|
Children's Eternal Rainforest
The Children's Eternal Rainforest () is a private land trust and preserve in Costa Rica. The preserve is run by the non-profit Monteverde Conservation League. History The Monteverde Conservation League was formed in 1986 to counteract agricultural development threatening Pacific Slope forests near the Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve. After U.S. biologist Sharon Kinsman gave a presentation about the rainforests to a class of Swedish schoolteacher Eha Kern, the children raised funds to protect the forest. Their efforts initially raised $18,000 for the forest. Kern and her husband formed the Swedish non-profit Barnens Regnskog (Children's Rainforest) in 1987. By 1998 the Children's Eternal Rainforest was the largest private biological reserve in Central America, spanning in the Guanacaste, Alajuela, and Puntarenas provinces. Biology The preserve's 23,000 hectares is one of the most biodiverse areas on Earth. It contains 450 species of birds, which is about 50% of Costa Ric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime boundary, maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of nearly . An estimated people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Presidential system, presidential republic. It has a long-standing and stable Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agriculture, has diversified to include sectors such as finance, corporate services for foreign companies, pharmaceut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Composition
Relative species abundance is a component of biodiversity and is a measure of how common or rare a species is relative to other species in a defined location or community.Hubbell, S. P. 2001. ''The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography''. Princeton University Press, Princeton, N.J. Relative abundance is the percent composition of an organism of a particular kind relative to the total number of organisms in the area. Relative species abundance (ecology), abundances tend to conform to specific patterns that are among the best-known and most-studied patterns in macroecology. Different populations in a community exist in relative proportions; this idea is known as relative abundance. Introduction Relative species abundance Relative species abundance and species richness describe key elements of biodiversity. Relative species abundance refers to how common or rare a species is relative to other species in a given location or community.McGill, B. J., Etienne R. S., Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reserves In Costa Rica
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history (Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn at the same time, especially after Charles Darwin. Within the various uses of the word t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainforests
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropical rainforests or temperate rainforests, but other types have been described. Estimates vary from 40% to 75% of all biotic community, biotic species being Indigenous (ecology), indigenous to the rainforests. There may be many millions of species of plants, insects and microorganisms still undiscovered in tropical rainforests. Tropical rainforests have been called the "jewels of the Earth" and the "medicine chest (idiom), world's largest pharmacy", because over one quarter of natural medicines have been discovered there. Rainforests as well as endemic rainforest species are rapidly disappearing due to #Deforestation, deforestation, the resulting habitat loss and air pollution, pollution of the atmosphere. Definition Rainforests are cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Trusts
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of Earth not submerged by the ocean or another body of water. It makes up 29.2% of Earth's surface and includes all continents and islands. Earth's land surface is almost entirely covered by regolith, a layer of rock, soil, and minerals that forms the outer part of the crust. Land plays an important role in Earth's climate system, being involved in the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle. One-third of land is covered in trees, another third is used for agriculture, and one-tenth is covered in permanent snow and glaciers. The remainder consists of desert, savannah, and prairie. Land terrain varies greatly, consisting of mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, glaciers, and other landforms. In physical geology, the land is divided into two major categories: Mountain ranges and relatively flat interiors called cratons. Both form over millions of years through plate tectonics. Streams – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Corridor
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of life. Central to biology are five fundamental themes: the cell as the basic unit of life, genes and heredity as the basis of inheritance, evolution as the driver of biological diversity, energy transformation for sustaining life processes, and the maintenance of internal stability (homeostasis). Biology examines life across multiple levels of organization, from molecules and cells to organisms, populations, and ecosystems. Subdisciplines include molecular biology, physiology, ecology, evolutionary biology, developmental biology, and systematics, among others. Each of these fields applies a range of methods to investigate biological phenomena, including observation, experimentation, and mathematical modeling. Modern biology is grounded i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deforestation In Costa Rica
Deforestation is a major threat to biodiversity and ecosystems in Costa Rica. The country has a rich biodiversity with some 12,000 species of plants, 1,239 species of Butterfly, butterflies, 838 species of birds, 440 species of reptiles and amphibians, and 232 species of mammals, which have been under threat from the effects of deforestation. Agricultural development, cattle ranching, and logging have caused major deforestation as more land is cleared for these activities. Despite government efforts to mitigate deforestation, it continues to cause harm to the environment of Costa Rica by impacting flooding, soil erosion, desertification, and Biodiversity loss, loss of biodiversity. History The land currently being used for forestry in Costa Rica was at one point used by the Cabécar people, Cabécar People. Like many other native cultures, they used Slash-and-burn, slash and burn agriculture to manage their small-scale agriculture. In the early 1900s, companies based in England b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
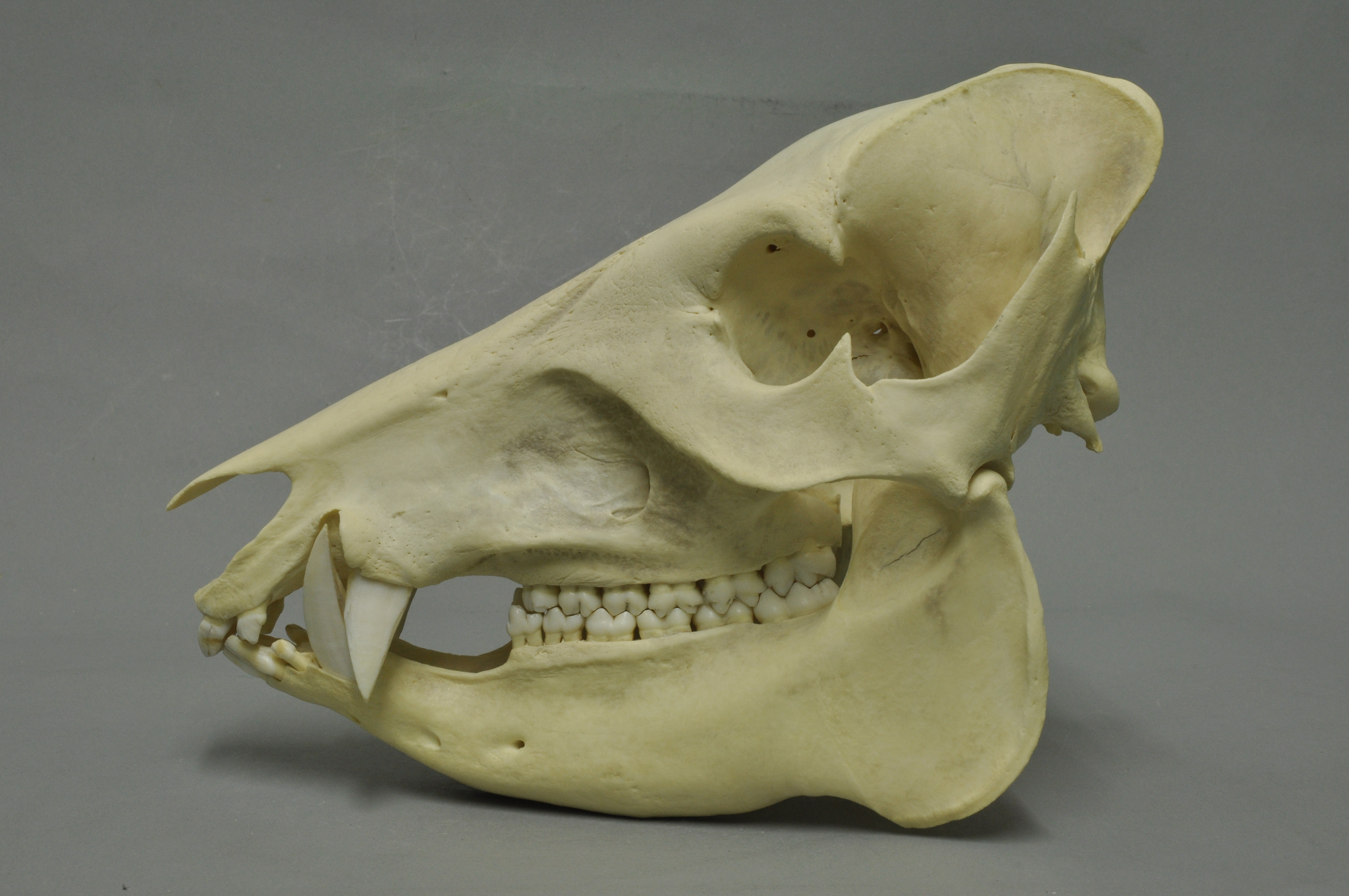
White-lipped Peccary
The white-lipped peccary (''Tayassu pecari'') is a species of peccary found in Central and South America and the only member of the genus ''Tayassu''. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair (except on certain regions, such as the throat, where it is cream). The range of ''T. pecari'', which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall (especially in Mexico and Central America). They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries. They are an important part of their ecosystem and multiple efforts are being made to preserve them in the wild. Not all disappearances are explained, but human activities play a role, with two major threats being deforestation and hunting; the latter is very common in rural areas, although it can be dan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth except glaciers. The world's richest diversity of orchid genera and species is in the tropics. Orchidaceae is one of the two largest families of flowering plants, the other being the Asteraceae. It contains about 28,000 currently accepted species in 702 genera. The Orchidaceae family encompasses about 6–11% of all species of seed plants. The largest genera are '' Bulbophyllum'' (2,000 species), '' Epidendrum'' (1,500 species), '' Dendrobium'' (1,400 species) and '' Pleurothallis'' (1,000 species). It also includes '' Vanilla'' (the genus of the vanilla plant), the type genus '' Orchis'', and many commonly cultivated plants such as '' Phalaenopsis'' and '' Cattleya''. Moreover, since the introduction of tropical species into cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Slope
The Pacific Slope describes geographic regions in North American, Central American, and South American countries that are west of the continental divide and slope down to the Pacific Ocean. In North America, the Rocky Mountains mark the eastern border of the Pacific Slope. In Central and South America, the region is much narrower, confined by the Sierra Madre Occidental in Central America, and by the Andes in South America. The phrase is still used today mostly for scientific purposes to refer to regions inhabited by specific species. It was and is still occasionally used to describe the region in North America during the 19th century and the expansion of the Old West. It includes the states and territories west of the continental divide that runs down the Rocky Mountains in North America. This included the territories and the states that emerged from them, including California, Oregon Territory, Washington Territory, Nevada Territory, Idaho Territory, Colorado Territory, and Utah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
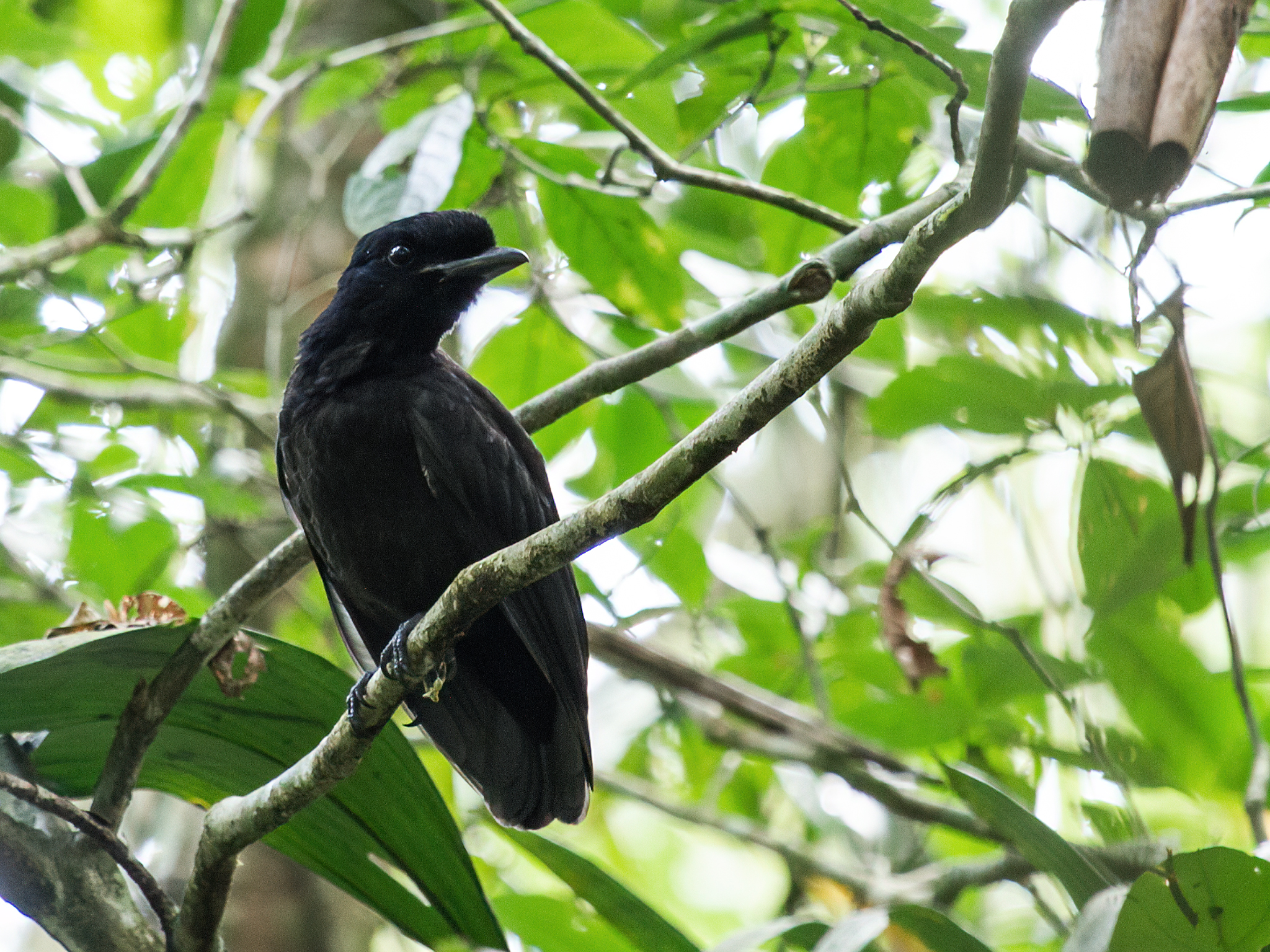
Bare-necked Umbrellabird
The bare-necked umbrellabird (''Cephalopterus glabricollis'') is a species of bird in the family Cotingidae. It is found in the Talamancan montane forests of Costa Rica and Panama. Bare-necked umbrellabirds live only in forests and their diet consists mainly of fruits. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical moist montane forest. It is threatened by habitat loss. Taxonomy and systematics The bare-necked umbrellabird is one of three species in the genus '' Cephalopterus'', commonly known as the umbrellabirds. It was first described by John Gould in 1851, on the basis of specimens collected by Warzewickz at elevations of in Panama. The generic name ''Cephalopterus'' comes from the Greek κεφαλη (''kephalē''), meaning head, and πτερος (''pteros''), meaning feathered, referring to the head plumes of the Amazonian umbrellabird. The specific epithet ''glabricollis'' is from the Latin ''glaber'', meaning bald, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |