|
Chenkuttuvan
Chenkuttuvan (c. 180 CE, literally 'the Righteous Kuttuvan'), title Kadal Pirakottiya, identified with Kadalottiya Vel Kezhu Kuttuvan, was the most celebrated Chera ruler of early historic South India. He is also mentioned in Chilappathikaram, the Tamil epic poem purportedly composed by the Chera prince Ilanko Adikal''.'' Chenkuttavan is eulogized by the poet Paranar in the fifth decade of the Pathitrupathu Collection, part of the Ettuthokai anthology of early Tamil literature. He was likely a member of the Muchiri-Karur branch (associated with present-day central Kerala) of the Chera dynasty. During his reign, the Chera territory encompassed the Malabar Coast (present-day Kerala) and the interior Kongu country (western Tamil Nadu). The influx of Yavana (Greco-Roman) gold into south India through the Indian Ocean spice trade during Chenkuttavan's reign is memorably described in ancient Tamil poems. According to Fifth Decade, Pathitrupathu, Chenkuttavan achieved a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nedum Cheralathan
Nedum Cheralathan (fl. c. 155 CE, title "Imayavarampan") was a Chera ruler from early historic south India (c. 1st - 4th century CE), noted for his interactions with the Yavanas (the Greco-Roman navigators) on the Malabar Coast. He likely belonged to the Muchiri-Karur branch of the Chera dynasty. He is praised in the Second Ten of Pathitruppathu Collection, composed by poet Kannanar. In return for his work, the poet was generously rewarded with 500 settlements in a region called "Umbar Kadu" (believed to be in present-day Kerala) and a share of the revenue from the thennadu ("the southern country") for 38 years. According to these poems, Nedum Cheralathan ruled the Chera country for 58 years. Nedum Cheralathan was born to his predecessor, Uthiyan Cheralathan, and his wife Venmal Nallini, the daughter of Veliyan—who is possibly also identified as the father of the Ay chieftain Eyinan. Some accounts suggest that before Nedum Cheralathan ascended the throne, Uthiyan Cheral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodungallur Bhagavathy Temple
Sree Kurumba Bhagavati Temple (alternatively Kodungallur Kav) is a Hindu temple at Kodungallur, Thrissur District, Kerala state, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Bhadrakali, a form of Kali, Mahakali worshipped and significantly revered in Kerala. The goddess is known also by the names ''"Sri Kurumba"'' (The Mother of Kodungallur). This temple is the head of 64 Bhadrakali kavus in Malabar district, Malabar. This Kali, Mahakali temple is one of the oldest functioning temples in India. The goddess of the temple represents the goddess in her fierce ('ugra') form, facing North, featuring eight hands with various attributes. One is holding the head of the demon king Daruka, another a sickle-shaped sword, next an anklet, another a bell, among others. The temple is often accredited as the original form of Goddess Kali. During the reign of Kulasekhara dynasty (Second Cheras), Later Cheras, Mahodayapuram (Kodungallur) was the capital of the Chera empire and one of the most importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silapathikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theological v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattini
Pattini (, ) is considered a guardian deity of Sri Lanka in both Sri Lankan Buddhism and Sinhalese people, Sinhalese folklore. She is also worshipped by Hinduism in Sri Lanka, Sri Lankan Tamil Hindus under the name Kannaki Amman. Pattini is regarded as the patron goddess of fertility and health, especially as a protector against smallpox, which is referred to in Sinhala language, Sinhala as ''deviyange ledé'' ("the divine affliction"). History Goddess Pattini is the deified form of Kannaki, the central character of the Tamil epic ''Cilappatikaram'', composed by Ilango Adigal in south India after the 2nd century CE. The worship of Pattini was introduced to Sri Lanka shortly thereafter, where it absorbed earlier local deities such as Kiri Amma ("the Milk Mother"). Historians attribute the introduction of Goddess Pattini to Gajabahu I, a Sinhalese ruler who reigned in Sri Lanka from 113 to 135 CE. According to some historians, the ''Cilappatikaram'' mentions Gajabahu's presence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gajabahu Synchronism
Gajabahu synchronism, also known as Gajabaju-Chenkuttuvan synchronism is a chronological tool used by scholars and historians to date early historic or pre-Pallava South India, especially the early Tamil history. The method was first proposed by scholar V. Kanakasabhai Pillai in 1904 in his work "The Tamils Eighteen Hundred Years Ago" and was later supported by scholars such as K. A. Nilakanta Sastri. Historian Kamil Zvelebil, while acknowledging the fragility of this synchronism, famously called it the "sheet anchor" for dating early Tamil literature (the Sangam literature). It is based on the contemporaneity of the early historic Chera king Senguttuvan with Gajabahu I, the 2nd century CE Sri Lankan ruler. Complementary epigraphical/archeological evidence broadly seems to support the Gajabahu dating. Method In the final sections of the Tamil epic Silappatikaram, there is a reference to a ruler of Lanka (Sri Lanka) named "Kayavaku". According to the verses, Kayavaku was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
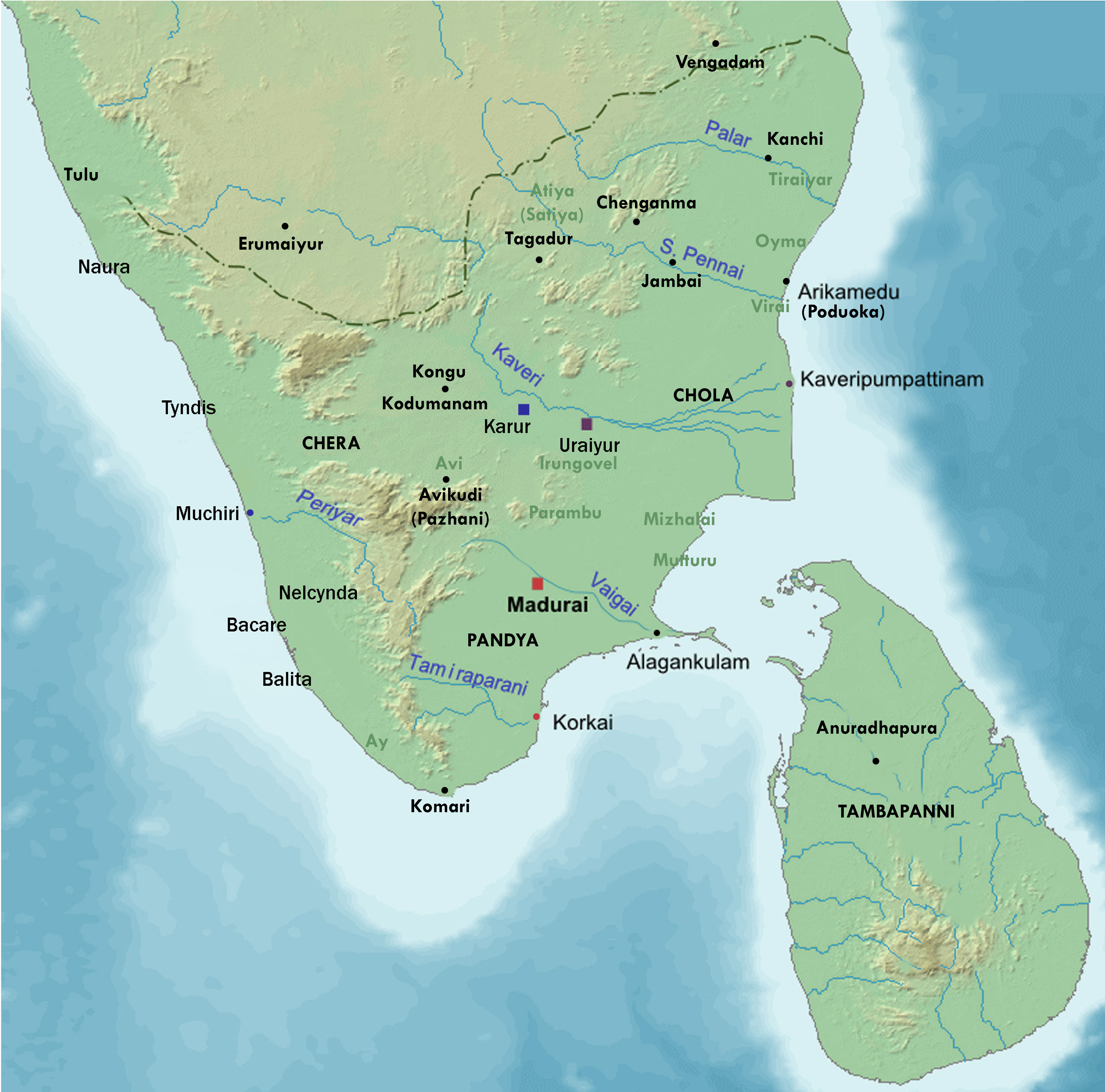
Chera Dynasty
The Chera dynasty ( or Cēra, ), also known as Keralaputra, from the early historic or the Sangam period in Tamil-speaking southern India, ruled over parts of present-day states Kerala and Tamil Nadu. The Cheras, known as one of the mu-ventar (the Three Crowned Kings) of Tamilakam (the Tamil Country) alongside the Cholas and Pandyas, have been documented as early as the third century BCE. The Chera country was geographically well placed at the tip of the Indian peninsula to profit from maritime trade via the extensive Indian Ocean networks. Exchange of spices, especially black pepper, with Middle Eastern or Graeco-Roman merchants is attested to in several sources. Chera influence extended over central Kerala and western Tamil Nadu until the end of the early historic period in southern India. The Cheras of the early historical period (c. second century BCE – c. third/fifth century CE) had their capital in interior Tamil country ( Vanchi-Karur, Kongu Nadu), and ports/capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ettuthokai
The Eight Anthologies, known as Eṭṭuttokai () or "Eight Collections" in the literature, is a classical Tamil poetic work that forms part of the Eighteen Greater Texts (''Patiṉeṇmēlkaṇakku'') anthology series of the Sangam Literature. The Eight Anthologies and its companion anthology, the Ten Idylls (''Pattuppāṭṭu''), is the oldest available Tamil literature. According to Kamil Zvelebil, a scholar of Tamil literature and history, dating these Eight Anthologies or their relative chronology is difficult, but the scholarship so far suggested that the earliest layers were composed sometime between the 1st century BCE and 2nd century CE, while the last layers were completed between 3rd and 5th century CE. Contents of the anthologies The Eight Anthologies consist of 2,371 poems varying from small stanzas of three lines in Ainkurnuru to stanzas of forty lines in Purananuru. The following poems form the Eight Anthologies: * '' Ainkurunuru'' (ஐங்குறுந ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satavahana Dynasty
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late 2nd century BCE and lasted until the early 3rd century CE, although some assign the beginning of their rule to as early as the 3rd century BCE based on the Puranas, but uncorroborated by archaeological evidence. The Satavahana kingdom mainly comprised the present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra. At different times, their rule extended to parts of modern Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. The dynasty had different capital cities at different times, including Pratishthana (Paithan) and Amaravati ( Dharanikota). The origin of the dynasty is uncertain, but according to the Puranas, their first king overthrew the Kanva dynasty. In the post-Maurya era, the Satavahanas established peace in the Decca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |