|
Catherine-Dominique De Pérignon
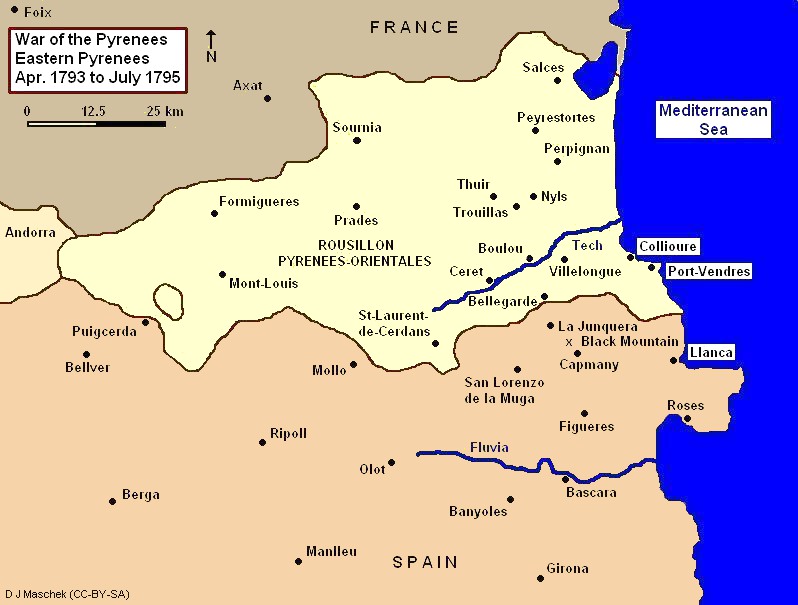
Catherine-Dominique de Pérignon, 1st Marquis de Pérignon (, 31 May 1754 in Grenade – 25 December 1818) was a French general during the French Revolutionary Wars, and was appointed Marshal of the Empire in 1804 by Napoleon Bonaparte. Early life Pérignon was born to a family of the lesser nobility in Grenade-sur-Garonne, Languedoc. After a ''roturier'' appointment in the grenadier corps of the Aquitaine Regiment, he retired to his estate. Pérignon welcomed the French Revolution, and gained a seat in the Legislative Assembly (1791), where he sat on the Right, but soon resigned and made his military career during the French Revolutionary Wars. Revolutionary Wars From 1793 to 1795, Pérignon held commands in the Army of the Eastern Pyrenees, defeating the Spanish troops at the battle of Escola with "a sombre kind of energy". He succeeded Jacques François Dugommier as army commander after that general's death at the Battle of the Black Mountain. He successfully conclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshal Of The Empire
Marshal of the Empire () was a civil dignity during the First French Empire. It was established by on 18 May 1804 and to a large extent reinstated the formerly abolished title of Marshal of France. According to the ''Sénatus-consulte'', a Marshal was a grand officer of the Empire, entitled to a high-standing position at the court and to the presidency of an electoral college. Although in theory reserved "to the most distinguished generals", in practice Emperor of the French, Emperor Napoleon granted the title according to his own wishes and convictions and made at least a few controversial choices. Although not a military rank, a Marshal displayed four silver stars, while the top military rank, General of Division, displayed three stars. Furthermore, the Marshalate quickly became the prestigious sign of the supreme military attainment and it became customary that the most significant commands be given to a Marshal. Each Marshal held his own coat of arms, was entitled to specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenadier (soldier)
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word ''grenade'') was historically an assault-specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in siege operation battles. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited from among the strongest and largest soldiers. By the 18th century, the grenadier dedicated to throwing hand grenades had become a less necessary specialist, yet in battle, the grenadiers were the physically robust soldiers who led vanguard assaults, such as storming fortifications in the course of siege warfare. Certain countries such as France ( Grenadiers à Cheval de la Garde Impériale) and Argentina ( Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers) established units of Horse Grenadiers, and for a time the British Army had Horse Grenadier Guards. Like their infantry grenadier counterparts, these horse-mounted soldiers were chosen for their size and strength ( heavy cavalry). In modern warfare, a grenadier is a specially t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or sovereign or appointed for a special and often temporary diplomatic assignment. The word is also used informally for people who are known, without national appointment, to represent certain professions, activities, and fields of endeavor, such as sales. An ambassador is the ranking government representative stationed in a foreign capital or country. The host country typically allows the ambassador control of specific territory called an embassy (which may include an official residence and an office, chancery (diplomacy), chancery, located together or separately, generally in the host nation's capital), whose territory, staff, and vehicles are generally afforded diplomatic immunity in the host country. Under the Vienna Convention on Diplomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Directory
The Directory (also called Directorate; ) was the system of government established by the Constitution of the Year III, French Constitution of 1795. It takes its name from the committee of 5 men vested with executive power. The Directory governed the French First Republic from 26 October 1795 (4 Brumaire an IV) until 10 November 1799, when it was overthrown by Napoleon Bonaparte in the Coup of 18 Brumaire and replaced by the French Consulate, Consulate. The Directory was continually at war with foreign coalitions, including Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, the Kingdom of Naples, Russian Empire, Russia and the Ottoman Empire. It annexed Austrian Netherlands, Belgium and the left bank of the Rhine, while Bonaparte conquered a large part of Italy. The Directory established 29 short-lived sister republics in Italy, Helvetic Republic, Switzerland and the Batavian Republic, Netherlands. The conquered cities and states were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Five Hundred
The Council of Five Hundred () was the lower house of the legislature of the French First Republic under the Constitution of the Year III. It operated from 31 October 1795 to 9 November 1799 during the French Directory, Directory () period of the French Revolution. Role and function The Council of Five Hundred was established under the Constitution of Year III which was 1795 French constitutional referendum, adopted by a referendum on 24 September 1795,Chronicle of the French Revolutions, Longman 1989 p.495 and constituted after the first elections which were held from 12–21 October 1795. Voting rights were restricted to citizens owning property bringing in income equal to 150 days of work. Each member elected had to be at least 30 years old, meet residency qualifications and pay taxes. To prevent them coming under the pressure of the sans-culottes and the Paris mob, the constitution allowed the Council of the Five Hundred to meet in closed session. A third of them would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Roses (1794–1795)
The siege of Roses (or siege of Rosas) began on 28 November 1794 and lasted until 4 February 1795 when the Spanish garrison abandoned the port and the forces of the First French Republic took control. Dominique Catherine de Pérignon commanded the French army and Domingo Salvator Izquierdo led the Spanish defenders. The siege took place during the War of the Pyrenees which was part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The war ended in July 1795 and Roses was soon restored to Spain. Roses is a coastal city in northeastern Spain, located northeast of Girona, Catalonia. The French inflicted a severe defeat on the Spanish army at the Black Mountain in November 1794. In the aftermath, the French army quickly captured Figueras and its fortress. At the same time, they undertook a formal siege of Roses. Pérignon and his lieutenant Pierre François Sauret soon realized that an outlying fort was the key to Roses and concentrated their energy on reducing it. A month after the fort fell, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Black Mountain
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques François Dugommier
Jacques François Coquille (), known as Dugommier (; 1 August 1738 – 18 November 1794), was a French military leader during the French Revolutionary Wars. Early life and career Jacques François Coquille was born on 1 August 1738 in Trois-Rivières in the island of Guadeloupe, in the French West Indies. He was the son of Germain Coquille, a planter and royal councilor, and Claire Laurent. In 1785, he took the name "Dugommier" after the coffee plantation "Le Gommier" in Basse-Terre, which he bought from his parents in 1768. Dugommier began his military career in the company of " gentlemen cadets" of the colonies in Rochefort, at the age of fifteen. He was employed in the naval batteries at La Rochelle and Île de Ré before being assigned to an infantry company in 1758. Dugommier fought in the West Indies theatre of the Seven Years' War, serving in the defense of Guadeloupe in 1759 and the defense of Martinique in 1762. He was discharged at his request in 1763, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Eastern Pyrenees
The Army of the Eastern Pyrenees (''Armée des Pyrénées Orientales'') was one of the French Revolutionary armies. It fought against the Kingdom of Spain in Roussillon, the Cerdanya and Catalonia during the War of the Pyrenees. This army and the '' Army of the Western Pyrenees'' were formed by splitting the original ''Army of the Pyrenees'' at the end of April 1793 soon after the war started. Shortly after the Peace of Basel on 22 July 1795, the fighting ended and the army was dissolved on 12 October that same year. Many of its units and generals were transferred to join the '' Army of Italy'' and fought under Napoleon Bonaparte in 1796. In the first dismal months of fighting, the ''Army of the Eastern Pyrenees'' was beaten at Mas Deu and Bellegarde and forced back under the walls of Perpignan. Then the French repelled two Spanish attacks at Perpignan and Peyrestortes. Though the army was defeated again at Truillas and in other actions, the Spanish invaders withdrew to the Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-wing
Right-wing politics is the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position based on natural law, economics, authority, property, religion, or tradition. Hierarchy and inequality may be seen as natural results of traditional social differences or competition in market economies. Right-wing politics are considered the counterpart to left-wing politics, and the left–right political spectrum is the most common political spectrum. The right includes social conservatives and fiscal conservatives, as well as right-libertarians. "Right" and "right-wing" have been variously used as compliments and pejoratives describing neoliberal, conservative, and fascist economic and social ideas. Positions The following positions are typically associated with right-wing politics. Anti-communism Early communists used the term "right-wing" in reference to conservatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Assembly (France)
The Legislative Assembly () was the legislature of the Kingdom of France from 1 October 1791 to 20 September 1792 during the years of the French Revolution. It provided the focus of political debate and revolutionary law-making between the periods of the National Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention. Legislative Assembly saw an unprecedented turnover of four ministers of Justice, four ministers of Navy, six ministers of the interior, seven ministers of foreign affairs, and eight ministers of war. History Background The National Constituent Assembly dissolved itself on 30 September 1791. Upon Maximilien Robespierre's motion, it decreed that none of its members would be eligible for the next legislature. Its successor body, the Legislative Assembly, operating over the liberal French Constitution of 1791, lasted until 20 September 1792 when the National Convention was established after the insurrection of 10 August just the month before. The Legislative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |