille'' or ''Rococo'', which appeared in France and Central Europe until the mid to late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
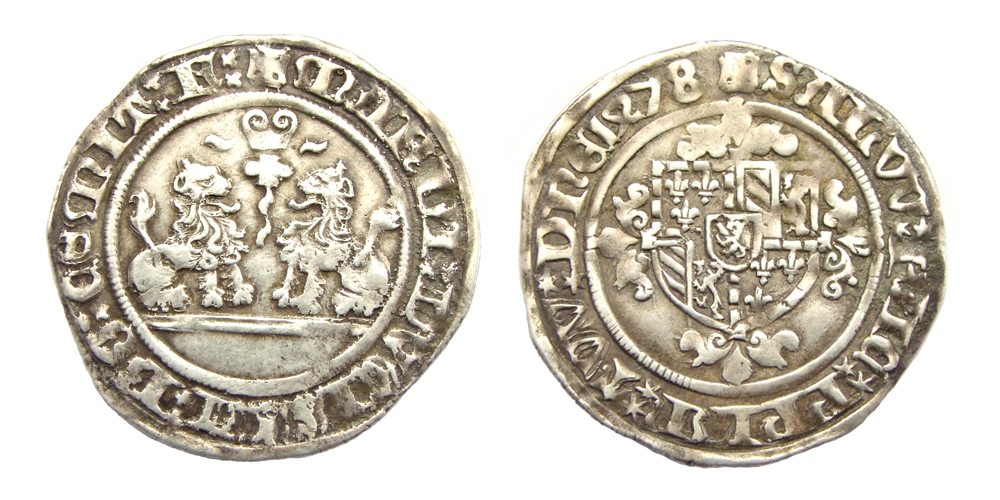
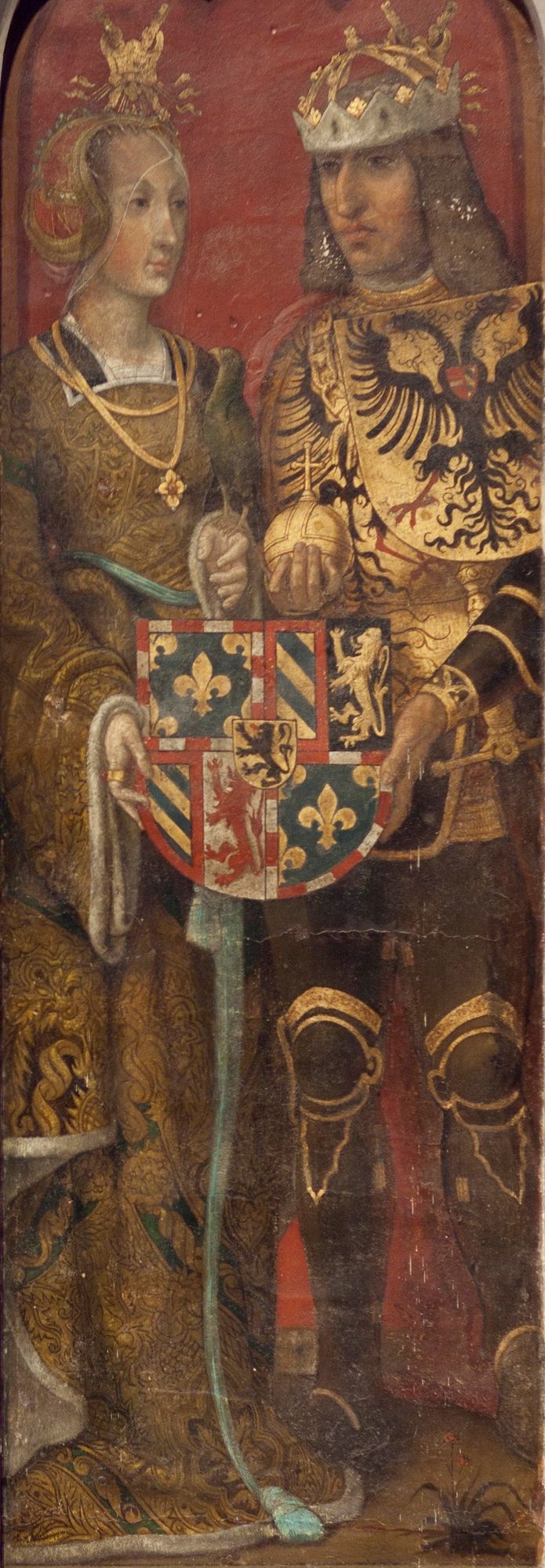
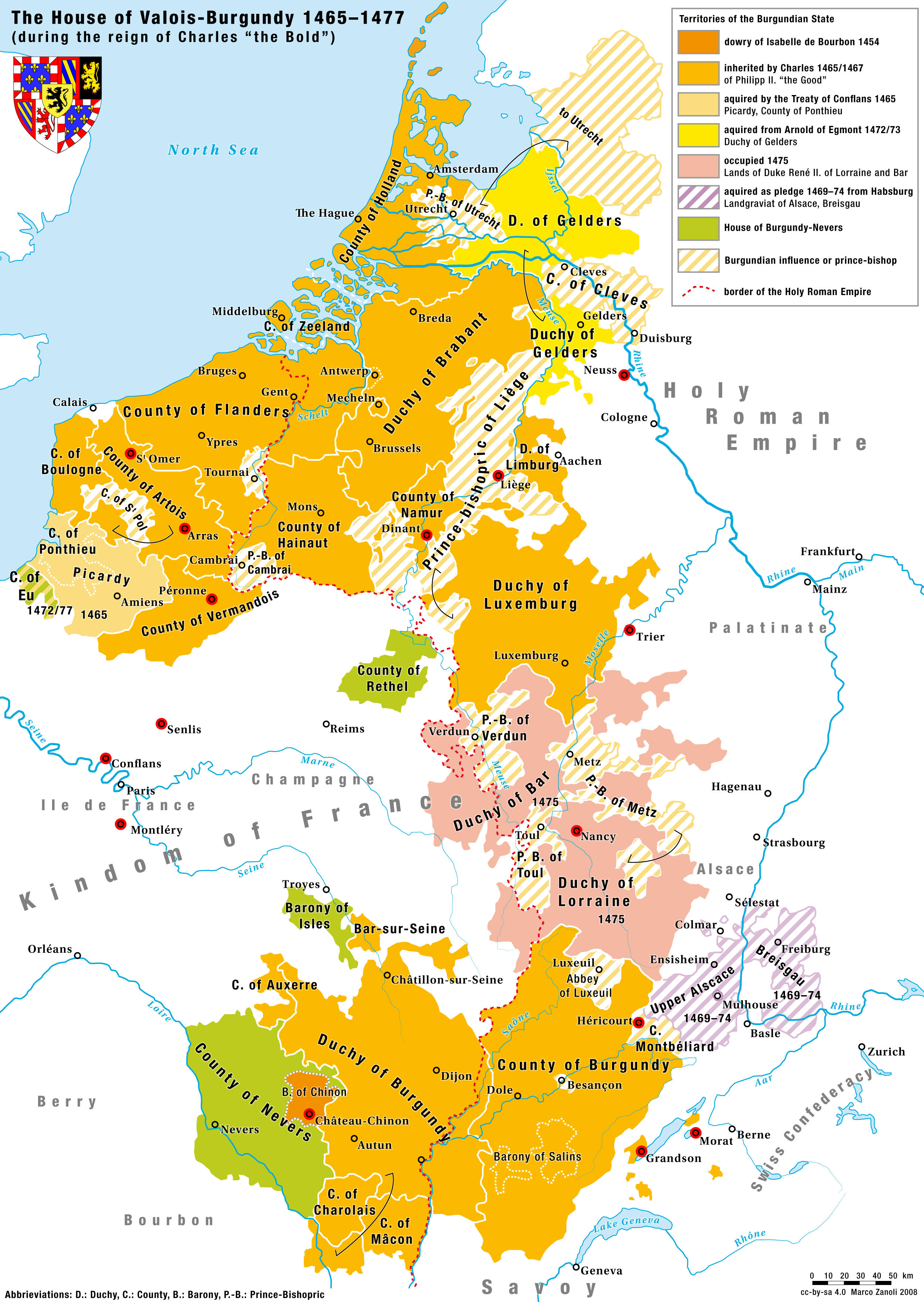
Charles The Bold
Charles Martin (10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), called the Bold, was the last duke of Burgundy from the House of Valois-Burgundy, ruling from 1467 to 1477. He was the only surviving legitimate son of Philip the Good and his third wife, Isabella of Portugal. As heir and as ruler, Charles vied for power and influence with rivals such as his overlord, King Louis XI of France. In 1465 Charles led a successful revolt of Louis's vassals in the War of the Public Weal. After becoming the Duke of Burgundy in 1467, Charles pursued his ambitions for a kingdom, independent from France, that would stretch contiguously from the North Sea in the north to the borders of Savoy in the south. For this purpose, he acquired Guelders and Upper Alsace; sought the title King of the Romans; and gradually became an enemy of the Germans. Charles married Margaret of York for an English alliance. He arranged the betrothal between his sole child, Mary, with Maximilian of Austria. A passiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siena Cathedral
Siena Cathedral () is a medieval church in Siena, Italy, dedicated from its earliest days as a Roman Catholic Marian church, and now dedicated to the Assumption of Mary. Since the early 13th-century the Siena Cathedral has been an important part of the Sienese identity. One way to see this is the continuous building projects constantly surrounding the cathedral from its earliest days, aiming at reinforcing and expanding this site. Indeed, it was the community of citizens that continually advocated for the cathedral to become one of the largest churches in Europe. For centuries the Cathedral acted as more than just a place of worship - it was the center of the city and a place to express civic pride. The cathedral was designed and completed between 1215 and 1263 on the site of an earlier structure. It has the form of a Latin cross with a slightly projecting transept, a dome and a bell tower. The dome rises from a hexagonal base with supporting columns. The dome was completed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrara
Carrara ( ; ; , ) is a town and ''comune'' in Tuscany, in central Italy, of the province of Massa and Carrara, and notable for the white or blue-grey Carrara marble, marble quarried there. It is on the Carrione River, some Boxing the compass, west-northwest of Florence. Its motto is Latin: '' "" ("My strength is in the wheel"), a reference firstly to the marble shipping industry from Roman times onwards. Toponymy The word ''Carrara'' likely comes from the pre-Roman (Celtic languages, Celtic or Ligurian language (ancient), Ligurian) element ''kar'' (stone), through Latin ''carrariae'' meaning 'quarries'. History There were known settlements in the area as early as the ninth century BC, when the Apuan Ligures lived in the region. The current town originated from the borough built to house workers in the marble quarries created by the ancient Rome, Romans after their conquest of Liguria in the early second century BC. Carrara has been linked with the process of quarrying and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (6March 147518February 1564), known mononymously as Michelangelo, was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was inspired by models from classical antiquity and had a lasting influence on Western art. Michelangelo's creative abilities and mastery in a range of artistic arenas define him as an archetypal Renaissance man, along with his rival and elder contemporary, Leonardo da Vinci. Given the sheer volume of surviving correspondence, sketches, and reminiscences, Michelangelo is one of the best-documented artists of the 16th century. He was lauded by contemporary biographers as the most accomplished artist of his era. Michelangelo achieved fame early. Two of his best-known works, the ''Pietà (Michelangelo), Pietà'' and ''David (Michelangelo), David'', were sculpted before the age of 30. Although he did not consider himself a painter, Michelangelo created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madonna Of Bruges
The ''Madonna of Bruges'' is a marble sculpture by Michelangelo of the Virgin and Child. Michelangelo's depiction of the ''Madonna and Child'' differs significantly from earlier representations of the same subject, which tended to feature a pious Virgin smiling down on an infant held in her arms. Instead, Jesus stands upright, almost unsupported, only loosely restrained by Mary's left hand, and appears to be about to step away from his mother. Meanwhile, Mary does not cling to her son or even look at him, but gazes down and away. It is believed the work was originally intended for an altar piece. If this is so, then it would have been displayed facing slightly to the right and looking down. The early 16th-century sculpture also displays the High Renaissance Pyramid style frequently seen in the works of Leonardo da Vinci during the late 1400s. ''Madonna and Child'' shares certain similarities with Michelangelo's ''Pietà'', which was completed shortly before – mainly, Mary' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Lovel
Mary Lovel (1564November12, 1628), born Jane Roper and also known as Mary Roper and Lady Lovel, was the founder of the English Carmelite convent in Antwerp. Life Lovel died in Bruges. Her parents were Elizabeth (born Parke) and John Roper, Baron Teynham who lived at the Lodge in Lynsted in Kent which was built in 1599. Her father was the chief clerk of the common pleas. She appears to have been called Jane but she was later called Mary. In 1597 she gave birth to Christina Lovel. The child's father was a soldier named Sir Robert Lovel of Merton Abbey in Kent (who she had married at some date before). The marriage was not a long one and Robert's death is thought to have been before 1606. The marriage resulted in Christina and her younger sister Elizabeth and making Lovel a widow. In 1606 she was questioned concerning her involvement in the Gunpowder Plot. It was admitted that she had known the major conspirator Sir Robert Catesby for some time and he had visited her house in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word ''fresco'' () is derived from the Italian adjective ''fresco'' meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting. The word ''fresco'' is commonly and inaccurately used in English to refer to any wall painting regardless of the plaster technology or binding medium. This, in part, contributes to a misconception that the most geographically and temporally common wall painting technology was the painting into wet lime plaster. Even in apparently '' buon fresco'' technology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Golden Fleece
The Distinguished Order of the Golden Fleece (, ) is a Catholic order of chivalry founded in 1430 in Brugge by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, to celebrate his marriage to Isabella of Portugal, Duchess of Burgundy, Isabella of Portugal. Today, two branches of the order exist, namely the Spanish Fleece and the Austrian Fleece; the current grand masters are Felipe VI, King Felipe VI of Spain and Karl von Habsburg, head of the House of Habsburg-Lorraine, respectively. The Grand Chaplain of the Austrian branch is Cardinal Christoph Schönborn, Archbishop of Vienna. The separation of the two existing branches took place as a result of the War of the Spanish Succession of 1701–1714. The grand master of the order, Charles II of Spain (a House of Habsburg , Habsburg), had died childless in 1700, and so the right to succeed to the throne of Spain (and thus to become the Sovereign of the Order of the Golden Fleece) initiated a global conflict. On one hand, Charles VI, Holy Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy (; ; 13 February 1457 – 27 March 1482), nicknamed the Rich, was a member of the House of Valois-Burgundy who ruled the Burgundian lands, comprising the Duchy of Burgundy, Duchy and Free County of Burgundy, County of Burgundy and the Burgundian Netherlands, from 1477 to her death. As the only child of Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, and his wife Isabella of Bourbon, Mary inherited the Burgundian lands at the age of 19 upon the death of her father in the Battle of Nancy on 5 January 1477. In order to counter the appetite of the French king Louis XI for her lands, she married Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian of Austria, with whom she had two children. The marriage kept large parts of the Burgundian lands from disintegration, but also changed the dynasty from Valois to Habsburg (the Duchy of Burgundy itself soon became a French possession). This was a turning point in European politics, leading to a French–Habsburg rivalry that would endure for c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Mary Of Burgundy
The Tomb of Mary of Burgundy is a funeral monument completed in 1501 for Mary of Burgundy's grave in the Church of Our Lady, Bruges. She died in March 1482, aged 25, following injuries sustained during a hunting accident a number of weeks earlier. Mary was born in 1457 as the only child of Charles the Bold and Isabella of Bourbon. On her father's death at the Battle of Nancy, she became the last of the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited the Duchy of Burgundy, making her the then-richest woman in Europe. The tomb was commissioned by her husband Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian of Austria and their eldest child Philip the Handsome, Philip the Fair, based on a rough design specified during her Dying declaration, deathbed wishes. A number of sculptors, stonemasons and painters, perhaps headed by the Flemish sculptor Renier van Thienen, were involved in its creation; records suggest contributions by Jan Borman, Pieter de Backere and Jehan Hervy, although the chronology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |