|
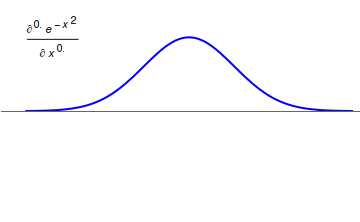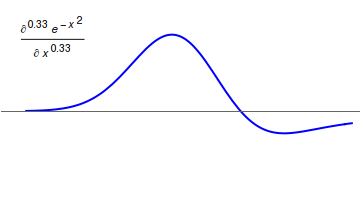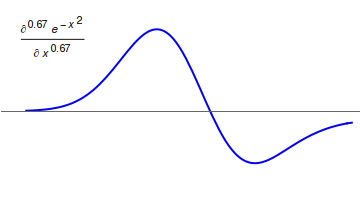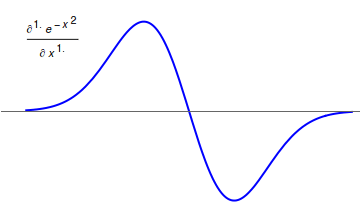
Caputo Fractional Derivative
In mathematics, the Caputo fractional derivative, also called Caputo-type fractional derivative, is a generalization of derivatives for non-integer orders named after Michele Caputo. Caputo first defined this form of fractional derivative in 1967. Motivation The Caputo fractional derivative is motivated from the Riemann–Liouville fractional integral. Let f be continuous on \left( 0,\, \infty \right), then the Riemann–Liouville fractional integral states that \left f\left( x \right) \right= \frac \cdot \int\limits_^ \frac \, \operatornamet where \Gamma\left( \cdot \right) is the Gamma function. Let's define \operatorname_^ := \frac, say that \operatorname_^ \operatorname_^ = \operatorname_^ and that \operatorname_^ = applies. If \alpha = m + z \in \mathbb \wedge m \in \mathbb_ \wedge 0 < z < 1 then we could say . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Derivative
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator D D f(x) = \frac f(x)\,, and of the integration operator J The symbol J is commonly used instead of the intuitive I in order to avoid confusion with other concepts identified by similar glyphs, such as identities. J f(x) = \int_0^x f(s) \,ds\,, and developing a calculus for such operators generalizing the classical one. In this context, the term ''powers'' refers to iterative application of a linear operator D to a function that is, repeatedly composing D with itself, as in \begin D^n(f) &= (\underbrace_n)(f) \\ &= \underbrace_n (f)\cdots))). \end For example, one may ask for a meaningful interpretation of \sqrt = D^ as an analogue of the functional square root for the differentiation operator, that is, an expression for some linear operator that, when applied to any f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemann–Liouville Integral
In mathematics, the Riemann–Liouville integral associates with a real function f: \mathbb \rightarrow \mathbb another function of the same kind for each value of the parameter . The integral is a manner of generalization of the repeated antiderivative of in the sense that for positive integer values of , is an iterated antiderivative of of order . The Riemann–Liouville integral is named for Bernhard Riemann and Joseph Liouville, the latter of whom was the first to consider the possibility of fractional calculus in 1832. The operator agrees with the Euler transform, after Leonhard Euler, when applied to analytic functions. It was generalized to arbitrary dimensions by Marcel Riesz, who introduced the Riesz potential. Motivation The Riemann-Liouville integral is motivated from Cauchy formula for repeated integration. For a function continuous on the interval the Cauchy formula for -fold repeated integration states that I^n f(x) = f^(x) = \frac \int_a^x\left(x-t\ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Function
In mathematics, the gamma function (represented by Γ, capital Greek alphabet, Greek letter gamma) is the most common extension of the factorial function to complex numbers. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, the gamma function \Gamma(z) is defined for all complex numbers z except non-positive integers, and for every positive integer z=n, \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\,.The gamma function can be defined via a convergent improper integral for complex numbers with positive real part: \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^ e^\textt, \ \qquad \Re(z) > 0\,.The gamma function then is defined in the complex plane as the analytic continuation of this integral function: it is a meromorphic function which is holomorphic function, holomorphic except at zero and the negative integers, where it has simple Zeros and poles, poles. The gamma function has no zeros, so the reciprocal gamma function is an entire function. In fact, the gamma function corresponds to the Mellin transform of the negative exponential functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floor And Ceiling Functions
In mathematics, the floor function is the function that takes as input a real number , and gives as output the greatest integer less than or equal to , denoted or . Similarly, the ceiling function maps to the least integer greater than or equal to , denoted or . For example, for floor: , , and for ceiling: , and . The floor of is also called the integral part, integer part, greatest integer, or entier of , and was historically denoted (among other notations). However, the same term, ''integer part'', is also used for truncation towards zero, which differs from the floor function for negative numbers. For an integer , . Although and produce graphs that appear exactly alike, they are not the same when the value of is an exact integer. For example, when , . However, if , then , while . Notation The ''integral part'' or ''integer part'' of a number ( in the original) was first defined in 1798 by Adrien-Marie Legendre in his proof of the Legendre's formula. Carl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform that converts a Function (mathematics), function of a Real number, real Variable (mathematics), variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a Complex number, complex variable s (in the complex-valued frequency domain, also known as ''s''-domain, or ''s''-plane). The transform is useful for converting derivative, differentiation and integral, integration in the time domain into much easier multiplication and Division (mathematics), division in the Laplace domain (analogous to how logarithms are useful for simplifying multiplication and division into addition and subtraction). This gives the transform many applications in science and engineering, mostly as a tool for solving linear differential equations and dynamical systems by simplifying ordinary differential equations and integral equations into algebraic equation, algebraic polynomial equations, and by simplifyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomplete Gamma Function
In mathematics, the upper and lower incomplete gamma functions are types of special functions which arise as solutions to various mathematical problems such as certain integrals. Their respective names stem from their integral definitions, which are defined similarly to the gamma function but with different or "incomplete" integral limits. The gamma function is defined as an integral from zero to infinity. This contrasts with the lower incomplete gamma function, which is defined as an integral from zero to a variable upper limit. Similarly, the upper incomplete gamma function is defined as an integral from a variable lower limit to infinity. Definition The upper incomplete gamma function is defined as: \Gamma(s,x) = \int_x^ t^\,e^\, dt , whereas the lower incomplete gamma function is defined as: \gamma(s,x) = \int_0^x t^\,e^\, dt . In both cases is a complex parameter, such that the real part of is positive. Properties By integration by parts we find the recurrence relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |