|
Chaetognatha
The Chaetognatha or chaetognaths (meaning ''bristle-jaws'') are a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, they are mostly pelagic; however about 20% of the known species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from . Chaetognaths were first recorded by the Dutch naturalist Martinus Slabber in 1775. As of 2021, biologists recognize 133 modern species assigned to over 26 genera and eight families. Despite the limited diversity of species, the number of individuals is large. Arrow worms are strictly related to and possibly belonging to Gnathifera, a clade of protostomes that do not belong to either Ecdysozoa or Lophotrochozoa. Anatomy Chaetognaths are transpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnathifera (clade)
Gnathifera (from the Greek language, Greek ''wikt:γνάθος#Greek, gnáthos'', “jaw”, and the Latin ''wikt:-fer#Latin, -fera'', “bearing”) is a clade of generally small spiralians characterized by complex jaws made of chitin. It comprises the phyla Gnathostomulida, Rotifera and Micrognathozoa. Chaetognatha has recently been recognised as closely related to the group, with it either being included within Gnathifera or the broader group Chaetognathifera. Gnathiferans include some of the most abundant phyla. Rotifers are among the most diverse and abundant freshwater animals and chaetognaths are among the most abundant marine plankton. Description In most gnathiferans, the anus opens on the dorsal surface of the animal. In micrognathozoans and gnathostomulids, the anus is transient and only forms during defecation. Unlike other gnathiferans, in chaetognaths and the extinct ''Amiskwia'' the anus is located on the ventral surface in a subterminal position. Both Gnatho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph Leuckart
Karl Georg Friedrich Rudolf Leuckart (7 October 1822 – 22 February 1898) was a German zoologist born in Helmstedt. He was a pioneer of parasitology research and was widely known for developing a series of illustrated wall charts for use in zoology instruction. He was a nephew to naturalist Friedrich Sigismund Leuckart (1794–1843). Academic career Leuckart earned his degree from the University of Göttingen, where he was a student of Rudolf Wagner (1805–1864). Afterwards he participated on a scientific expedition to the North Sea for the study marine invertebrates. Later he became a professor of zoology at the University of Giessen (1850) and the University of Leipzig (1869).ADB: Leuckart, Rudolf @ ''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie''. In 1877 he became honorary foreign member of the Linnean Society of London. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martinus Slabber
Martinus is a given name or surname. It comes from the Latin name ''Martinus'', which is a late derived form of the name of the Roman god Mars, protective godhead of the Latins and, therefore, god of war. New completed edition by Marie-Thérèse Morlet. Given name People primarily known only by the given name * Martin (magister militum per Armeniam), 6th-century Byzantine/East Roman general * Martinus (son of Heraclius), 7th-century Byzantine/East Roman co-emperor * Martinus of Arles, doctor of theology, priest, and author on demonology and witches * Saint Martinus or Saint Martin of Tours Other * Martinus Beijerinck (1851–1931), Dutch microbiologist * Martinus von Biberach (died 1498), theologian from Heilbronn, Germany * Martinus Bosselaar (1936–2018), Dutch football (soccer) player * Martinus Brandal (born 1960), Norwegian engineer and businessman * Martinus Dom (1791–1873), first abbot of the Trappist Abbey of Westmalle * Martinus Fabri, Dutch composer of the late 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orange (colour)
Orange is the colour between yellow and red on the spectrum of visible light. The human eyes perceive orange when observing light with a dominant wavelength between roughly 585 and 620 nanometres. In traditional colour theory, it is a secondary colour of pigments, produced by mixing yellow and red. In the RGB colour model, it is a tertiary colour. It is named after the orange (fruit), fruit of the same name. The orange colour of many fruits and vegetables, such as carrots, pumpkins, sweet potatoes, and Orange (fruit), oranges, comes from carotenes, a type of photosynthetic pigment. These pigments convert the light energy that the plants absorb from the Sun into chemical energy for the plants' growth. Similarly, the hues of autumn leaves are from the same pigment after chlorophyll is removed. In Europe and the United States, surveys show that orange is the colour most associated with amusement, the unconventional, extroversion, warmth, fire, energy, activity, danger, taste and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Regions Of Earth
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are Earth's polar ice caps, the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by floating sea ice covering much of the Arctic Ocean in the north, and by the Antarctic ice sheet on the continent of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean in the south. Definitions The Arctic has various definitions, including the region north of the Arctic Circle (currently Epoch 2010 at 66°33'44" N), or just the region north of 60° north latitude, or the region from the North Pole south to the timberline. The Antarctic is usually defined simply as south of 60° south latitude, or the continent of Antarctica. The 1959 Antarctic Treaty uses the former definition. The two polar regions are distinguished from the other two climatic and biometric belts of Earth, a tropics belt near the equator, and two middle latitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
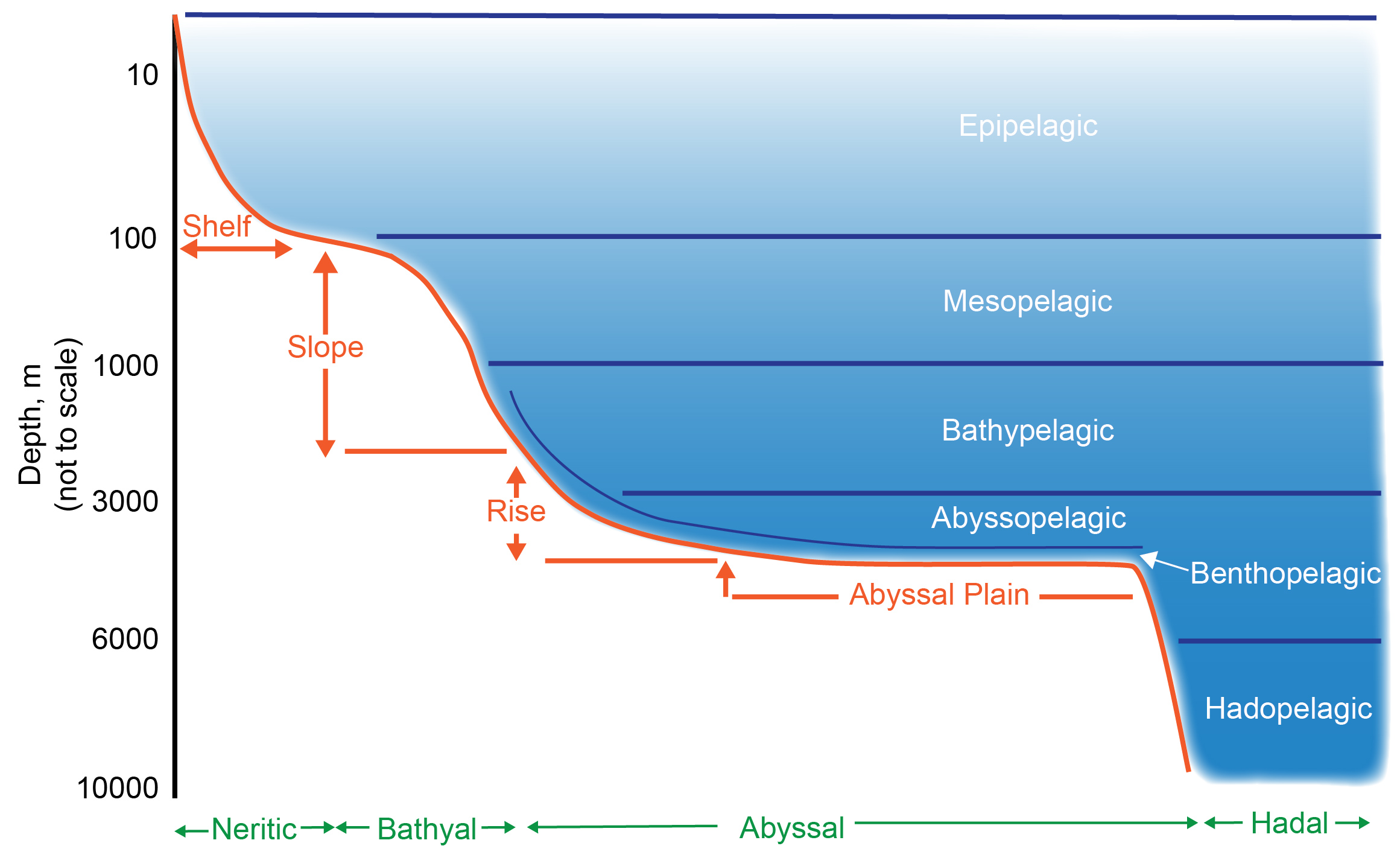
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness, and high pressure. The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome as the extreme conditions make the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, its peak would be more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's axial tilt; the width of the tropics (in latitude) is twice the tilt. The tropics are also referred to as the tropical zone and the torrid zone (see geographical zone). Due to the overhead sun, the tropics receive the most solar energy over the course of the year, and consequently have the highest temperatures on the planet. Even when not directly overhead, the sun is still close to overhead throughout the year, therefore the tropics also have the lowest seasonal variation on the planet; "winter" and "summer" lose their temperature contrast. Instead, seasons are more commonly divided by precipitation variations than by temperature variations. The tropics maintain wide diversity of local climates, such as rain forests, monsoons, sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |