|
Chauvenet's Criterion
In statistical theory, Chauvenet's criterion (named for William Chauvenet) is a means of assessing whether one piece of experimental data — an outlier — from a set of observations, is likely to be spurious. Derivation The idea behind Chauvenet's criterion is to find a probability band, centered on the mean of a normal distribution, that should reasonably contain all n samples of a data set. By doing this, any data points from the n samples that lie outside this probability band can be considered to be outliers, removed from the data set, and a new mean and standard deviation based on the remaining values and new sample size can be calculated. This identification of the outliers will be achieved by finding the number of standard deviations that correspond to the bounds of the probability band around the mean (D_) and comparing that value to the absolute value of the difference between the suspected outliers and the mean divided by the sample standard deviation (Eq.1). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chauvenet
William Chauvenet (24 May 1820 in Milford, Pennsylvania – 13 December 1870 in St. Paul, Minnesota) was a professor of mathematics, astronomy, navigation, and surveying who was instrumental in the establishment of the U.S. Naval Academy at Annapolis, Maryland, and later the second chancellor of Washington University in St. Louis. Early life William Chauvenet was born on a farm near Milford, Pennsylvania to Guillaume Marc Chauvenet, a former soldier of Napoleon's army reconverted in silk trade after the Emperor's fall, and Mary B. Kerr and was raised in Philadelphia. He entered Yale University at age 16, and graduated in 1840 with high honors. While at Yale, Chauvenet contributed to the school newspaper and was a pianist with the Beethoven Society. He was one of eight founding members of the Skull and Bones Society. United States Navy In 1841, he was appointed a professor of mathematics in the United States Navy, and for a while served on the USS ''Mississippi'' teaching ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the '' arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the '' population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lower case Greek letter σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin letter '' s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. It is algebraically simpler, though in practice less robust, than the average absolute deviation. A useful property of the standard deviation is that, unlike the variance, it is expressed in the same unit as the data. The standard deviation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability
Probability is the branch of mathematics concerning numerical descriptions of how likely an Event (probability theory), event is to occur, or how likely it is that a proposition is true. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1, where, roughly speaking, 0 indicates impossibility of the event and 1 indicates certainty."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th Ed, (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', (Vol 1), 3rd Ed, (1968), Wiley, . The higher the probability of an event, the more likely it is that the event will occur. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantile Function
In probability and statistics, the quantile function, associated with a probability distribution of a random variable, specifies the value of the random variable such that the probability of the variable being less than or equal to that value equals the given probability. Intuitively, the quantile function associates with a range at and below a probability input the likelihood that a random variable is realized in that range for some probability distribution. It is also called the percentile function, percent-point function or inverse cumulative distribution function. Definition Strictly monotonic distribution function With reference to a continuous and strictly monotonic cumulative distribution function F_X\colon \mathbb \to ,1/math> of a random variable ''X'', the quantile function Q\colon , 1\to \mathbb returns a threshold value ''x'' below which random draws from the given c.d.f. would fall ''100*p'' percent of the time. In terms of the distribution function ''F'', the q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peirce's Criterion
In robust statistics, Peirce's criterion is a rule for eliminating outliers from data sets, which was devised by Benjamin Peirce. Outliers removed by Peirce's criterion The problem of outliers In data sets containing real-numbered measurements, the suspected outliers are the measured values that appear to lie outside the cluster of most of the other data values. The outliers would greatly change the estimate of location if the arithmetic average were to be used as a summary statistic of location. The problem is that the arithmetic mean is very sensitive to the inclusion of any outliers; in statistical terminology, the arithmetic mean is not robust. In the presence of outliers, the statistician has two options. First, the statistician may remove the suspected outliers from the data set and then use the arithmetic mean to estimate the location parameter. Second, the statistician may use a robust statistic, such as the median statistic. Peirce's criterion is a statistical procedu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grubbs's Test For Outliers
In statistics, Grubbs's test or the Grubbs test (named after Frank E. Grubbs, who published the test in 1950), also known as the maximum normalized residual test or extreme studentized deviate test, is a test used to detect outliers in a univariate data set assumed to come from a normally distributed population. Definition Grubbs's test is based on the assumption of normality. That is, one should first verify that the data can be reasonably approximated by a normal distribution before applying the Grubbs test. Grubbs's test detects one outlier at a time. This outlier is expunged from the dataset and the test is iterated until no outliers are detected. However, multiple iterations change the probabilities of detection, and the test should not be used for sample sizes of six or fewer since it frequently tags most of the points as outliers. Grubbs's test is defined for the hypothesis: :H0: There are no outliers in the data set :Ha: There is exactly one outlier in the data set The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outlier
In statistics, an outlier is a data point that differs significantly from other observations. An outlier may be due to a variability in the measurement, an indication of novel data, or it may be the result of experimental error; the latter are sometimes excluded from the data set. An outlier can be an indication of exciting possibility, but can also cause serious problems in statistical analyses. Outliers can occur by chance in any distribution, but they can indicate novel behaviour or structures in the data-set, measurement error, or that the population has a heavy-tailed distribution. In the case of measurement error, one wishes to discard them or use statistics that are robust to outliers, while in the case of heavy-tailed distributions, they indicate that the distribution has high skewness and that one should be very cautious in using tools or intuitions that assume a normal distribution. A frequent cause of outliers is a mixture of two distributions, which may be two dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
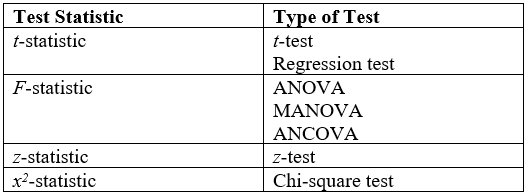
Statistical Tests
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |