|
Chips And Technologies
Chips and Technologies, Inc. (C&T), was an early fabless semiconductor company founded in Milpitas, California, in December 1984 by Gordon A. Campbell and Dado Banatao. Its first product, announced September 1985, was a four chip Enhanced Graphics Adapter, EGA chipset that handled the functions of 19 of IBM's proprietary chips on the Enhanced Graphics Adapter. By that November's COMDEX, more than a half dozen companies had introduced EGA-compatible boards based on C&T's chipset.The Enhanced Graphics Standard Comes of Age ''PC Magazine'', August 1986 This was followed by chipsets for PC motherboards and other computer graphics chips. C&T was acquired by Intel in 1997, primarily for its graphics chip business. Former members of C&T founded Asiliant Technologies in January 2000 to continue the supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milpitas, California
Milpitas (Spanish for or little cornfields) is a city in Santa Clara County, California, part of Silicon Valley and the broader San Francisco Bay Area. Located on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay, it is bordered by San Jose, California, San Jose to the south, Fremont, California, Fremont to the north, and the Coyote Creek (Santa Clara County), Coyote Creek and Calaveras Reservoir to the west. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city population was 80,273. The city is located at the junction of Interstates Interstate 680 (California), 680 and Interstate 880 (California), 880 and is served by the Milpitas Transit Center, Milpitas BART station. Historically inhabited by the Ohlone people, the area served as a crossroads between Mission San José de Guadalupe in present-day Fremont and Mission Santa Clara de Asis in present-day Santa Clara. The city’s modern development began in the mid-20th century, driven by postwar suburbanization and its incorporation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
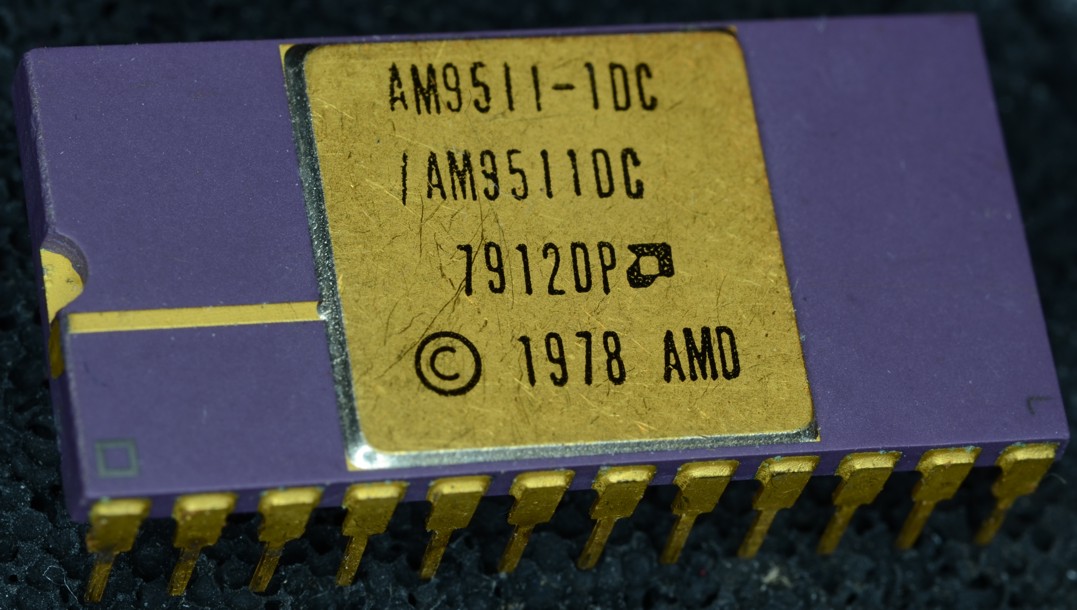
Coprocessor
A coprocessor is a computer processor used to supplement the functions of the primary processor (the CPU). Operations performed by the coprocessor may be floating-point arithmetic, graphics, signal processing, string processing, cryptography or I/O interfacing with peripheral devices. By offloading processor-intensive tasks from the main processor, coprocessors can accelerate system performance. Coprocessors allow a line of computers to be customized, so that customers who do not need the extra performance do not need to pay for it. Functionality Coprocessors vary in their degree of autonomy. Some (such as FPUs) rely on direct control via coprocessor instructions, embedded in the CPU's instruction stream. Others are independent processors in their own right, capable of working asynchronously; they are still not optimized for general-purpose code, or they are incapable of it due to a limited instruction set focused on accelerating specific tasks. It is common for these to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8259
The Intel 8259 is a programmable interrupt controller (PIC) designed for the Intel 8085 and Intel 8086, 8086 microprocessors. The initial part was 8259, a later A suffix version was upward compatible and usable with the 8086 or Intel 8088, 8088 processor. The 8259 combines multiple interrupt input sources into a single interrupt output to the host microprocessor, extending the interrupt levels available in a system beyond the one or two levels found on the processor chip. The 8259A was the interrupt controller for the ISA bus in the original IBM PC and IBM PC AT. The 8259 was introduced as part of Intel's Intel 8085#MCS-85 family, MCS 85 family in 1976. The 8259A was included in the original PC introduced in 1981 and maintained by the PC/XT when introduced in 1983. A second 8259A was added with the introduction of the PC/AT. The 8259 has coexisted with the Intel APIC Architecture since its introduction in symmetric multiprocessor PCs. Modern PCs have begun to phase out the 8259A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8237
Intel 8237 is a direct memory access (DMA) controller, a part of the MCS 85 microprocessor family. It enables data transfer between memory and the I/O with reduced load on the system's main processor by providing the memory with control signals and memory address information during the DMA transfer. The 8237 is a four-channel device that can be expanded to include any number of DMA channel inputs. The 8237 is capable of DMA transfers at rates of up to per second. Each channel is capable of addressing a full 64k-byte section of memory and can transfer up to 64k bytes with a single programming. A single 8237 was used as the DMA controller in the original IBM PC and IBM XT. The IBM PC AT added another 8237 in master-slave configuration, increasing the number of DMA channels from four to seven. Later IBM-compatible personal computers may have chip sets that emulate the functions of the 8237 for backward compatibility. The Intel 8237 was actually designed by AMD (called Am9517). I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8288
The Intel 8288 is a bus controller designed for Intel 8086/8087/8088/ 8089. The chip is supplied in 20-pin DIP package. The 8086 (and 8088) operate in maximum mode, so they are configured primarily for multiprocessor operation or for working with coprocessors. Necessary control signals are generated by the 8288. It was used in the IBM PC, XT and its clones. IBM PC AT The IBM Personal Computer AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 802 ... used its successor Intel 82288. Pin assignment and function for the control lines Variants Both Intel 8288 and I8288 (industrial grade) version were available for US$14.30 and $33.75 in quantities of 100 respectively. The available 82C88 CMOS version was outsourced to Oki Electronic Industry Co., Ltd. The package version of Intel 82C88 branded in 20-pin PLCC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8284
The Intel 8284 is a clock oscillator chip developed primarily for supplying clock signals for the Intel 8086, Intel-8086/Intel 8087, 8087/Intel 8088, 8088/Intel 8089, 8089 series of processors. The commercial variant of the chip comes in 18-pin Dual in-line package, DIL and 20-pin Chip carrier#Plastic leaded chip carrier, PLCC packages, and originally was priced at $4.90 USD. The industrial version, rated for the temperatures range of -40 °C to +85 °C was priced at $13.50 USD. The available 82C84A CMOS version was outsourced to Oki_Electric_Industry, Oki Electronic Industry Co., Ltd. The available packaged Intel 82C84A version of 20-pin Chip_carrier#Plastic-leaded_chip_carrier, PLCC in sampling at first quarter of 1986.Ashborn, Jim; "Advanced Packaging: A Little Goes A Long Way", Intel Corporation, Solutions, January/February 1986, Page 2 Function The 8284 contains a clock generator capable of a third the frequency of the input clock (5 or 8MHz with the 8284A, and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC/XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT (model 5160, often shortened to PC/XT) is the second computer in the IBM Personal Computer line, released on March 8, 1983. Except for the addition of a built-in hard drive and extra expansion slots, it is very similar to the original IBM PC model 5150 from 1981. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of "XT" on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some publications expanded the term as "''eXtended Technology''" or just "''eXTended''". Features The XT was regarded as an incremental improvement over the PC and a disappointment compared to the next-generation successor that some had anticipated. Compared to the original IBM PC, the XT has the following major differences: * The number of expansion slots was increased from five to eight * Base RAM was increased to at least 128 KB * 2x32KB ROM ICs replace the previous 5x8KB ROM ICs * A 10 MB hard drive was included on most sub-models, with a disk controller featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC V20
The NEC V20 is a microprocessor that was designed and produced by NEC. It is both pin compatible and object-code compatible with the Intel 8088, with an instruction set architecture (ISA) similar to that of the Intel 80188 with some extensions. The V20 was introduced in March 1984. Features The V20's die comprised 63,000 transistors; more than double the 29,000 of the 8088 CPU. The chip was designed for a clock duty cycle of 50%, compared to the 33% duty cycle used by the 8088. The V20 has two 16-bit wide internal databuses, allowing two data transfers to occur concurrently. Differences like that meant that a V20 could typically complete more instructions in a given time than an Intel 8088 running at the same frequency. The V20 was fabricated in 2-micron CMOS technology. Early versions ran at speeds of 5, 8, and 10 MHz. In 1990, an upgrade to the fabrication process technology resulted in the V20H and V20HL, with improved performance and reduced power consumption. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range are unchanged, however. In fact, according to the Intel documentation, the 8086 and 8088 have the same execution unit (EU)—only the bus interface unit (BIU) is different. The 8088 was used in the original IBM PC and in IBM PC compatible clones. History and description The 8088 was designed at Intel's laboratory in Haifa, Israel, as were a large number of Intel's processors. The 8088 was targeted at economical systems by allowing the use of an eight-bit data path and eight-bit support and peripheral chips; complex circuit boards were still fairly cumbersome and expensive when it was released. The prefetch queue of the 8088 was shortened to four bytes, from the 8086's six bytes, and the prefetch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC V30
The NEC V20 is a microprocessor that was designed and produced by NEC. It is both pin compatible and object-code compatible with the Intel 8088, with an instruction set architecture (ISA) similar to that of the Intel 80188 with some extensions. The V20 was introduced in March 1984. Features The V20's die comprised 63,000 transistors; more than double the 29,000 of the 8088 CPU. The chip was designed for a clock duty cycle of 50%, compared to the 33% duty cycle used by the 8088. The V20 has two 16-bit wide internal databuses, allowing two data transfers to occur concurrently. Differences like that meant that a V20 could typically complete more instructions in a given time than an Intel 8088 running at the same frequency. The V20 was fabricated in 2-micron CMOS technology. Early versions ran at speeds of 5, 8, and 10 MHz. In 1990, an upgrade to the fabrication process technology resulted in the V20H and V20HL, with improved performance and reduced power consumption. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allowing the use of cheaper and fewer supporting ICs),Fewer TTL buffers, latches, multiplexers (although the amount of TTL logic was not drastically reduced). It also permits the use of cheap 8080-family ICs, where the 8254 CTC, 8255 PIO, and 8259 PIC were used in the IBM PC design. In addition, it makes PCB layout simpler and boards cheaper, as well as demanding fewer (1- or 4-bit wide) DRAM chips. and is notable as the processor used in the original IBM PC design. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture, which eventually became Intel's most successful line of processors. On June 5, 2018, Intel released a limited-edition CPU celebrating the 40th anniversary of the Intel 8086, called the Intel Core i7-8086K. History Background In 1972 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrix
Cyrix Corporation was a microprocessor developer that was founded in 1988 in Richardson, Texas, as a specialist supplier of floating point units for 286 and 386 microprocessors. The company was founded by Tom Brightman and Jerry Rogers. Terry Rogers was also serving as the company Chief Executive Officer and president up until December 9, 1996, when he stepped down from this role, but remained on the Board of Directors. In 1992, Cyrix introduced its own i386 compatible processors, the 486SLC and 486DLC. These had higher performance than the Intel parts, but a lower price. They were primarily marketed to users looking to upgrade existing machines. Their release sparked a lengthy series of lawsuits with Intel while their foundry partner IBM was releasing the same designs under their own branding. The combination of these events led Cyrix to begin losing money, and the company merged with National Semiconductor on 11 November 1997. National released Cyrix's latest designs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |