|
Cerium Nitrate
Cerium nitrate refers to a family of nitrates of cerium in the +3 or +4 oxidation state. Often these compounds contain water, hydroxide, or hydronium ions in addition to cerium and nitrate. Double nitrates of cerium also exist. Cerium(III) nitrates Anhydrous cerous nitrate, also called cerium(III) nitrate, is the anhydrous salt with the formula Ce(NO3)3.(CAS number 10108-73-3). Cerium nitrate hexahydrate, with the formula Ce(NO3)3·6H2O (CAS number 10294-41-4) is the most common nitrate of cerium(III). It is a component in a burn treatment cream that also includes silver sulphadiazine. Concentrations used are 0.5 M for the cerium nitrate. For very serious burns it reduces the death rate. At 150 °C the hexahydrate loses water of crystallization to make a trihydrate, which itself decomposes above 200 °C. Cerous nitrate hexahydrate has pinacoidal triclinic crystals. Hydronium cerium(III) nitrate hydrate, Ce(NO3)5(H3O)2⋅H2O is monoclinic with space group ''P''2/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it often shows the oxidation state of +3 characteristic of the series, it also has a stable +4 state that does not oxidize water. It is considered one of the rare-earth elements. Cerium has no known biological role in humans but is not particularly toxic, except with intense or continued exposure. Despite always occurring in combination with the other rare-earth elements in minerals such as those of the monazite and bastnäsite groups, cerium is easy to extract from its ores, as it can be distinguished among the lanthanides by its unique ability to be oxidized to the +4 state in aqueous solution. It is the most common of the lanthanides, followed by neodymium, lanthanum, and praseodymium. Its estimated abundance of elements in Earth's crust, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
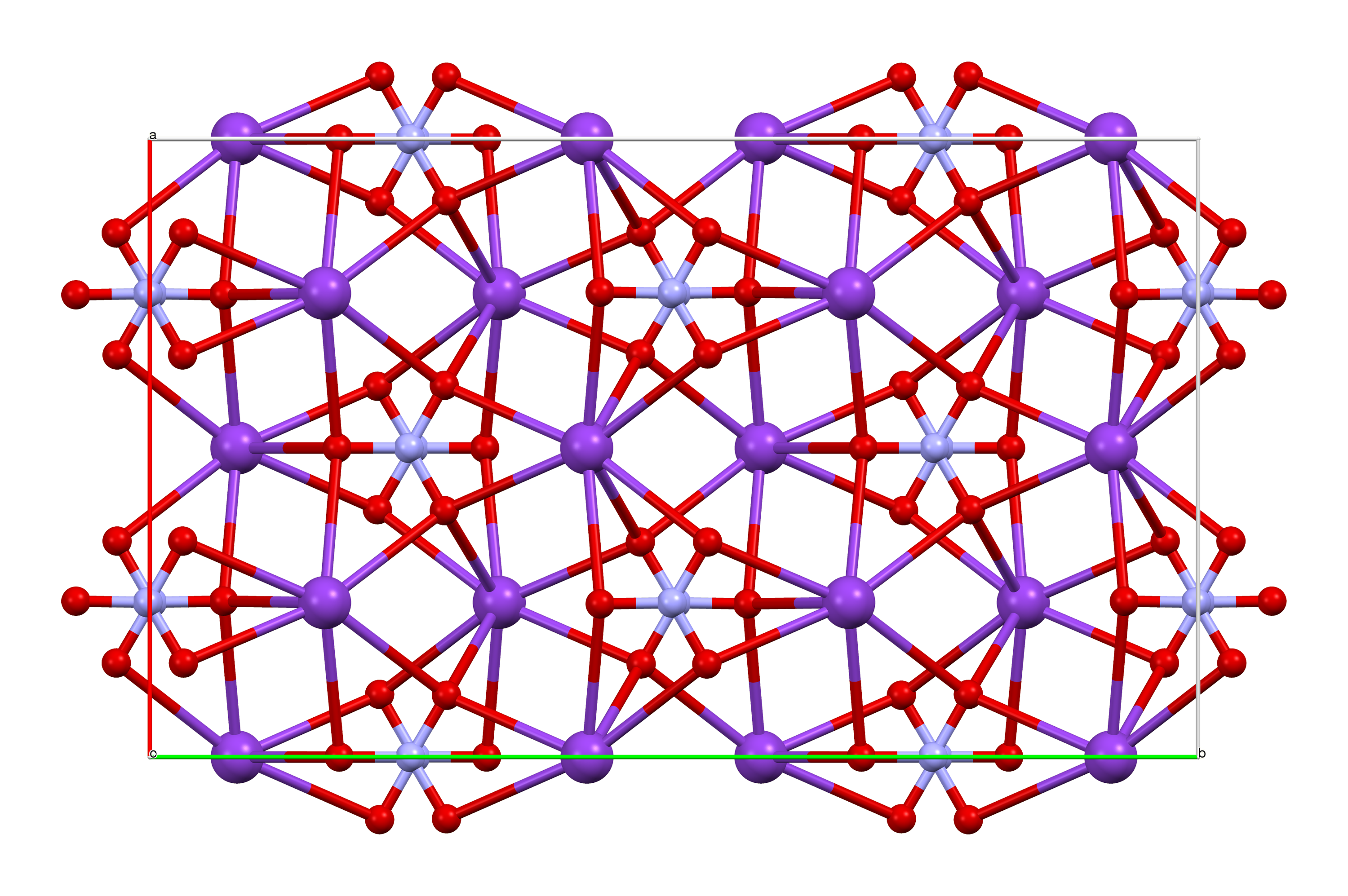
Ceric Manganese Nitrate , a chemical element
*
{{disambig ...
Ceric may refer to: * Cerium Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thallium
Thallium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a silvery-white post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently, in 1861, in residues of sulfuric acid production. Both used the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy, in which thallium produces a notable green spectral line. Thallium, from Greek language, Greek , , meaning "green shoot" or "twig", was named by Crookes. It was isolated by both Lamy and Crookes in 1862, Lamy by electrolysis and Crookes by precipitation and melting of the resultant powder. Crookes exhibited it as a powder precipitated by zinc at the 1862 International Exhibition, International Exhibition, which opened on 1 May that year. Thallium tends to form the +3 and +1 oxidation states. The +3 state resembles that of the other elements in Boron Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceric Caesium Nitrate , a chemical element
*
{{disambig ...
Ceric may refer to: * Cerium Cerium is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a hardness, soft, ductile, and silvery-white metal that tarnishes when exposed to air. Cerium is the second element in the lanthanide series, and while it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or ''nitre'' outside the United States). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in the United States). Major uses of potassium nitrate are in fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks. It is one of the major constituents of traditional gunpowder (black powder). In processed meats, potassium nitrate reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin generating a red color. Etymology Nitre, or potassium nitrate, because of its early and global use and production, has many names. As for nitrate, Egyptian and Hebrew words for it had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium(IV) Hydroxide
Cerium(IV) hydroxide, also known as ceric hydroxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ce(OH)4. It is a yellowish powder that is insoluble in water but soluble in concentrated acids. Production Cerium(IV) hydroxide can be produced by reacting cerium(III) carbonate and acetic acid, then oxidizing it with hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ... in base. The reactions are: : Ce2(CO3)3 + 6 CH3COOH → 2 Ce(CH3COO)3 + 3 CO2↑ + 3 H2O : 2 Ce(CH3COO)3 + 3 H2O2 + 4 H2O → 2 Ce(OH)3(OOH) + 6 CH3COOH : CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O : 2 Ce(OH)3(OOH) → 2 Ce(OH)4↓ + O2↑ The net equation is: : Ce2(CO3)3 + 6 CH3COOH + 3 H2O2 + 6 NaOH —343 K→ 2 Ce(OH)4 + 6 CH3COONa + O2↑ + 3 CO2↑ + 5 H2O If using cerium(III) nitrate as ingredient, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |