|
Carothers' Equation
In step-growth polymerization, the Carothers equation (or Carothers' equation) gives the degree of polymerization, , for a given fractional monomer conversion, . There are several versions of this equation, proposed by Wallace Carothers, who invented nylon in 1935. Linear polymers: two monomers in equimolar quantities The simplest case refers to the formation of a strictly linear polymer by the reaction (usually by condensation) of two monomers in equimolar quantities. An example is the synthesis of nylon-6,6 whose formula is from one mole of hexamethylenediamine, , and one mole of adipic acid, . For this case :\bar_n=\frac In this equation * is the number-average value of the degree of polymerization, equal to the average number of monomer units in a polymer molecule. For the example of nylon-6,6 \bar_n = 2n ( diamine units and diacid units). *p=\tfrac is the extent of reaction (or conversion to polymer), defined by ** is the number of molecules present initially as monome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step-growth Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, step-growth polymerization refers to a type of polymerization mechanism in which bi-functional or multifunctional monomers react to form first dimers, then trimers, longer oligomers and eventually long chain polymers. Many naturally-occurring and some synthetic polymers are produced by step-growth polymerization, e.g. polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, etc. Due to the nature of the polymerization mechanism, a high extent of reaction is required to achieve high molecular weight. The easiest way to visualize the mechanism of a step-growth polymerization is a group of people reaching out to hold their hands to form a human chain—each person has two hands (= reactive sites). There also is the possibility to have more than two reactive sites on a monomer: In this case branched polymers production take place. IUPAC has deprecated the term ''step-growth polymerization'', and recommends use of the terms polyaddition (when the propagation steps are addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harry R
Harry may refer to: Television * ''Harry'' (American TV series), 1987 comedy series starring Alan Arkin * ''Harry'' (British TV series), 1993 BBC drama that ran for two seasons * ''Harry'' (New Zealand TV series), 2013 crime drama starring Oscar Kightley * ''Harry'' (talk show), 2016 American daytime talk show hosted by Harry Connick Jr. People and fictional characters *Harry (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name, including **Prince Harry, Duke of Sussex (born 1984) *Harry (surname), a list of people with the surname Other uses *"Harry", the tunnel used in the Stalag Luft III escape Stalag Luft III (; literally "Main Camp, Air, III"; SL III) was a ''Luftwaffe''-run German prisoner-of-war camps in World War II, prisoner-of-war (POW) camp during the Second World War, which held captured Allies of World War II, Western Allied ... ("The Great Escape") of World War II * ''Harry'' (album), a 1969 album by Harry Nilsson * Harry (derogatory term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal friction, frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (physics), stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Reaction
A side reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs at the same time as the actual main reaction, but to a lesser extent. It leads to the formation of by-product, so that the Yield (chemistry), yield of main product is reduced: : + B ->[] P1 : + C ->[] P2 P1 is the main product if k1> k2. The by-product P2 is generally undesirable and must be Separation process, separated from the actual main product (usually in a Industrial separation processes, costly process). In organic synthesis B and C from the above equations usually represent different Compound (chemistry), compounds. However, they could also just be different positions in the same molecule. A side reaction is also referred to as competing reaction when different compounds (B, C) compete for another Reagent, reactant (A). If the side reaction occurs about as often as the main reaction, it is spoken of parallel reactions (especially in the kinetics, see below). Also there may be more complicated relationships: Compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain-growth Polymerization
Chain-growth polymerization (American English, AE) or chain-growth polymerisation (British English, BE) is a polymerization technique where monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics. Chain-growth polymerization involves 3 types of reactions : # Initiation: An active species I* is formed by some decomposition of an initiator molecule I # Propagation: The initiator fragment reacts with a monomer M to begin the conversion to the polymer; the center of activity is retained in the adduct. Monomers continue to add in the same way until polymers Pi* are formed with the degree of polymerization i # Termination: By some reaction generally involving two polymers containing active centers, the growth center is deactivated, resulting in dead polymer Introduction In 1953, Paul Flory first classified polymeriza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersity
In chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsistent size, shape and mass distribution is called non-uniform. The objects can be in any form of chemical dispersion, such as particles in a colloid, droplets in a cloud, crystals in a rock, or polymer macromolecules in a solution or a solid polymer mass. Polymers can be described by molecular mass distribution; a population of particles can be described by size, surface area, and/or mass distribution; and thin films can be described by film thickness distribution. IUPAC has deprecated the use of the term ''polydispersity index'', having replaced it with the term ''dispersity'', represented by the symbol Đ (pronounced D-strokeStepto, R. F. T.; Gilbert, R. G.; Hess, M.; Jenkins, A. D.; Jones, R. G.; Kratochvíl P. (2009).Dispersity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weight Average Molecular Weight
In polymer chemistry, the molar mass distribution (or molecular weight distribution) describes the relationship between the number of moles of each polymer species () and the molar mass () of that species. In linear polymers, the individual polymer chains rarely have exactly the same degree of polymerization and molar mass, and there is always a distribution around an average value. The molar mass distribution of a polymer may be modified by polymer fractionation. Definitions of molar mass average Different average values can be defined, depending on the statistical method applied. In practice, four averages are used, representing the weighted mean taken with the mole fraction, the weight fraction, and two other functions which can be related to measured quantities: *''Number average molar mass'' (), also loosely referred to as ''number average molecular weight'' (NAMW). *''Mass average molar mass'' (), where stands for weight; also commonly referred to as ''weight av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branching (polymer Chemistry)
In polymer chemistry, branching is the regular or irregular attachment of side chains to a polymer's backbone chain. It occurs by the replacement of a substituent (e.g. a hydrogen atom) on a monomer subunit by another covalently-bonded chain of that polymer; or, in the case of a graft copolymer, by a chain of another type. Branched polymers have more compact and symmetrical molecular conformations, and exhibit intra-heterogeneous dynamical behavior with respect to the unbranched polymers. In crosslinking rubber by vulcanization, short sulfur branches link polyisoprene chains (or a synthetic variant) into a multiple-branched thermosetting elastomer. Rubber can also be so completely vulcanized that it becomes a rigid solid, so hard it can be used as the bit in a smoking pipe. Polycarbonate chains can be crosslinked to form the hardest, most impact-resistant thermosetting plastic, used in safety glasses. Branching may result from the formation of carbon-carbon or vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limiting Reagent
The limiting reagent (or limiting reactant or limiting agent) in a chemical reaction is a reactant that is totally consumed when the chemical reaction is completed. The amount of product formed is limited by this reagent, since the reaction cannot continue without it. If one or more other reagents are present in excess of the quantities required to react with the limiting reagent, they are described as ''excess reagents'' or ''excess reactants'' (sometimes abbreviated as "xs"), or to be in ''abundance''. The limiting reagent must be identified in order to calculate the percentage yield of a reaction since the theoretical yield is defined as the amount of product obtained when the limiting reagent reacts completely. Given the balanced chemical equation, which describes the reaction, there are several equivalent ways to identify the limiting reagent and evaluate the excess quantities of other reagents. Method 1: Comparison of reactant amounts This method is most useful when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and Product (chemistry), products before, during, and following chemical reactions. Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must equal the total mass of products, so the relationship between reactants and products must form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of the products can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated. This is illustrated in the image here, where the unbalanced equation is: : : However, the current equation is imbalanced. The reactants have 4 hydrogen and 2 oxygen atoms, while the product has 2 hydrogen and 3 oxygen. To balance the hydrogen, a coefficient of 2 is added to the product H2O, and to fix the imbalance of oxygen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
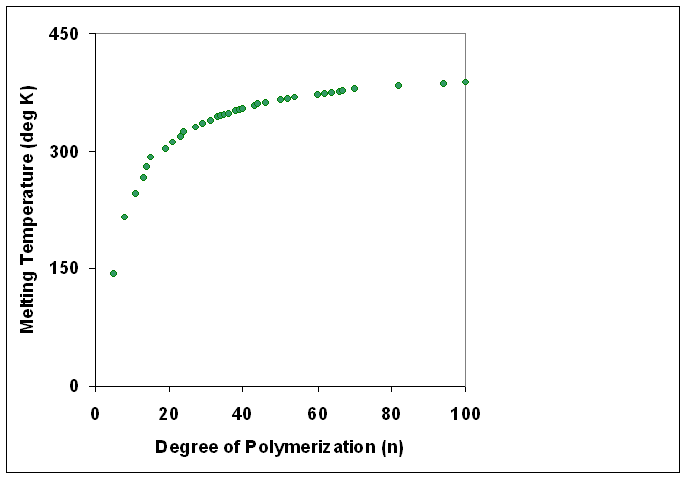
Degree Of Polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of structural unit, monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule. For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given by \overline_n\equiv\overline_n=\frac, where \overline_n is the Molar mass distribution#Number average molar mass, number-average molecular weight and M_0 is the molecular weight of the monomer unit. The overlines indicate arithmetic mean values. For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired. This number does not reflect the variation in molecule size of the polymer that typically occurs, it only represents the mean number of monomeric units. Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat units, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit.Fried J.R. "Polymer Science and Technology" (Pearson Prentice-Hall, 2nd edn 2003), p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |