|
Cellular Senescence
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approximately 50 cell population doublings before becoming senescent. This process called the Hayflick limit is also known as "replicative senescence", since it is brought about through replication. Hayflick's discovery of mortal cells paved the path for the discovery and understanding of cellular aging molecular pathways. Cellular senescence can be initiated by a wide variety of stress inducing factors. These stress factors include both environmental and internal damaging events, abnormal cellular growth, oxidative stress, autophagy factors, among many other things. The physiological importance for cell senescence has been attributed to prevention of carcinogenesis, and more recently, aging, development, and tissue repair. Senescent cells c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in cells, by internal metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair processes fail, including apoptosis, irreparable DNA damage may occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senescence-associated Secretory Phenotype
Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) is a phenotype associated with senescent cells wherein those cells secrete high levels of inflammatory cytokines, immune modulators, growth factors, and proteases. SASP may also consist of exosomes and ectosomes containing enzymes, microRNA, DNA fragments, chemokines, and other bioactive factors. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator surface receptor is part of SASP, and has been used to identify senescent cells for senolytic therapy. Initially, SASP is immunosuppressive (characterized by TGF-β1 and TGF-β3) and profibrotic, but progresses to become proinflammatory (characterized by IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8) and fibrolytic. SASP is the primary cause of the detrimental effects of senescent cells. SASP is heterogenous, with the exact composition dependent upon the senescent-cell inducer and the cell type. Interleukin 12 (IL-12) and Interleukin 10 (IL-10) are increased more than 200-fold in replicative senescence in contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
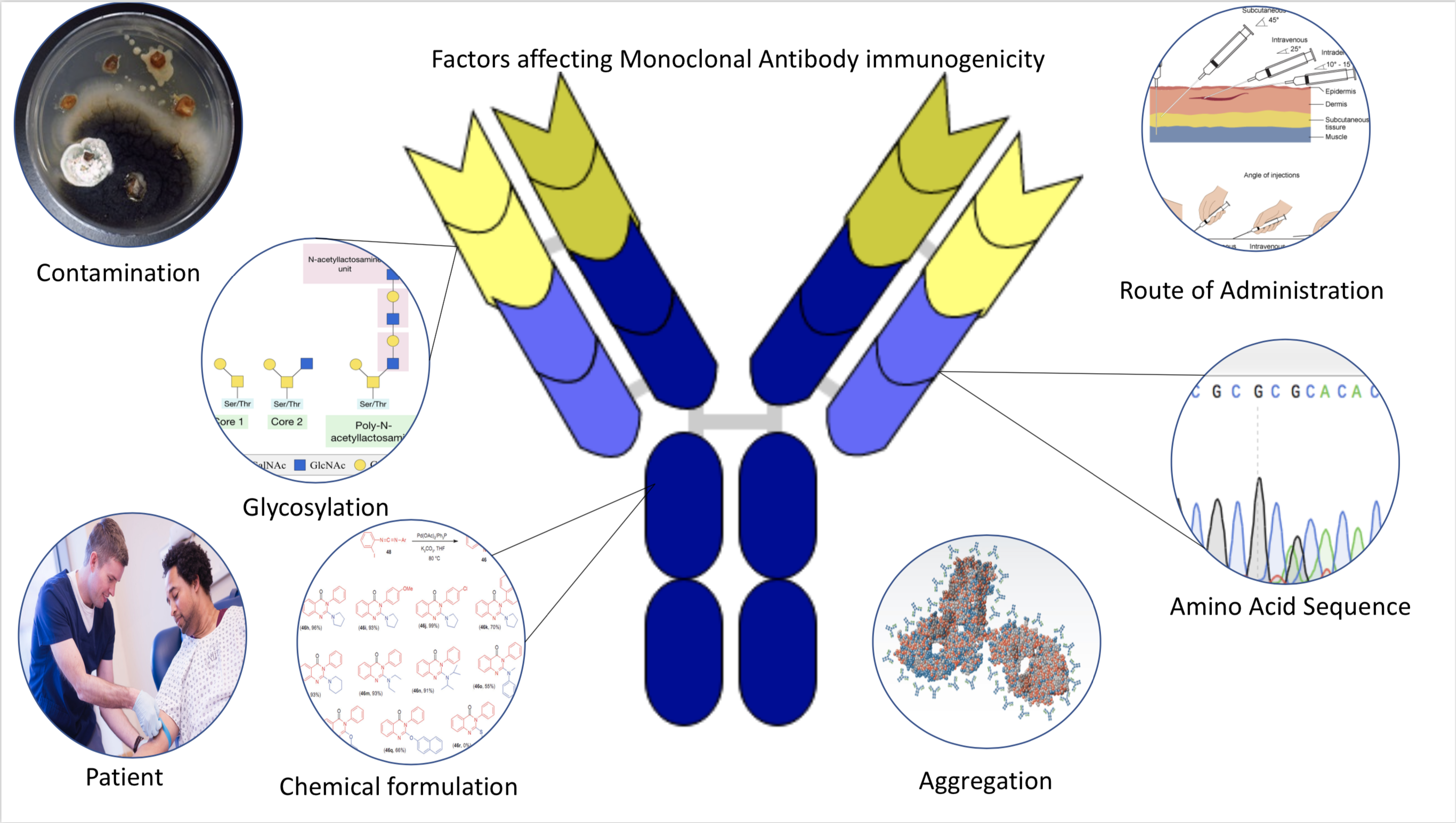
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Smooth Muscle
Vascular smooth muscle is the type of smooth muscle that makes up most of the walls of blood vessels. Structure Vascular smooth muscle refers to the particular type of smooth muscle found within, and composing the majority of the wall of blood vessels. Nerve supply Vascular smooth muscle is innervated primarily by the sympathetic nervous system through adrenergic receptors (adrenoceptors). The three types present are: alpha-1, alpha-2 and beta-2 adrenergic receptors, . The main endogenous agonist of these cell receptors is norepinephrine (NE). The adrenergic receptors exert opposite physiologic effects in the vascular smooth muscle under activation: * alpha-1 receptors. Under NE binding alpha-1 receptors cause vasoconstriction (contraction of the vascular smooth muscle cells decreasing the diameter of the vessels). These receptors are activated in response to shock or low blood pressure as a defensive reaction trying to restore the normal blood pressure. Antagonists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a Cofactor (biochemistry), coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cell (biology), cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an Redox, oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In cellular metabolism, NAD is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another, so it is found in two forms: NAD is an oxidizing agent, accepting electrons from other molecules and becoming reduced; with H+, this reaction forms NADH, which can be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. It is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate (biochemistry), substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to or fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progeroid Syndromes
Progeroid syndromes (PS) are a group of rare genetic disorders that mimic physiological aging, making affected individuals appear to be older than they are. The term ''progeroid syndrome'' does not necessarily imply progeria ( Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome), which is a specific type of progeroid syndrome. ''Progeroid'' means "resembling premature aging", a definition that can apply to a broad range of diseases. Familial Alzheimer's disease and familial Parkinson's disease are two well-known accelerated-aging diseases that are more frequent in older individuals. They affect only one tissue and can be classified as unimodal progeroid syndromes. Segmental progeria, which is more frequently associated with the term ''progeroid syndrome,'' tends to affect multiple or all tissues while causing affected individuals to exhibit only some of the features associated with aging. All disorders within this group are thought to be monogenic, meaning they arise from mutations of a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ageing
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing, or to the population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA oxidation) may cause biological systems to fail, or to the programmed ageing concept, whereby the internal processes (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell (biology), cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified in Cell (biology), cells, by internal metabolism, metabolic by-products, and by external ionizing radiation, ultraviolet light, and medicines, resulting in spontaneous DNA damage involving tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. DNA modifications can also be programmed. Molecular lesions can cause structural damage to the DNA molecule, and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability for Transcription (biology), transcription and gene expression. Other lesions may induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells following mitosis. Consequently, DNA repair as part of the DNA damage response (DDR) is constantly active. When normal repair proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Damage (naturally Occurring)
Natural DNA damage is an alteration in the chemical structure of DNA, such as a break in a strand of DNA, a nucleobase missing from the backbone of DNA, or a chemically changed base such as 8-OHdG. DNA damage can occur naturally or via environmental factors, but is distinctly different from mutation, although both are types of error in DNA. DNA damage is an abnormal chemical structure in DNA, while a mutation is a change in the sequence of base pairs. DNA damages cause changes in the structure of the genetic material and prevents the replication mechanism from functioning and performing properly. The DNA damage response (DDR) is a complex signal transduction pathway which recognizes when DNA is damaged and initiates the cellular response to the damage. DNA damage and mutation have different biological consequences. While most DNA damages can undergo DNA repair, such repair is not 100% efficient. Un-repaired DNA damages accumulate in non-replicating cells, such as cells in the brai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Fusion
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells (cells with a single nucleus) combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis. Cell fusion is a necessary event in the maturation of cells so that they maintain their specific functions throughout growth. History In 1839, Theodor Schwann, in his '' Microscopical Researches,'' expanded upon the theory that all living organisms are composed of cells when he added that discrete cells are the basis of life. Schwann observed that in certain cells the walls and cavities of the cells coalesce ('' verschmelzen'') together. This observation provided the first hint that cells fuse. It was not until 1960 that cell biologists deliberately fused cells for the first time. To fuse the cells, biologists combined isolated mouse cells and induced fusion of their outer membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |