|
Chance Fracture
A Chance fracture is a type of vertebral fracture that results from excessive flexion of the Vertebral column, spine. Symptoms may include abdominal bruising (seat belt sign), or less commonly paraplegia, paralysis of the legs. In around half of cases there is an associated abdominal injury such as a splenic rupture, small bowel injury, pancreatic injury, or mesenteric tear. Injury to the bowel may not be apparent on the first day. The cause is classically a head-on motor vehicle collision in which the affected person is wearing only a lap belt. Being hit in the abdomen with an object like a tree or a fall may also result in this fracture pattern. It often involves disruption of all three columns of the vertebral body (anterior, middle, and posterior). The most common area affected is the lower thoracic spine, thoracic and upper lumbar spine. A CT scan is recommended as part of the diagnostic work-up to detect any potential abdominal injuries. The fracture is often unstable fratur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraplegia
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
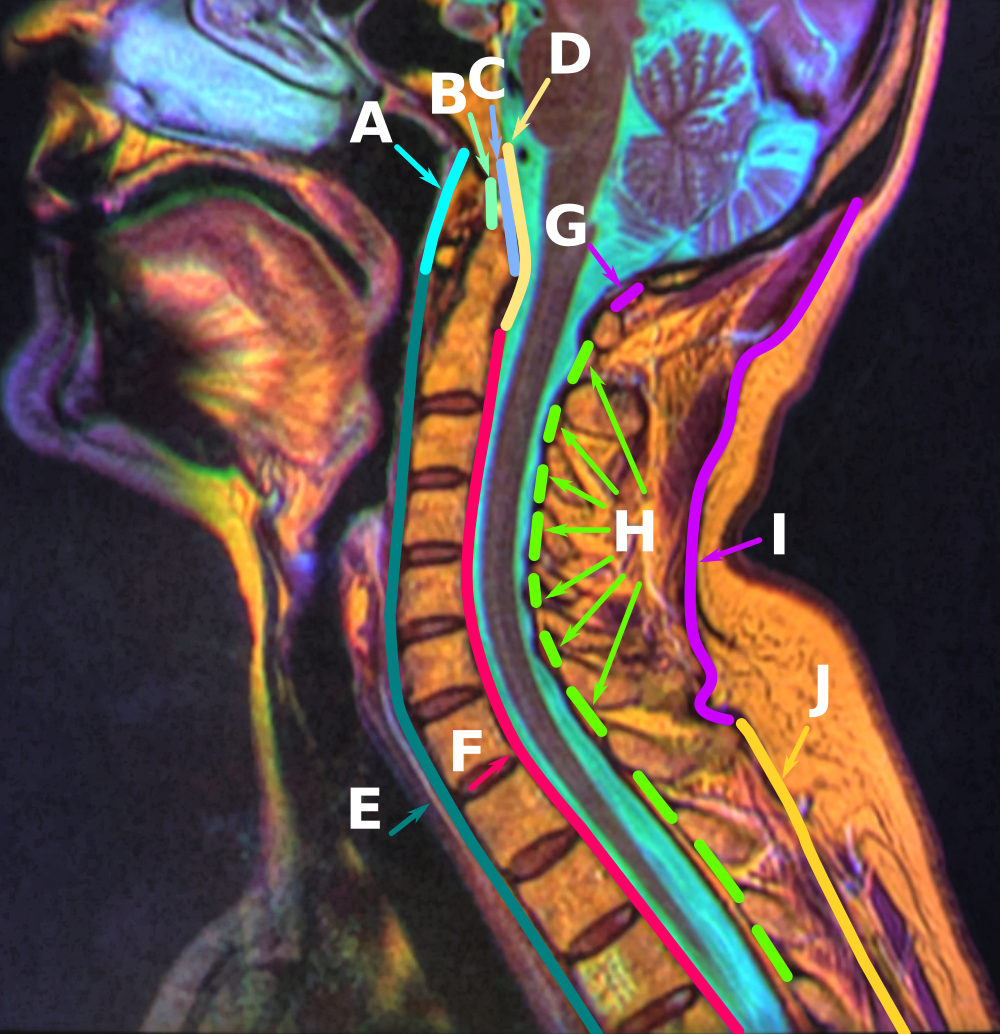
Thoracic Spine
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
The posterior longitudinal ligament is a ligament connecting the posterior surfaces of the Vertebra, vertebral bodies of all of the Vertebra, vertebrae. It weakly prevents Anatomical terms of motion, hyperflexion of the vertebral column. It also prevents posterior spinal disc herniation, although problems with the ligament can cause it. Structure The posterior longitudinal ligament is situated within the vertebral canal. It extends along the posterior surfaces of the bodies of the vertebrae, from the body of the Axis (anatomy), axis to the sacrum and possibly the coccyx. It is continuous with the tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint. The ligament is thicker in the thoracic vertebrae, thoracic than in the cervical vertebrae, cervical and lumbar vertebrae, lumbar regions. In the thoracic and lumbar regions, it presents a series of dentations with intervening concave margins. The posterior longitudinal ligament is narrow at the vertebral bodies, where it covers the basivertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interspinous Ligament
The interspinous ligaments (interspinal ligaments) are thin and membranous ligaments, that connect adjoining spinous processes of the vertebra in the spine. They extend from the root to the apex of each spinous process. They meet the ligamenta flava in front and blend with the supraspinous ligament behind. The ligaments are narrow and elongated in the thoracic region, broader, thicker, and quadrilateral in form in the lumbar region, and only slightly developed in the neck. In the neck they are often considered part of the nuchal ligament. The function of the interspinous ligaments is to limit flexion Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ... of the spine. References External links Interspinous ligaments on AnatomyExpert.comInterspinous ligament- BlueLink Anatomy - Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamentum Flavum
The ligamenta flava (singular, ''ligamentum flavum'', Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring that the vertebral column straightens after flexion. Hypertrophy can cause spinal stenosis. Structure Each ligamentum flavum connects the laminae two adjacent vertebrae. They begin with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra, continuing down to the junction of the fifth lumbar vertebra and the sacrum. They are best seen from the interior of the vertebral canal. when looked at from the outer surface they appear short, being overlapped by the lamina of the vertebral arch. Each ligament consists of two lateral portions which commence one on either side of the roots of the articular processes, and extend backward to the point where the laminae meet to form the spinous process; the posterior margins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraspinous Ligament
The supraspinous ligament, also known as the supraspinal ligament, is a ligament found along the vertebral column. Structure The supraspinous ligament connects the tips of the spinous processes from the seventh cervical vertebra to the sacrum. Above the seventh cervical vertebra, the supraspinous ligament is continuous with the nuchal ligament. Between the spinous processes it is continuous with the interspinous ligaments. It is thicker and broader in the lumbar than in the thoracic region, and intimately blended, in both situations, with the neighboring fascia. The most superficial fibers of this ligament extend over three or four vertebrae; those more deeply seated pass between two or three vertebrae while the deepest connect the spinous processes of neighboring vertebrae. Development Function The supraspinous ligament, along with the posterior longitudinal ligament, interspinous ligaments and ligamentum flavum, help to limit hyperflexion of the vertebral column. Clinica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinous Process
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Harnesses
A seat belt (also known as a safety belt, or spelled seatbelt) is a vehicle safety device designed to secure the driver or a passenger of a vehicle against harmful movement that may result during a collision or a sudden stop. A seat belt reduces the likelihood of death or serious injury in a traffic collision by reducing the force of secondary impacts with interior strike hazards, by keeping occupants positioned correctly for maximum effectiveness of the airbag (if equipped), and by preventing occupants being ejected from the vehicle in a crash or if the vehicle rolls over. When in motion, the driver and passengers are traveling at the same speed as the vehicle. If the vehicle suddenly stops or crashes, the occupants continue at the same speed the vehicle was going before it stopped. A seatbelt applies an opposing force to the driver and passengers to prevent them from falling out or making contact with the interior of the car (especially preventing contact with, or going t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester, UK
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The two cities and the surrounding towns form one of the United Kingdom's most populous conurbations, the Greater Manchester Built-up Area, which has a population of 2.87 million. The history of Manchester began with the civilian settlement associated with the Roman fort ('' castra'') of ''Mamucium'' or ''Mancunium'', established in about AD 79 on a sandstone bluff near the confluence of the rivers Medlock and Irwell. Historically part of Lancashire, areas of Cheshire south of the River Mersey were incorporated into Manchester in the 20th century, including Wythenshawe in 1931. Throughout the Middle Ages Manchester remained a manorial township, but began to expand "at an astonishing rate" around the turn of the 19th century. Manchester's un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotics
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal system". Orthotists are professionals who specialize in the provision of orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the lower extremities, orthotics of the upper extremities, orthotics for the trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses, relief orthoses, and soft braces. Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, a knee-ankle-foot orthosis (English abbreviation: KAFO for Knee-ankle-foot orthoses) spans the kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Treatment
Conservative management is a type of medical treatment defined by the avoidance of invasive measures such as surgery or other invasive procedures, usually with the intent to preserve function or body parts. For example, in appendicitis, conservative management may include watchful waiting Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed. Related terms include ''expe ... and treatment with antibiotics, as opposed to surgical removal of the appendix. References Medical terminology {{treatment-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |