|
Cerium(IV) Oxide
Cerium(IV) oxide, also known as ceric oxide, ceric dioxide, ceria, cerium oxide or cerium dioxide, is an oxide of the rare-earth metal cerium. It is a pale yellow-white powder with the chemical formula CeO2. It is an important commercial product and an intermediate in the purification of the element from the ores. The distinctive property of this material is its reversible conversion to a Non-stoichiometric compound, non-stoichiometric oxide. Production Cerium occurs naturally as oxides, always as a mixture with other rare-earth elements. Its principal ores are bastnaesite and monazite. After extraction of the metal ions into aqueous base, Ce is separated from that mixture by addition of an oxidant followed by adjustment of the pH. This step exploits the low solubility of CeO2 and the fact that other rare-earth elements resist oxidation.. Cerium(IV) oxide is formed by the calcination of cerium oxalate or cerium hydroxide. Cerium also forms cerium(III) oxide, , which is unst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopy
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g. changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they dissolve in the water they absorb, forming an aqueous solution. Hygroscopy is essential for many plant and animal species' attainment of hydration, nutrition, reproduction and/or seed dispersal. Biological evolution created hygroscopic solutions for water harvesting, filament tensile strength, bonding and passive motion – natural so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonstoichiometric Compound
Non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); most often, in such materials, some small percentage of atoms are missing or too many atoms are packed into an otherwise perfect lattice work. Contrary to earlier definitions, modern understanding of non-stoichiometric compounds view them as homogeneous, and not mixtures of stoichiometric chemical compounds. Since the solids are overall electrically neutral, the defect is compensated by a change in the charge of other atoms in the solid, either by changing their oxidation state, or by replacing them with atoms of different elements with a different charge. Many metal oxides and sulfides have non-stoichiometric examples; for example, stoichiometric iron(II) oxide, which is rare, has the formula , whereas the more common material is nonstoichiometric, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust. Iron oxides and oxyhydroxides are widespread in nature and play an important role in many geological and biological processes. They are used as iron ores, pigments, catalysts, and in thermite, and occur in hemoglobin. Iron oxides are inexpensive and durable pigments in paints, coatings and colored concretes. Colors commonly available are in the " earthy" end of the yellow/orange/red/brown/black range. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E172. Stoichiometries Iron oxides feature as ferrous ( Fe(II)) or ferric ( Fe(III)) or both. They adopt octahedral or tetrahedral coordination geometry. Only a few oxides are significant at the earth's surface, particularly wüstite, magnetite, and hematite. * Oxides of FeII ** FeO: ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
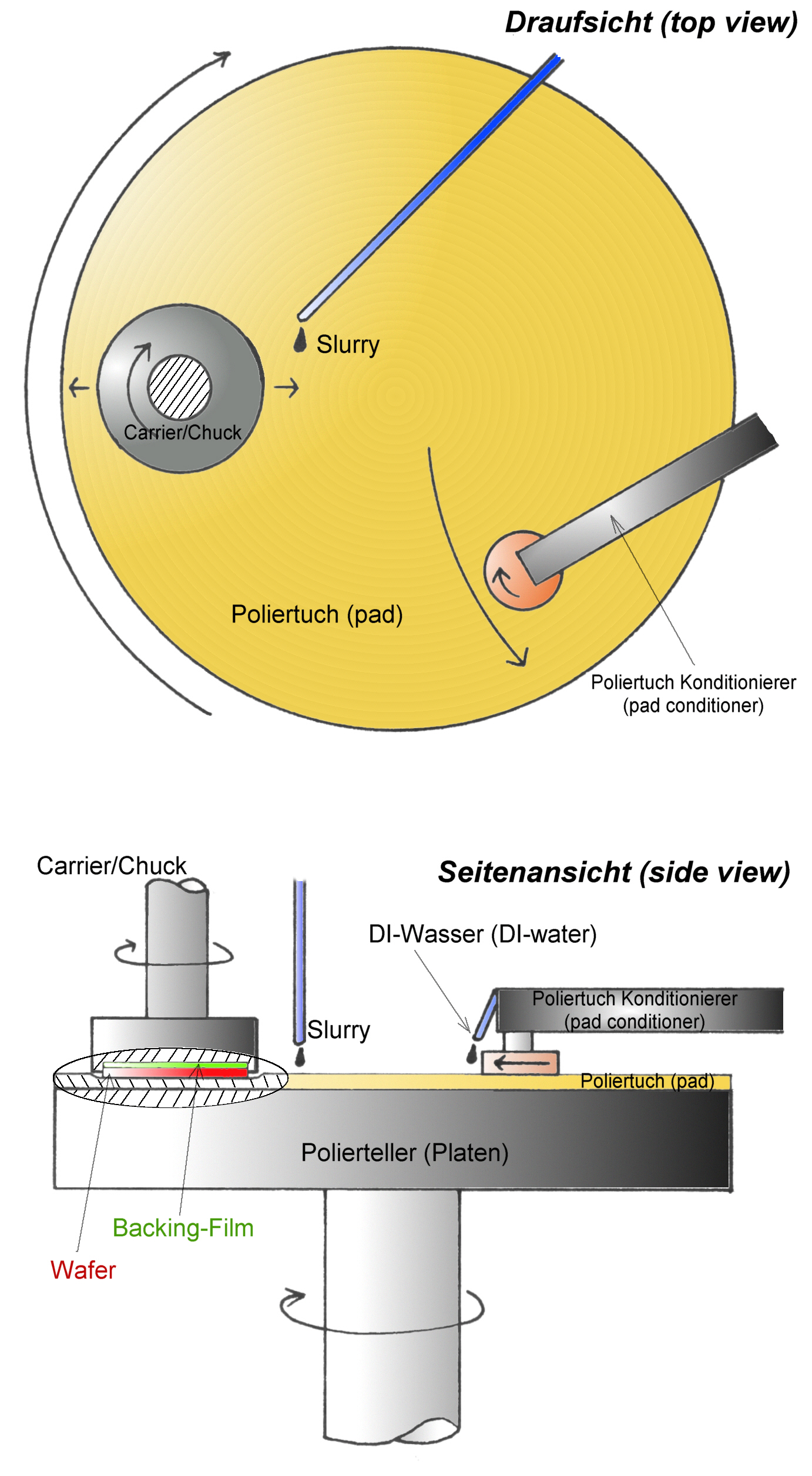
Chemical-mechanical Polishing
Chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) (also called chemical mechanical planarization) is a process of smoothing surfaces with the combination of chemical and mechanical forces. It can be thought of as a wikt:hybrid, hybrid of chemical etching and free abrasive polishing. It is used in the semiconductor industry to polish semiconductor wafers as part of the integrated circuit manufacturing process. Description The process uses an abrasive and corrosive chemical slurry (commonly a colloid) in conjunction with a polishing pad and retaining ring, typically of a greater diameter than the wafer. The pad and wafer are pressed together by a dynamic polishing head and held in place by a plastic retaining ring. The dynamic polishing head is rotated with different axes of rotation (i.e., not wiktionary:concentric, concentric). This removes material and tends to even out any irregular topography, making the wafer flat or planar. This may be necessary to set up the wafer for the formation of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium Anomaly
The cerium anomaly, in geochemistry, is the phenomenon whereby cerium (Ce) concentration is either depleted or enriched in a rock relative to the other rare-earth elements (REEs). A Ce anomaly is said to be "negative" if Ce is depleted relative to the other REEs and is said to be "positive" if Ce is enriched relative to the other REEs. Cerium oxidation states Cerium is a rare-earth element (lanthanide) characterized by two different redox states: III and IV. Contrary to other lanthanide elements, which are only trivalent (with the notable exception of Europium anomaly, Eu2+), Ce3+ can be oxidized by atmospheric oxygen (O2) to Ce4+ under alkaline conditions. The cerium anomaly relates to the decrease in solubility, which accompanies the oxidation of Ce(III) to Ce(IV). Under reducing conditions, Ce3+ is relatively soluble, while under oxidizing conditions CeO2 precipitates. Sediments deposited under oxic or anoxic conditions can preserve on the long term the geochemical signature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare Earth Elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. The term "rare-earth" is a misnomer because they are not actually scarce, but historically it took a long time to isolate these elements. They are relatively plentiful in the entire Earth's crust (cerium being the 25th-most-abundant element at 68 parts per million, more abundant than copper), but in practice they are spread thinly as trace impurities, so to obtain rare earths at usable purity requires processing enormous amounts of raw ore at great expense; thus the name "rare" earths. Scandium and yttrium are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyrnaesite-(La)
Dyrnaesite-(La) is a rare-earth phosphate Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus. In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ... mineral with the formula . Dyrnaesite-(La) is related to vitusite-(Ce), another rare-earth phosphate mineral. It comes from lujavrite, a type of alkaline syenite rock, of South Greenland. Dyrnaesite-(La) is one of few known minerals with essential tetravalent cerium, the other two being cerianite-(Ce) and stetindite. References Phosphate minerals Cerium minerals Lanthanide minerals Sodium minerals Orthorhombic minerals Minerals in space group 62 {{phosphate-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerianite-(Ce)
Cerianite-(Ce) is a relatively rare oxide mineral, belonging to uraninite group with the formula . It is one of a few currently known minerals containing essential tetravalent cerium, the other examples being stetindite and dyrnaesite-(La). Occurrence and association Cerianite-(Ce) is associated with alkaline rocks, mostly nepheline syenites. It may be found in carbonatites. Cerianite-(Ce) associates with minerals of the apatite group, bastnäsite-group minerals, calcite, feldspar, "fluocerite", "hydromica", ilmenite, nepheline, magnetite, "törnebohmite" and tremolite. It is the most simple cerium mineral known. Notes on chemistry Beside thorium cerianite-(Ce) may contain trace niobium, yttrium, lanthanum, ytterbium, zirconium and tantalum. Crystal structure For details on crystal structure see cerium(IV) oxide. Both ceria and thoria have a fluorite structure The fluorite structure refers to a common motif for compounds with the formula MX2. The X ions occupy the eight tetrah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to displace gas to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. These interactions occur in the presence of either a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with the wetting liquid. The degree of wetting (wettability) is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. There are two types of wetting: non-reactive wetting and reactive wetting. Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of two materials. The wetting power of a liquid, and surface forces which control wetting, are also responsible for related effects, including capillary effects. Surfactants can be used to increase the wetting power of liquids such as water. Wetting has gained increasing attention in nanotechnology and nanoscience research, following the development of nanomaterials over the past two decades (i.e., graphene, carbon nanotube, boron nitride nanomesh). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-oxide Fuel Cell
A solid oxide fuel cell (or SOFC) is an electrochemical conversion device that produces electricity directly from oxidizing a fuel. Fuel cells are characterized by their electrolyte material; the SOFC has a solid oxide or ceramic electrolyte. Advantages of this class of fuel cells include high combined heat and power efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, low emissions, and relatively low cost. The largest disadvantage is the high operating temperature which results in longer start-up times and mechanical and chemical compatibility issues. Introduction Solid oxide fuel cells are a class of fuel cells characterized by the use of a solid oxide material as the electrolyte. SOFCs use a solid oxide electrolyte to conduct negative oxygen ions from the cathode to the anode. The electrochemical oxidation of the hydrogen, carbon monoxide or other organic intermediates by oxygen ions thus occurs on the anode side. More recently, proton-conducting SOFCs (PC-SOFC) are being dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Conductivity (solid State)
Ionic conductivity (denoted by ) is a measure of a substance's tendency towards ionic conduction. Ionic conduction is the movement of ions. The phenomenon is observed in solids and solutions. Ionic conduction is one mechanism of current. In crystalline solids In most solids, ions rigidly occupy fixed positions, strongly embraced by neighboring atoms or ions. In some solids, selected ions are highly mobile allowing ionic conduction. The mobility increases with temperature. Materials exhibiting this property are used in batteries. A well-known ion conductive solid is β''-alumina ("BASE"), a form of aluminium oxide that has channels through which sodium cations can hop. When this ceramic is complexed with a mobile ion, such as Na+, it behaves as so-called fast ion conductor. BASE is used as a membrane in several types of molten salt electrochemical cell. History Ionic conduction in solids has been a subject of interest since the beginning of the 19th century. Michael Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |