|
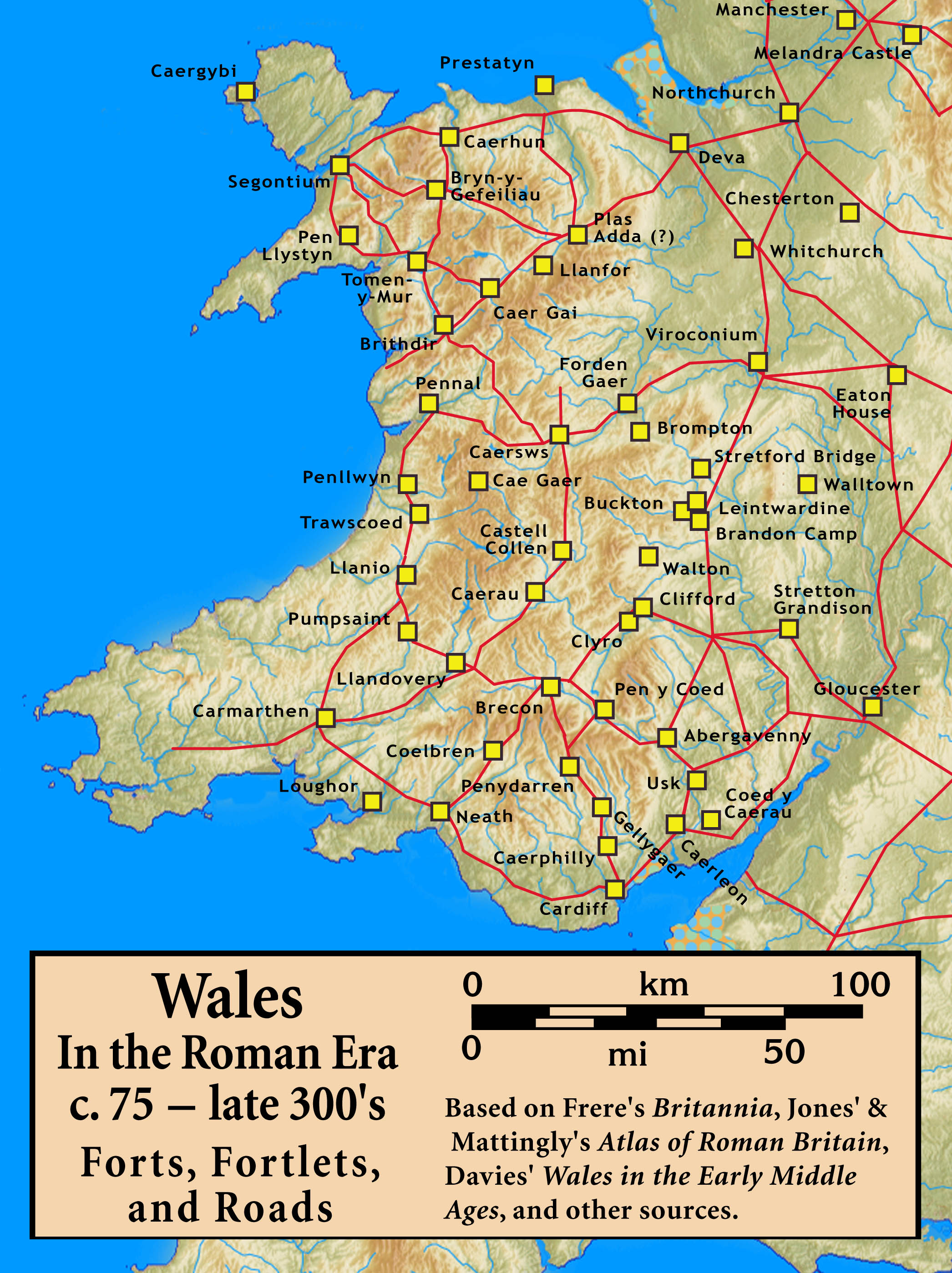
Castra Of Duleu - Odăi
The castra of Duleu - Odăi was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia. It was built in the 2nd century and abandoned in the 4th century. A contemporary necropolis was also unearthed near the fort. The ruins of the ''castra'' are located in Duleu (commune Fârliug, Romania). See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra refl ... Notes External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman auxiliary forts in Romania History of Banat Historic monuments in Caraș-Severin County {{Dacia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier-emperor who presided over one of the greatest military expansions in Roman history, during which, by the time of his death, the Roman Empire reached its maximum territorial extent. He was given the title of ('the best') by the Roman Senate. Trajan was born in the of Italica in the present-day Andalusian province of province of Seville, Seville in southern Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his came from the town of Todi, Tuder in the Regio VI Umbria, Umbria region of central Italy. His namesake father, Marcus Ulpius Traianus (father of Trajan), Marcus Ulpius Traianus, was a general and distinguished senator. Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of Domitian; in AD 89, serving as a in , he supported t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia Superior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Superi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English language, English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". Scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large Roman legion, legionary fortresses, smaller forts for Cohort (military unit), cohorts or for auxiliary forces, military camp, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a ''centuria''. Etymology ''Castrum'' appears in Oscan language, Oscan and Umbrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fârliug
Fârliug () is a Commune in Romania, commune in Caraș-Severin County, western Romania. It is composed of six villages: Dezești (''Dezesd''), Duleu (''Dulló''), Fârliug, Remetea-Pogănici (''Pogányosremete''), Scăiuș (''Bojtorjános''), and Valea Mare (''Pogányosvölgy''). The commune is situated in the historical region of Banat, in the northern part of the county, on the border with Timiș County. Fârliug is located north of Reșița, the capital of Caraș-Severin County, and south of Lugoj. It is crossed by Roads in Romania, national road . At the 2011 Romanian census, 2011 census, the commune had a population of 1,956 people, of which 88.65% were Romanians, 2.2% Ukrainians of Romania, Ukrainians, 1.69% Romani people in Romania, Roma, and 1.18% Czechs of Romania, Czechs. At the 2021 Romanian census, 2021 census, the commune had a population of 1,736; of those, 92% were Romanians. Natives * Jiří Kormaník (1935–2017), amateur wrestler. * Ioan Sauca (born 1956), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castra
Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the military policy of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |